
Complex X of composition $Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}C{{l}_{n}}$ has a spin only magnetic moment of 3.83 BM. It reacts with $AgN{{O}_{3}}$ and shows geometrical isomerism. The IUPAC nomenclature of X is:
A.Hexaaqua chromium(iii) chloride
B.Tetraaquadichlorido chromium (iii) dihydrate
C.Dichlorotetraaqua chromium(iv) chloride dihydrate
D.Tetraaquadichlorido chromium(iv) chloride dihydrate
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: First find out the number of unpaired electrons present in the compound. Then with the help of oxidation number, find the value of ‘n’. Finally use the concept of reaction with $AgN{{O}_{3}}$ and find the IUPAC name.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about the IUPAC nomenclature. Coordination compounds are formulated and named according to the system set up by IUPAC. It is important for writing systematic names and formulas, particularly when dealing with isomers. Now, we have been given the compound $Cr({{H}_{2}}){{)}_{6}}C{{l}_{n}}$, and it’s magnetic moment is given to be 3.83 Bm. As we know that the formula for magnetic moment is $\sqrt{n(n+2)}$, where n is the number of unpaired electrons. On solving the equation, we have
$\sqrt{n(n+2)}=3.83$
$\begin{align}
& n(n+2)=15 \\
& So,\,n=3 \\
\end{align}$
There are 3 unpaired electrons. Now, the electronic configuration of chromium is $[Ar]4{{s}^{1}}3{{d}^{5}}$. Also it has 3 unpaired electrons. So, in the final compound chromium will have +3 oxidation state; chromium exhibits ${{d}^{3}}$ configuration. Now, let us find the value of ‘n’ again, by using the oxidation number method, to verify. We have
$\begin{align}
& Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}C{{l}_{n}} \\
& \,\,3+0-n=0 \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,n=3 \\
\end{align}$
So the compound is $Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}C{{l}_{3}}$, However, it is the skeletal structure and we have to find out how many chlorine are attached to the compound. It is given that compounds react with $AgN{{O}_{3}}$. Now, the given possibilities are:
$[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]C{{l}_{3}},\,[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{5}}]C{{l}_{2}}.{{H}_{2}}O,\,[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl.2{{H}_{2}}O\,and\,[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{3}}C{{l}_{3}}].3{{H}_{2}}O$
The last compound is not possible as Cl must be outside the sphere, in order to react with $AgN{{O}_{3}}$. Cl has to be dissociated. As it shows geometrical isomerism, option 1 and 2 are eliminated as they do not exhibit geometrical isomerism. However, compound 3 exhibits geometrical isomerism and they look like this:
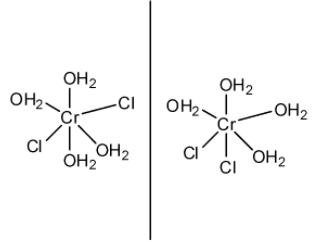
So, our final compound has the formula $[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl.2{{H}_{2}}O$, and it’s name is Tetraaquadichlorido chromium (iii) dihydrate.
So, we obtain our answer as option B.
NOTE: The compounds which show geometrical isomerism have two configurations, cis and trans. In cis configuration, same groups or toms are present on the same side and in trans, same groups are present on opposite sides. In the diagram, first one is trans and second one is cis.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about the IUPAC nomenclature. Coordination compounds are formulated and named according to the system set up by IUPAC. It is important for writing systematic names and formulas, particularly when dealing with isomers. Now, we have been given the compound $Cr({{H}_{2}}){{)}_{6}}C{{l}_{n}}$, and it’s magnetic moment is given to be 3.83 Bm. As we know that the formula for magnetic moment is $\sqrt{n(n+2)}$, where n is the number of unpaired electrons. On solving the equation, we have
$\sqrt{n(n+2)}=3.83$
$\begin{align}
& n(n+2)=15 \\
& So,\,n=3 \\
\end{align}$
There are 3 unpaired electrons. Now, the electronic configuration of chromium is $[Ar]4{{s}^{1}}3{{d}^{5}}$. Also it has 3 unpaired electrons. So, in the final compound chromium will have +3 oxidation state; chromium exhibits ${{d}^{3}}$ configuration. Now, let us find the value of ‘n’ again, by using the oxidation number method, to verify. We have
$\begin{align}
& Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}C{{l}_{n}} \\
& \,\,3+0-n=0 \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,n=3 \\
\end{align}$
So the compound is $Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}C{{l}_{3}}$, However, it is the skeletal structure and we have to find out how many chlorine are attached to the compound. It is given that compounds react with $AgN{{O}_{3}}$. Now, the given possibilities are:
$[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]C{{l}_{3}},\,[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{5}}]C{{l}_{2}}.{{H}_{2}}O,\,[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl.2{{H}_{2}}O\,and\,[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{3}}C{{l}_{3}}].3{{H}_{2}}O$
The last compound is not possible as Cl must be outside the sphere, in order to react with $AgN{{O}_{3}}$. Cl has to be dissociated. As it shows geometrical isomerism, option 1 and 2 are eliminated as they do not exhibit geometrical isomerism. However, compound 3 exhibits geometrical isomerism and they look like this:

So, our final compound has the formula $[Cr{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl.2{{H}_{2}}O$, and it’s name is Tetraaquadichlorido chromium (iii) dihydrate.
So, we obtain our answer as option B.
NOTE: The compounds which show geometrical isomerism have two configurations, cis and trans. In cis configuration, same groups or toms are present on the same side and in trans, same groups are present on opposite sides. In the diagram, first one is trans and second one is cis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




