
Compound ‘X’ having molecular formula\[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\]. It evolves$\text{ C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }$, with$\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$’ X’ on reaction with $\text{ LiAl}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$gives achiral compound ‘X’ is /are:
A)
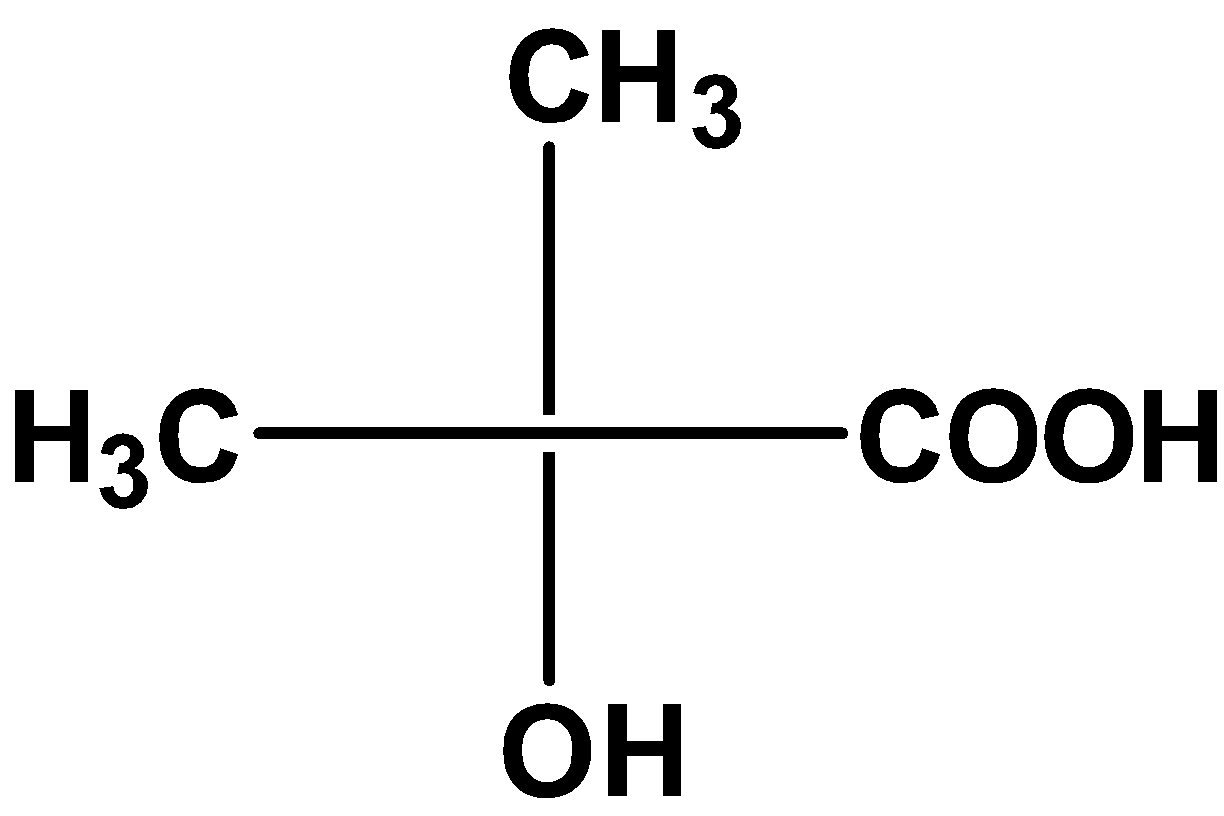
B)
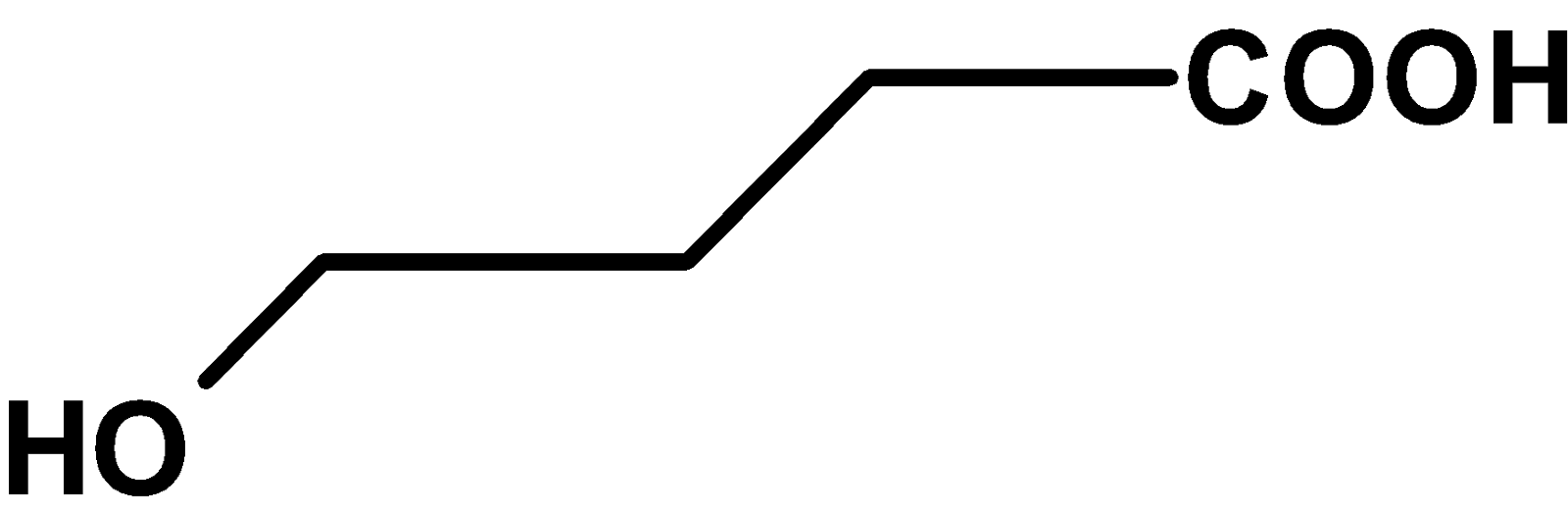
C)
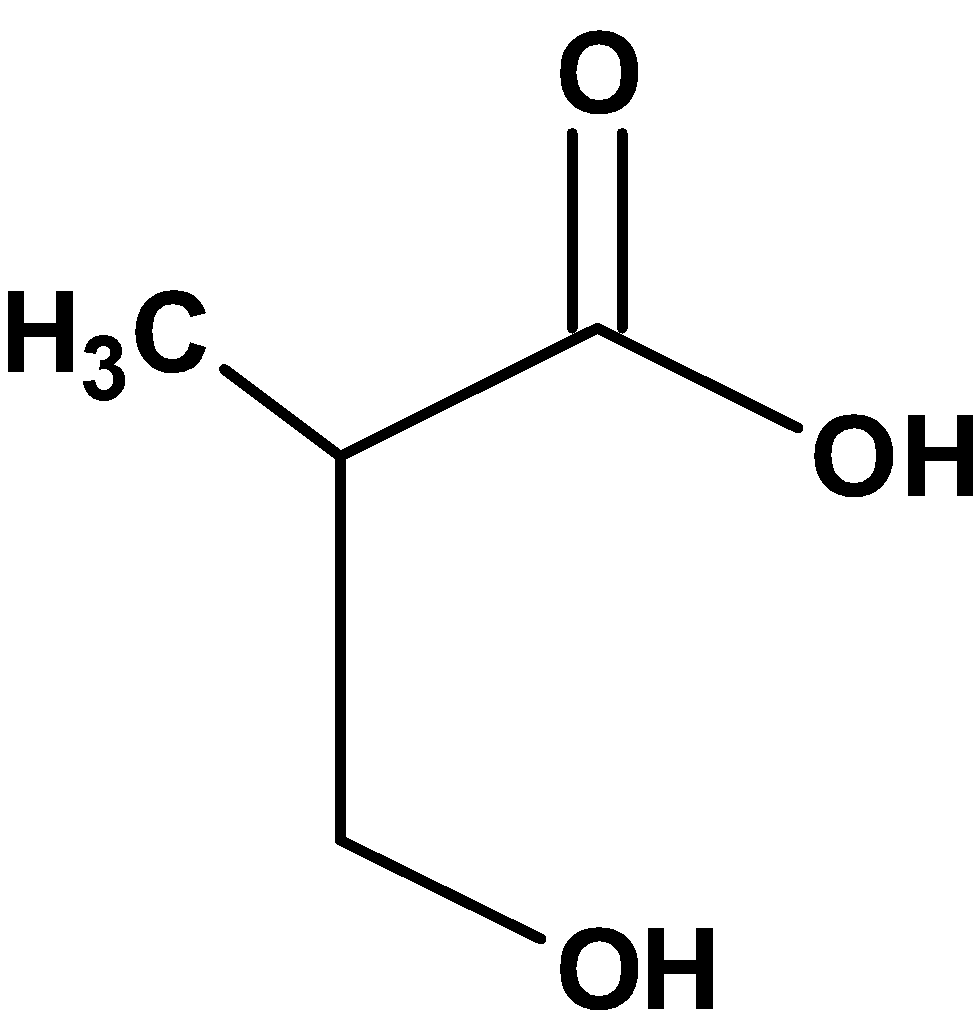
D)
