
Compound $ {{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{8}}} $ have:
(A) $ {\text{S - S}} $ bond
(B) $ {\text{S - O}} $ bridge
(C) $ {\text{O - O}} $ bridge
(D) None of the above
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the structure of the given chemical species. First we draw the chemical structure of the compound and then see which of the following given conditions is satisfied in its structure.
Complete step by step solution
$ {{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{8}}} $ is an ionic species and carries a charge of $ - 2 $ . It is known as the peroxy disulfate ion. It is an oxyanion of sulphur and the conjugate base of the peroxydisulfuric acid. The ion is commonly known as persulfate ion or as peroxo disulphate anions. Another similar species is peroxo- monosulphate ion which similarly is the conjugate base of the peroxy mono sulphuric acid.
The structure of $ {{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{8}}} $ can be imagined as two sulphate groups joined together. Each sulphur is bonded to four carbon atoms, doubly bonded to two and single bonds are formed with the other two. The two terminal oxygen atoms satisfy their valency by carrying a negative charge which accounts for the -2 charge on the species. The inner oxygen atoms are bonded to each other and form a bridging oxygen- oxygen bond between the two sulphur atoms. The structure can be drawn as:
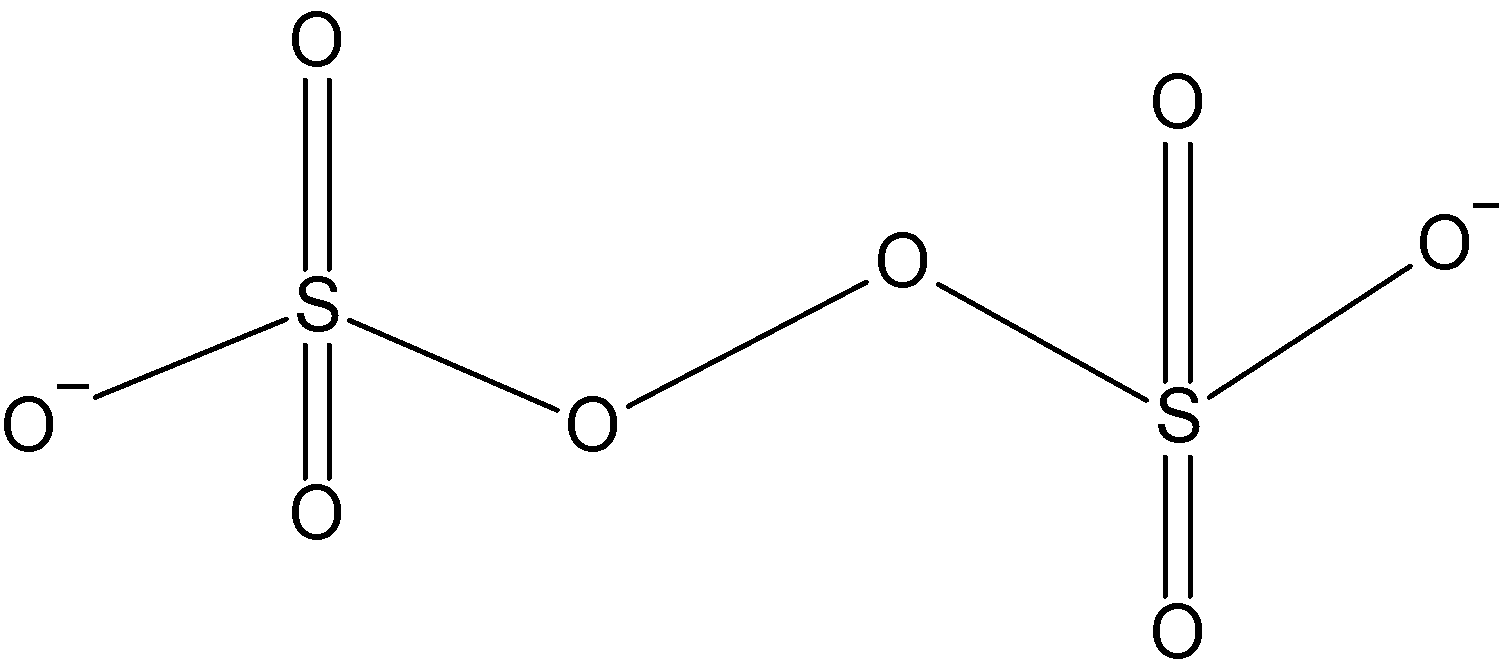
The correct answer is C.
Note
We can see the peroxodisulphate ions as the combination of two sulphate groups. We know that a peroxy bond breaks readily forming free radicals. Due to this property, salts of peroxodisulphate ions are used for the polymerization of many alkenes namely styrene, acrylonitrile, and fluoroalkenes. The oxygen- oxygen bond cleaves homolytically. It is also used for the treatment of wastewater.
Complete step by step solution
$ {{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{8}}} $ is an ionic species and carries a charge of $ - 2 $ . It is known as the peroxy disulfate ion. It is an oxyanion of sulphur and the conjugate base of the peroxydisulfuric acid. The ion is commonly known as persulfate ion or as peroxo disulphate anions. Another similar species is peroxo- monosulphate ion which similarly is the conjugate base of the peroxy mono sulphuric acid.
The structure of $ {{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{8}}} $ can be imagined as two sulphate groups joined together. Each sulphur is bonded to four carbon atoms, doubly bonded to two and single bonds are formed with the other two. The two terminal oxygen atoms satisfy their valency by carrying a negative charge which accounts for the -2 charge on the species. The inner oxygen atoms are bonded to each other and form a bridging oxygen- oxygen bond between the two sulphur atoms. The structure can be drawn as:

The correct answer is C.
Note
We can see the peroxodisulphate ions as the combination of two sulphate groups. We know that a peroxy bond breaks readily forming free radicals. Due to this property, salts of peroxodisulphate ions are used for the polymerization of many alkenes namely styrene, acrylonitrile, and fluoroalkenes. The oxygen- oxygen bond cleaves homolytically. It is also used for the treatment of wastewater.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




