
Consider a thin metallic sheet perpendicular to the plane of the paper moving with speed $'v'$ in a uniform magnetic field $B$ going into the plane of the paper (See figure). If charge densities ${\sigma _1}$ and ${\sigma _2}$ are induced on the left and right surfaces, respectively, on the sheet then (ignore fringe effects):
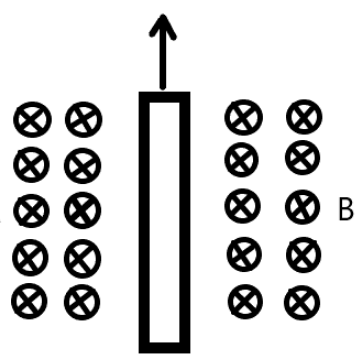
A. ${\sigma _1} = \dfrac{{ - {\varepsilon _0}vB}}{2}$ , ${\sigma _2} = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}vB}}{2}$
B. ${\sigma _1} = {\varepsilon _0}vB$ , ${\sigma _2} = - {\varepsilon _0}vB$
C. ${\sigma _1} = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}vB}}{2}$ , ${\sigma _2} = \dfrac{{ - {\varepsilon _0}vB}}{2}$
D. ${\sigma _1} = {\sigma _2} = {\varepsilon _0}vB$

Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: Here, we will use the force formula in case of both electric field and magnetic field. The system will be in equilibrium because the charge on both the left and right side will be the same. Therefore, we will equate the forces in both the cases to calculate the charge densities.
Complete step by step answer:
The following terms are given in the question,
Speed of metallic sheet $ = v$.
Magnetic field induced in the plane of paper $ = B$.
Charge densities that are induced in the plane of paper $ = {\sigma _1}\,and\,{\sigma _2}$.
Now, as the charge is moving, it will induce a magnetic field $B$ in the plane of the paper.
Now, the force acting on the charges is given below,
${F_1} = qE$
Here, $E$ is the electric field and is shown as $E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Now, the force due to magnetic field $\vec B$ is given below,
${\vec F_2} = q\left( {\vec v \times \vec B} \right)$
As given in the question, $v$ is perpendicular to $B$ , therefore, the angle between them is $90^\circ $ . Therefore, the above equation will become
${\vec F_2} = qvB\sin 90^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \,{\vec F_2} = qvB$
As we know that the charges are induced on the same material, therefore, ${\sigma _1} = {\sigma _2}$ but the charges will be opposite. Also, we know that the velocity is acting upwards than ${\sigma _1}$ will be positive and ${\sigma _2}$ will be negative.
Now, at equilibrium, ${F_1} = {F_2}$
$ qE = qvB$
$ \Rightarrow \,E = vB$
$ \Rightarrow \,\dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = vB$
$ \Rightarrow \,\sigma = {\varepsilon _0}vB$
Now, as discussed above, ${\sigma _1}$ will be positive and ${\sigma _2}$ will be negative.
$\therefore \,{\sigma _1} = {\varepsilon _0}vB$ and ${\sigma _2} = - {\varepsilon _0}vB$
Therefore, charge densities ${\sigma _1}$ and ${\sigma _2}$ induced on the sheets are ${\varepsilon _0}vB$ and $ - {\varepsilon _0}vB$ respectively.
Hence, option B is the correct option.
Note:We have forces in case of electric field and magnetic field because the charges are moving and will produce both the electric field and magnetic field. Also, charge densities are of opposite signs because the velocity of the charge is in upward direction. Also, it is given in the question that the plane of paper is perpendicular to the metallic sheet.
Complete step by step answer:
The following terms are given in the question,
Speed of metallic sheet $ = v$.
Magnetic field induced in the plane of paper $ = B$.
Charge densities that are induced in the plane of paper $ = {\sigma _1}\,and\,{\sigma _2}$.
Now, as the charge is moving, it will induce a magnetic field $B$ in the plane of the paper.
Now, the force acting on the charges is given below,
${F_1} = qE$
Here, $E$ is the electric field and is shown as $E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Now, the force due to magnetic field $\vec B$ is given below,
${\vec F_2} = q\left( {\vec v \times \vec B} \right)$
As given in the question, $v$ is perpendicular to $B$ , therefore, the angle between them is $90^\circ $ . Therefore, the above equation will become
${\vec F_2} = qvB\sin 90^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \,{\vec F_2} = qvB$
As we know that the charges are induced on the same material, therefore, ${\sigma _1} = {\sigma _2}$ but the charges will be opposite. Also, we know that the velocity is acting upwards than ${\sigma _1}$ will be positive and ${\sigma _2}$ will be negative.
Now, at equilibrium, ${F_1} = {F_2}$
$ qE = qvB$
$ \Rightarrow \,E = vB$
$ \Rightarrow \,\dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = vB$
$ \Rightarrow \,\sigma = {\varepsilon _0}vB$
Now, as discussed above, ${\sigma _1}$ will be positive and ${\sigma _2}$ will be negative.
$\therefore \,{\sigma _1} = {\varepsilon _0}vB$ and ${\sigma _2} = - {\varepsilon _0}vB$
Therefore, charge densities ${\sigma _1}$ and ${\sigma _2}$ induced on the sheets are ${\varepsilon _0}vB$ and $ - {\varepsilon _0}vB$ respectively.
Hence, option B is the correct option.
Note:We have forces in case of electric field and magnetic field because the charges are moving and will produce both the electric field and magnetic field. Also, charge densities are of opposite signs because the velocity of the charge is in upward direction. Also, it is given in the question that the plane of paper is perpendicular to the metallic sheet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