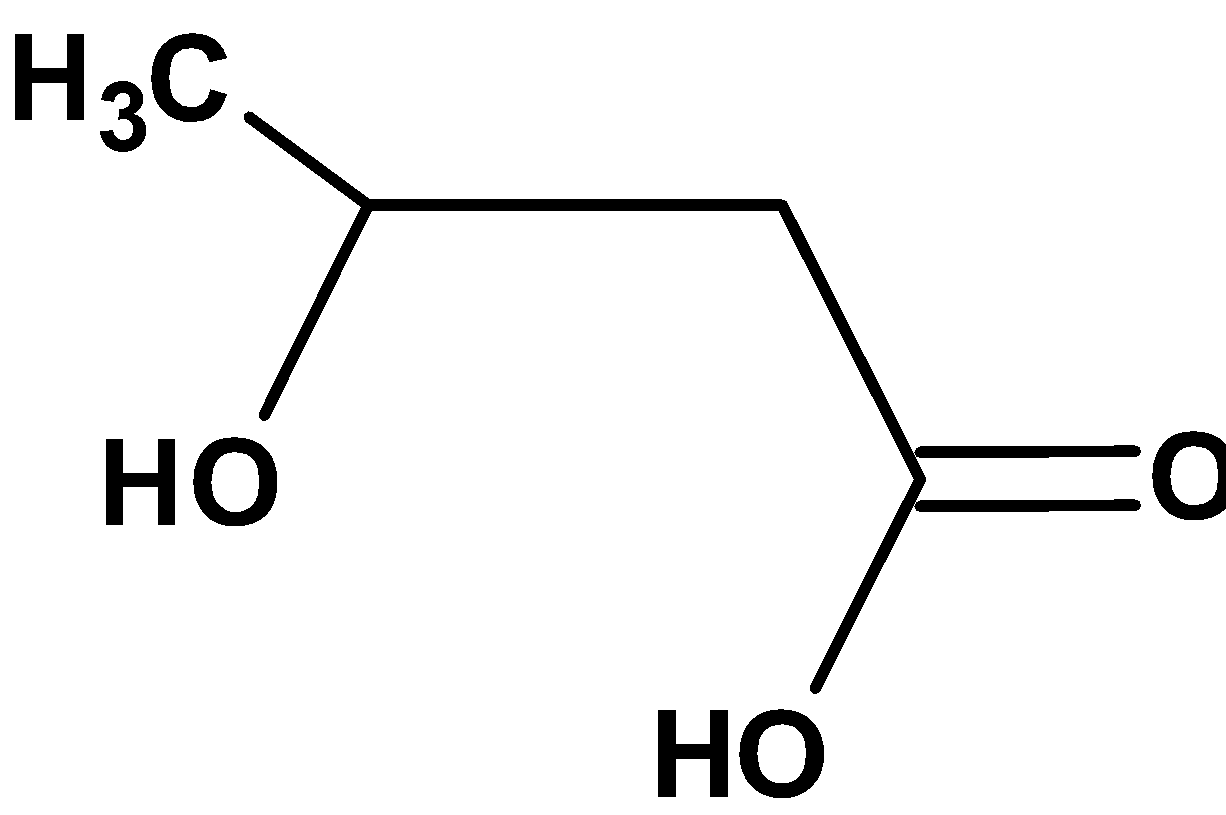
| A) | 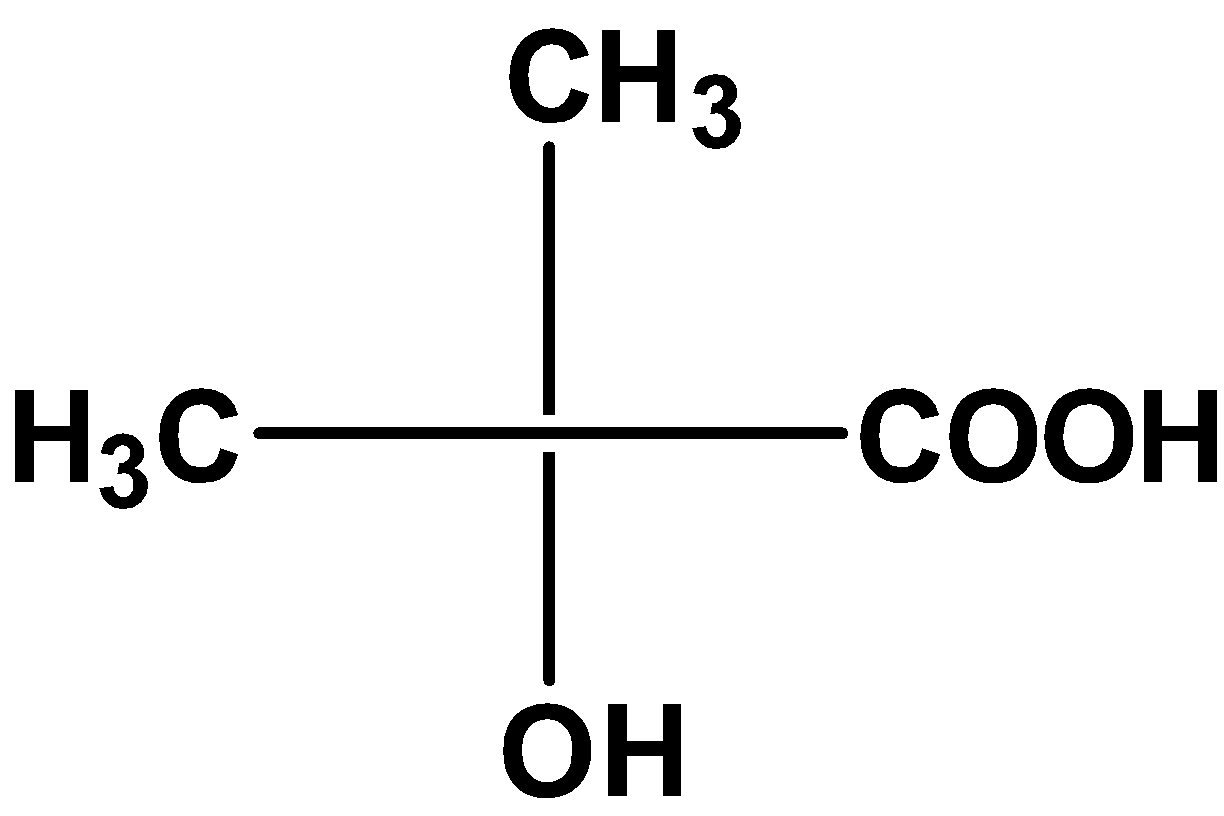
|
| B) | 
|
| C) | 
|
| D) | 
|
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: Carboxylic acid reacts with the carbonate or the bicarbonate. The reaction results in the evolution of carbon dioxide. The reducing agent like lithium aluminium hydride (LAH) adds the hydrogen atom across the compound. The carbonyl group in the compound is reduced to the hydroxyl group. Here, the compound on reduction with LAH forms an achiral compound.
