
Compound A and B respectively are:
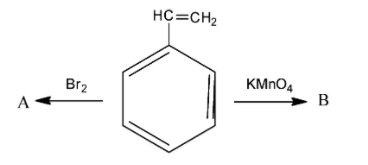
A. o-Bromostyrene, benzoic acid
B. p-bromostyrene, benzaldehyde
C. m-bromostyrene, benzaldehyde
D. styrene dibromide, benzoic acid

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: When bromine is added to alkenes, anti addition takes place. Whereas, when potassium permanganate is added to the double bond, it is replaced by two OH groups, from where the water molecule exits.
Complete step-by step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to know the action of bromine and potassium permanganate on alkenes. In alkenes, bromine is added across the double bonds. Now, the compound we have been given in the question is called styrene. As we can see that styrene is a benzene ring that has a double bond at the tip. When bromine is reacted, it is added across the double bonds. Generally, during addition of bromine in double bonds, some amount of carbon tetrachloride is also used as a reagent. Remember that when bromine is added across double bonds, then both the bromide atoms are added on the same side, hence we obtain a cis isomer. The reaction is as follows:
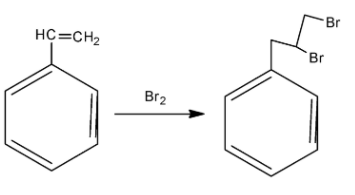
So, we obtain styrene dibromide, which is the compound A. Now, in order to find out the compound B, we need to know about the action of potassium permanganate. Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidising agent and is used for oxidation of alkenes. Initially, the potassium permanganate converts the double bond of the carbon to two alcohol or -OH groups. However, two OH groups are very unstable. So, at a suitable temperature, ${{H}_{2}}O$ gets released and we finally obtain the acidic group. Potassium permanganate is a purple coloured compound but as the reaction proceeds, the purple colour goes away. This is how the reaction proceeds:
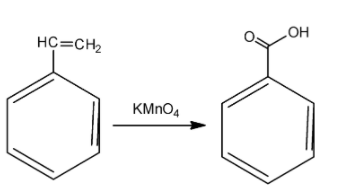
So, the compound we have obtained is benzoic acid. The correct answer for this question is option D.
NOTE: Addition of iodine to alkenes generally does not take place because the compounds get very unstable and eliminate iodine at high temperatures. The addition of $C{{l}_{2}}/B{{r}_{2}}$ is always anti-addition.
Complete step-by step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to know the action of bromine and potassium permanganate on alkenes. In alkenes, bromine is added across the double bonds. Now, the compound we have been given in the question is called styrene. As we can see that styrene is a benzene ring that has a double bond at the tip. When bromine is reacted, it is added across the double bonds. Generally, during addition of bromine in double bonds, some amount of carbon tetrachloride is also used as a reagent. Remember that when bromine is added across double bonds, then both the bromide atoms are added on the same side, hence we obtain a cis isomer. The reaction is as follows:

So, we obtain styrene dibromide, which is the compound A. Now, in order to find out the compound B, we need to know about the action of potassium permanganate. Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidising agent and is used for oxidation of alkenes. Initially, the potassium permanganate converts the double bond of the carbon to two alcohol or -OH groups. However, two OH groups are very unstable. So, at a suitable temperature, ${{H}_{2}}O$ gets released and we finally obtain the acidic group. Potassium permanganate is a purple coloured compound but as the reaction proceeds, the purple colour goes away. This is how the reaction proceeds:

So, the compound we have obtained is benzoic acid. The correct answer for this question is option D.
NOTE: Addition of iodine to alkenes generally does not take place because the compounds get very unstable and eliminate iodine at high temperatures. The addition of $C{{l}_{2}}/B{{r}_{2}}$ is always anti-addition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




