
Consider a magnetic dipole which on switching ON external magnetic field orient only in two possible ways i.e., one along the direction of the magnetic field ( parallel to the field) and another anti-parallel to the magnetic field. Compute the energy for the possible orientation. Sketch the graph.
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint:The magnetic dipole switches in two possible ways such as parallel to the field and antiparallel to the field, therefore work is done by the dipole. Hence, potential energy exists. Use the equation of energy and put the values of the angle for these two directions to compute the energy orientation. By using these values of energy the graph can be drawn.
Formula Used:
The potential energy of a magnetic dipole ${P_m}$ in a magnetic field $B$ is,
$U(\theta ) = - {P_m}B\cos \theta $
Complete step-by-step solution:
In a magnetic field, $B$the potential energy of the dipole moment of a magnet ${P_m}$is given by,
$U(\theta ) = - {P_m}B\cos \theta $
The relation is coming from the cross multiplication i.e.the potential energy is the cross product of magnetic dipole moment vector and magnetic field vector.
Now before switching, the orientation does not exist and the energy is zero.
After the switching on the magnetic dipole goes along the parallel direction to the magnetic field, hence the angle $\theta = 0^\circ $ .
So, the potential energy $U(0) = - {P_m}B\cos 0$
$ \Rightarrow U(0) = - {P_m}B$
Else, the magnetic dipole goes along the anti-parallel direction to the magnetic field, hence the angle $\theta = 180^\circ $ .
So, the potential energy $U(180) = - {P_m}B\cos 180$
$ \Rightarrow U(180) = {P_m}B$
The graph will be:
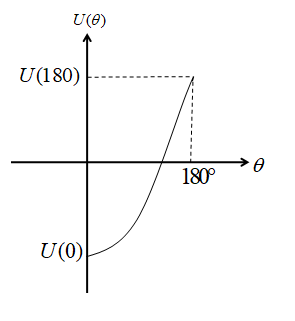
Note:When the magnetic dipole moment is rotated about an angle (say, $\varphi $ ) from its initial position, a torque occurs that is the cross product of the dipole moment and the magnetic field and also a vector quantity. The torque acts on the perpendicular plane of the dipole moment and the magnetic field.
The torque $\vec \tau = {\vec P_m} \times \vec B$
$ \Rightarrow \tau = {P_m}B\cos \varphi $
If the angular displacement is $d\varphi $
The work done will be $ \Rightarrow dW = {P_m}B\sin \varphi d\varphi $
Hence, to rotate the magnet bar from $0^\circ $ to $\theta $ total work-done is,
$W = {P_m}B\int\limits_0^\theta {\sin \varphi d\varphi } $
$ \Rightarrow W = {P_m}B(1 - \cos \theta )$
Formula Used:
The potential energy of a magnetic dipole ${P_m}$ in a magnetic field $B$ is,
$U(\theta ) = - {P_m}B\cos \theta $
Complete step-by-step solution:
In a magnetic field, $B$the potential energy of the dipole moment of a magnet ${P_m}$is given by,
$U(\theta ) = - {P_m}B\cos \theta $
The relation is coming from the cross multiplication i.e.the potential energy is the cross product of magnetic dipole moment vector and magnetic field vector.
Now before switching, the orientation does not exist and the energy is zero.
After the switching on the magnetic dipole goes along the parallel direction to the magnetic field, hence the angle $\theta = 0^\circ $ .
So, the potential energy $U(0) = - {P_m}B\cos 0$
$ \Rightarrow U(0) = - {P_m}B$
Else, the magnetic dipole goes along the anti-parallel direction to the magnetic field, hence the angle $\theta = 180^\circ $ .
So, the potential energy $U(180) = - {P_m}B\cos 180$
$ \Rightarrow U(180) = {P_m}B$
The graph will be:

Note:When the magnetic dipole moment is rotated about an angle (say, $\varphi $ ) from its initial position, a torque occurs that is the cross product of the dipole moment and the magnetic field and also a vector quantity. The torque acts on the perpendicular plane of the dipole moment and the magnetic field.
The torque $\vec \tau = {\vec P_m} \times \vec B$
$ \Rightarrow \tau = {P_m}B\cos \varphi $
If the angular displacement is $d\varphi $
The work done will be $ \Rightarrow dW = {P_m}B\sin \varphi d\varphi $
Hence, to rotate the magnet bar from $0^\circ $ to $\theta $ total work-done is,
$W = {P_m}B\int\limits_0^\theta {\sin \varphi d\varphi } $
$ \Rightarrow W = {P_m}B(1 - \cos \theta )$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