Complete answer:
We have given that the compound ‘X’ which have the molecular formula \[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\] . When it is reacted with $\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$evolves$\text{ C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }$. The general reaction can be written as,
$\text{ X }\xrightarrow{\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}}\text{ C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }$
The compound ‘X’ also reacts with lithium aluminium hydride$\text{ LiAl}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$.
Carboxylic acid reacts with the carbonates or the bicarbonates .The reaction of the carboxylic acid with aqueous sodium bicarbonate leads to the evolution of carbon dioxide producing brisk effervesces.
It may be noted that the carboxylic acid with the $\text{ N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$ or$\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$, the carbon dioxide comes from the $\text{ N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$or $\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$and not from the carboxyl groups. The general reaction of the carboxylic acid with the sodium bicarbonate is given as follows,
$\text{ RCOOH + NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\to \text{ RCOONa + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O }$
The compound \[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\]contains three oxygen atoms. Thus, the compound includes carboxylic acid groups and aldehydic groups or carboxylic acid groups and hydroxyl groups.
However, the 4 carbon atom compound with the aldehydic group and carboxylic acid group has the molecular formula equal to\[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\].
The reaction between the $\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$and compound X is given as,
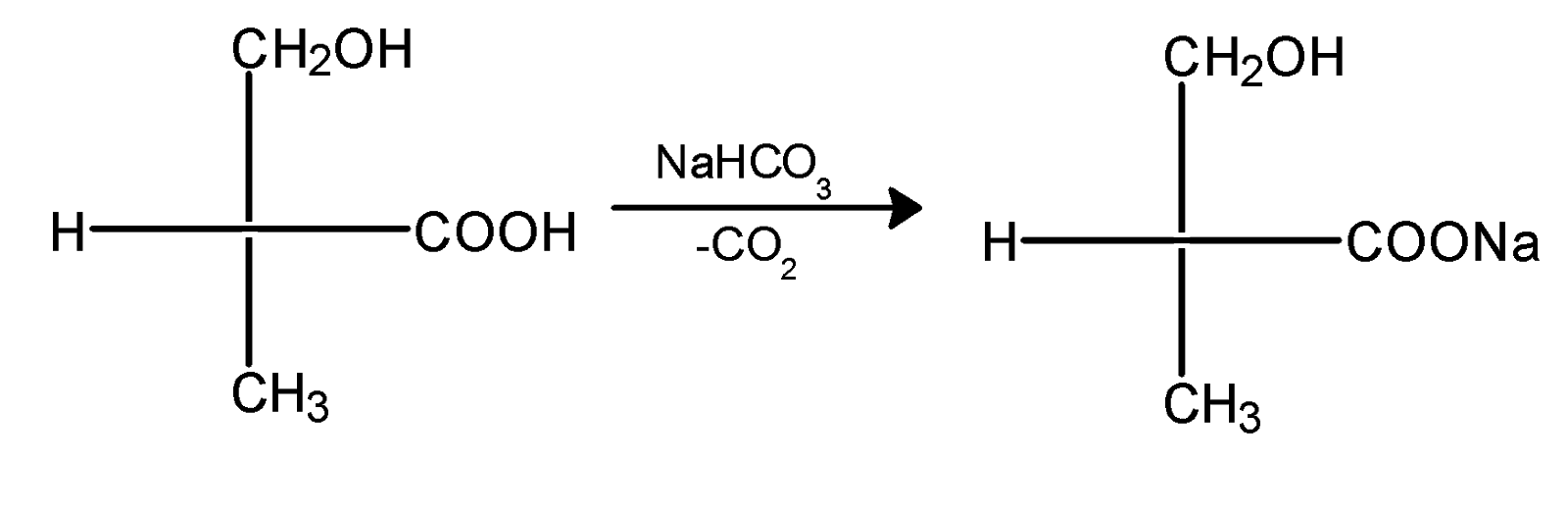
