
Compound D is,
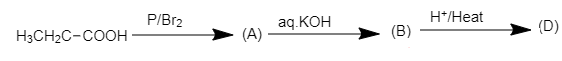
A. $H_2C=CH-COOH$
B.
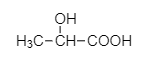
C.
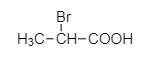
D. $CH\equiv C-COOH$
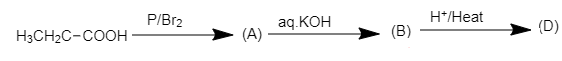
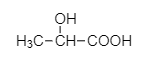
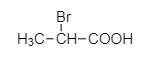
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: The reaction of carboxylic acid with phosphorus and bromine leads to the bromination of \[\alpha \] carbon atom of the carboxylic acid, producing a dibromo product. The reaction is known as Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reduction reaction. The reaction is used for the halogenation of carboxylic acid. To initiate this reaction, a catalytic amount of phosphorus tribromide is used and then bromine is added for further reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we have to find the structure of compound (D) in the following chemical reaction.
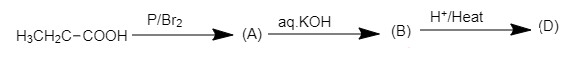
When propionic acid is treated with a catalytic amount of phosphorus and bromine, $\alpha - H$ substitution takes place, producing dibromo product. The substitution of $\alpha - H$ of propionic acid by bromine takes place on action of bromine in the presence of phosphorus. The $\alpha - H$ atoms of propionic acid are substituted by bromine atoms.
The chemical reaction of formation of (A) is shown below.
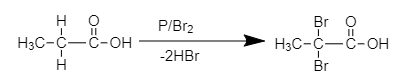
2,2-dibromo propionic acid
The product (A) is 2, 2 –dibromo propionic acid.
When the dibromo derivative of propionic acid is treated with aqueous $KOH$, the bromine atoms in the acid will be replaced by hydroxyl groups which on acidification will yield propionic acid with a double bond.
The complete reaction is shown below.
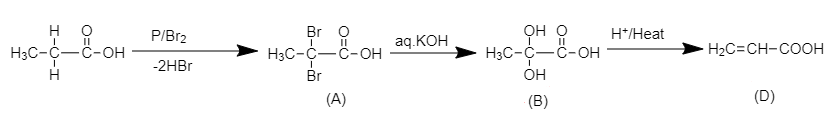
Here, compound (D) is acrylic acid and the structure of the compound is shown below.
$H_2C=CH-COOH$
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional information:
Here, the dibromo derivative of propionic acid that is compound (A) is formed by Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reduction reaction. The reaction is used for introducing halogen such as chlorine and bromine in carboxylic acid. This reaction is not applicable in case of introducing iodine and fluorine in carboxylic acid. The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reduction reaction.
Note: Students should keep in mind that the action of alcoholic $KOH$ and aqueous $KOH$ on carboxylic acid is different. The use of aqueous $KOH$ is done in case of the chemical reactions which are not water sensitive and used for carrying out the hydrolysis reaction. The alcoholic $KOH$ is used in case of water sensitive reaction and to carry out dehydration of the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we have to find the structure of compound (D) in the following chemical reaction.
When propionic acid is treated with a catalytic amount of phosphorus and bromine, $\alpha - H$ substitution takes place, producing dibromo product. The substitution of $\alpha - H$ of propionic acid by bromine takes place on action of bromine in the presence of phosphorus. The $\alpha - H$ atoms of propionic acid are substituted by bromine atoms.
The chemical reaction of formation of (A) is shown below.

2,2-dibromo propionic acid
The product (A) is 2, 2 –dibromo propionic acid.
When the dibromo derivative of propionic acid is treated with aqueous $KOH$, the bromine atoms in the acid will be replaced by hydroxyl groups which on acidification will yield propionic acid with a double bond.
The complete reaction is shown below.

Here, compound (D) is acrylic acid and the structure of the compound is shown below.
$H_2C=CH-COOH$
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional information:
Here, the dibromo derivative of propionic acid that is compound (A) is formed by Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reduction reaction. The reaction is used for introducing halogen such as chlorine and bromine in carboxylic acid. This reaction is not applicable in case of introducing iodine and fluorine in carboxylic acid. The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reduction reaction.
Note: Students should keep in mind that the action of alcoholic $KOH$ and aqueous $KOH$ on carboxylic acid is different. The use of aqueous $KOH$ is done in case of the chemical reactions which are not water sensitive and used for carrying out the hydrolysis reaction. The alcoholic $KOH$ is used in case of water sensitive reaction and to carry out dehydration of the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




