
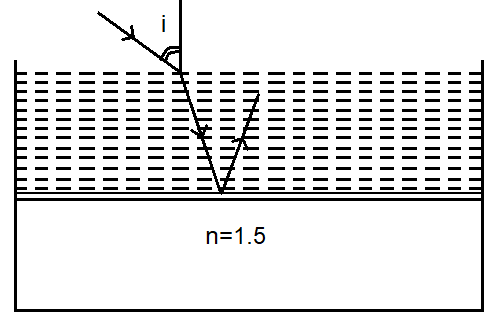
Consider a tank made of glass (refractive index $ 1.5 $ ) with a thick bottom. It is filled with a liquid of refractive index $ \mu $ . A student finds that, irrespective of what the incident angle $ i $ (see figure) is for a beam of light entering the liquid, the light reflected from the liquid glass interface is never completely polarized. For this to happen, the minimum value of μ is
(A) $ \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 5 }} $
(B) $ \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
(C) $ \sqrt {\dfrac{5}{3}} $
(D) $ \dfrac{4}{3} $

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: For finding out the minimum value of the refractive index, we need to use the relation between Brewster angle and the critical angle which is given as $ sin{\text{ }}c < sin{\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $ . Brewster angle is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection.
Formula used:
$ sin{\text{ c}} < sin{\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $
$ \
sin90 = \mu \sin c \\
\Rightarrow sinc = \dfrac{1}{\mu } \\
$
Where, the critical angle be $ {\text{ c}} $ , the Brewster angle be $ {\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $ , $ {\text{ }}\mu $ is the refractive index.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the critical angle be c, the Brewster angle be ib.
The relation comes between the critical angle and the Brewster angle is,
$ sin{\text{ }}c < sin{\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $
For the ray travelling from air to liquid,
$ sin90 = \mu \sin c $
Now the value of $ sin90 $ is 1 so we get
$ sinc = \dfrac{1}{\mu } $
Since, we know that,
$ \tan {i_b} = {\mu _{{0_{rel}}}} $
And,
$ sin{\text{ }}c < sin{\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $
Then substituting the values in the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\mu } < \dfrac{{1.5}}{{\sqrt {{\mu ^2} + {{(1.5)}^2}} }} $
Thus, after simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \mu < \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 5 }} $
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
There are numerous applications of Brewster angle in real life. It includes,
-Polarized sunglasses use the principle of Brewster's angle to reduce glare from the sun reflecting off horizontal surfaces such as water or road.
-Photographers use the same principle to remove reflections from water so that they can photograph objects beneath the surface.
-Brewster angle prisms are used in laser physics. The polarized laser light enters the prism at Brewster's angle without any reflective losses.
-In surface science, Brewster angle microscopes are used in imaging layers of particles or molecules at air-liquid interfaces.
Formula used:
$ sin{\text{ c}} < sin{\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $
$ \
sin90 = \mu \sin c \\
\Rightarrow sinc = \dfrac{1}{\mu } \\
$
Where, the critical angle be $ {\text{ c}} $ , the Brewster angle be $ {\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $ , $ {\text{ }}\mu $ is the refractive index.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the critical angle be c, the Brewster angle be ib.
The relation comes between the critical angle and the Brewster angle is,
$ sin{\text{ }}c < sin{\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $
For the ray travelling from air to liquid,
$ sin90 = \mu \sin c $
Now the value of $ sin90 $ is 1 so we get
$ sinc = \dfrac{1}{\mu } $
Since, we know that,
$ \tan {i_b} = {\mu _{{0_{rel}}}} $
And,
$ sin{\text{ }}c < sin{\text{ }}{i_{b\;}} $
Then substituting the values in the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\mu } < \dfrac{{1.5}}{{\sqrt {{\mu ^2} + {{(1.5)}^2}} }} $
Thus, after simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \mu < \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 5 }} $
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
There are numerous applications of Brewster angle in real life. It includes,
-Polarized sunglasses use the principle of Brewster's angle to reduce glare from the sun reflecting off horizontal surfaces such as water or road.
-Photographers use the same principle to remove reflections from water so that they can photograph objects beneath the surface.
-Brewster angle prisms are used in laser physics. The polarized laser light enters the prism at Brewster's angle without any reflective losses.
-In surface science, Brewster angle microscopes are used in imaging layers of particles or molecules at air-liquid interfaces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