Lithium aluminium hydride is a reducing agent. It provides the hydrogen atom to the organic molecule. The acids can be reduced by lithium aluminium hydride. The carboxylic acid can be converted into the primary alcohol .T
The reaction of compound X with the LAH is as follows,
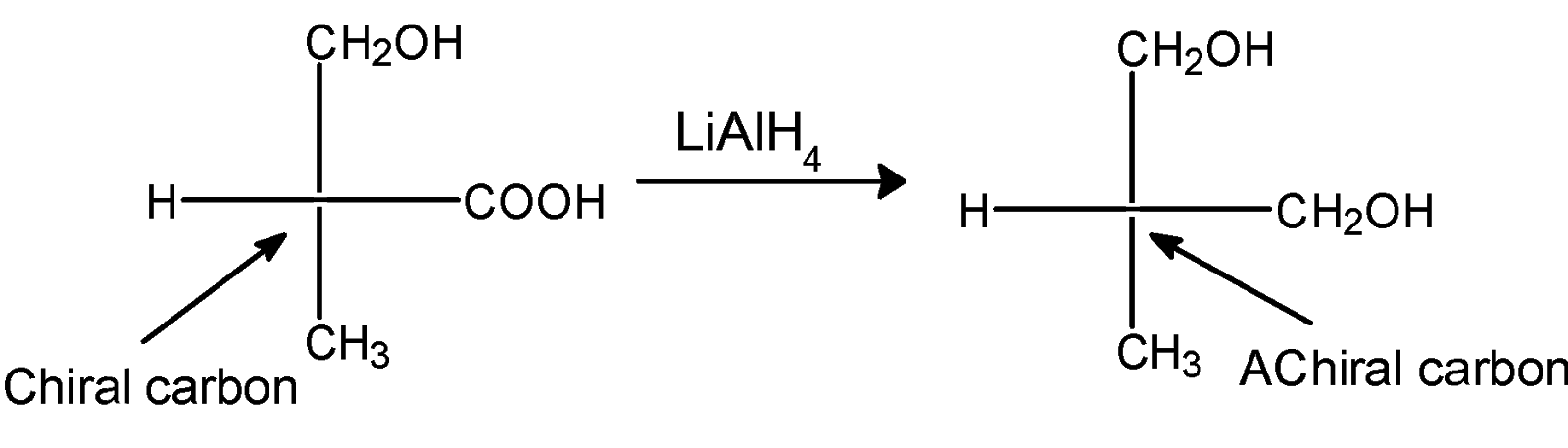
Thus, compound X from the option is,
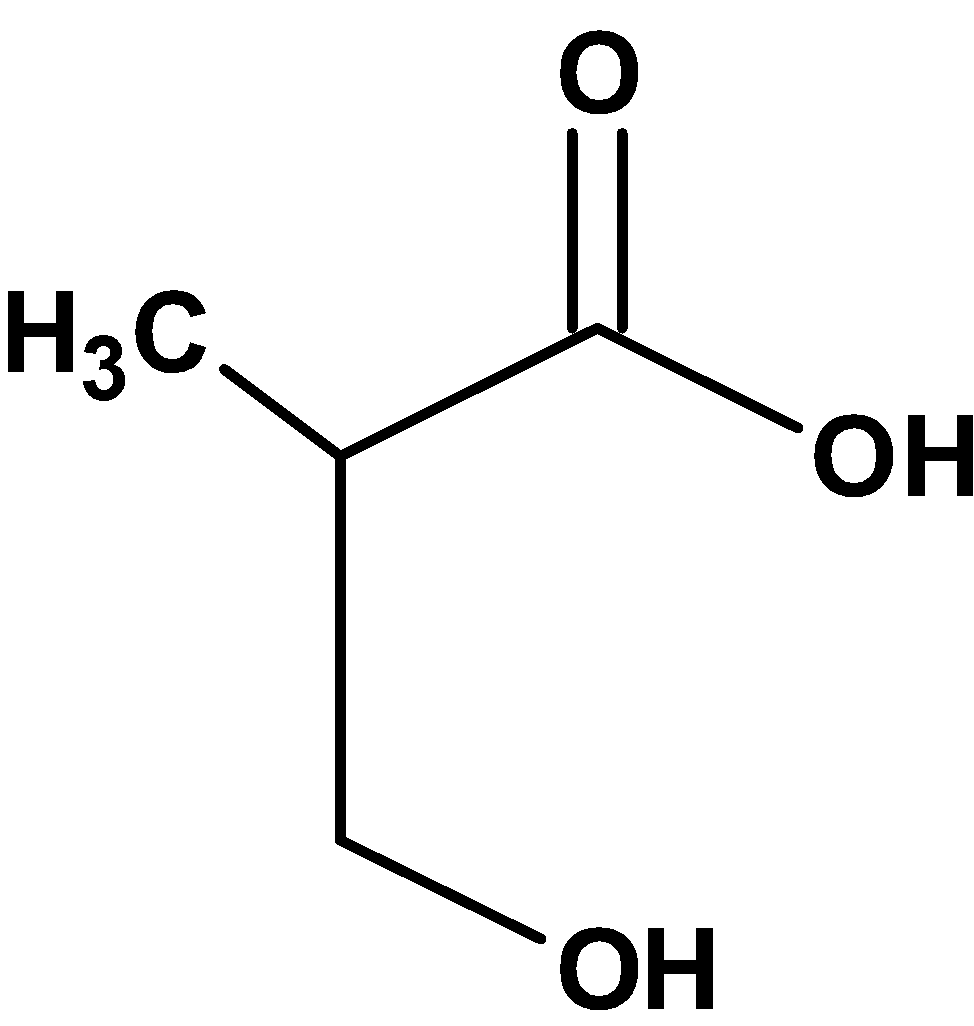
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Note that, the reduction of acid or ester to the alcohol is easily carried out in presence of lithium aluminium hydride, but the reduction is not easily carried out by the sodium borohydride $\text{ NaB}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$ . This is because $\text{ NaB}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$is a mild and selective reducing agent. The phenols do not produces effervescence when reacted with the bicarbonate, thus reaction with bicarbonate is used to distinguish between the phenol and carboxylic acid
Complete answer:
We have given that the compound ‘X’ which have the molecular formula \[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\] . When it is reacted with $\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$evolves$\text{ C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }$. The general reaction can be written as,
$\text{ X }\xrightarrow{\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}}\text{ C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }$
The compound ‘X’ also reacts with lithium aluminium hydride$\text{ LiAl}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$.
Carboxylic acid reacts with the carbonates or the bicarbonates .The reaction of the carboxylic acid with aqueous sodium bicarbonate leads to the evolution of carbon dioxide producing brisk effervesces.
It may be noted that the carboxylic acid with the $\text{ N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$ or$\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$, the carbon dioxide comes from the $\text{ N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$or $\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$and not from the carboxyl groups. The general reaction of the carboxylic acid with the sodium bicarbonate is given as follows,
$\text{ RCOOH + NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\to \text{ RCOONa + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O }$
The compound \[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\]contains three oxygen atoms. Thus, the compound includes carboxylic acid groups and aldehydic groups or carboxylic acid groups and hydroxyl groups.
However, the 4 carbon atom compound with the aldehydic group and carboxylic acid group has the molecular formula equal to\[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\].
The reaction between the $\text{ NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$and compound X is given as,

Lithium aluminium hydride is a reducing agent. It provides the hydrogen atom to the organic molecule. The acids can be reduced by lithium aluminium hydride. The carboxylic acid can be converted into the primary alcohol .T
The reaction of compound X with the LAH is as follows,

Thus, compound X from the option is,

Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Note that, the reduction of acid or ester to the alcohol is easily carried out in presence of lithium aluminium hydride, but the reduction is not easily carried out by the sodium borohydride $\text{ NaB}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$ . This is because $\text{ NaB}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$is a mild and selective reducing agent. The phenols do not produces effervescence when reacted with the bicarbonate, thus reaction with bicarbonate is used to distinguish between the phenol and carboxylic acid
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




