
Complete the table:







Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint: A tissue is a collection of cells that share a common origin and usually perform the same function. A plant is made up of different kinds of tissues. Tissues are divided into two categories: meristematic and permanent tissues, depending on whether the cells forming them are capable of dividing. Meristematic tissues have the capacity to divide while permanent tissue loses this capacity. Here, we will discuss the permanent tissue in detail.
Complete answer:
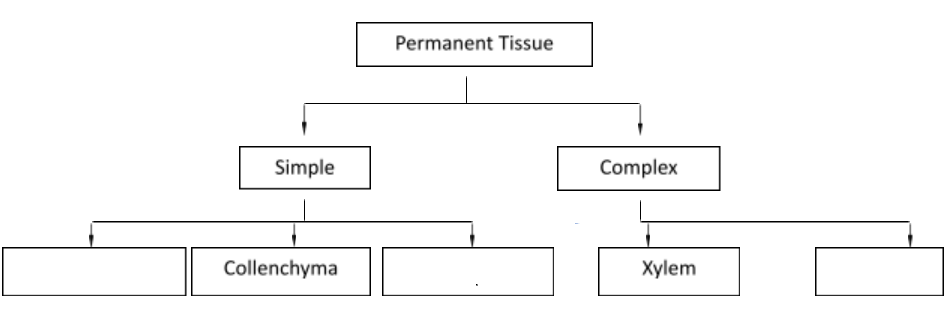
Permanent tissue cells do not usually divide any further. Permanent tissues having all cells similar in structure and function are called simple tissues while those having many different types of cells are called complex tissues.
1. Simple Tissue
Just one type of cell makes up a basic tissue. Plants include parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, which are simple tissues.
Parenchyma: These are living cells and form a thin and cellulosic primary wall. Intercellular spaces are present, and the shape may vary (spherical/oval/round/polygonal). Chloroplasts are present in parenchymatous cells. Pits are not found. Mostly found in all plant parts and is the most abundant filling tissue. Mainly performs the function of food storage.
Collenchyma: It is the living mechanical tissue and forms the primary wall and has pectin present at corners which makes it non uniformly thick. Intercellular spaces are absent, and its shape also varies. It also does not have pits. It is found in dicot hypodermis, petiole of leaves. Mainly performs the function of mechanical support.
Sclerenchyma: It is the dead tissue (without protoplast). It forms the secondary wall which is made of lignin and is uniformly thick. No intercellular spaces. These are long and narrow in shape. Pits are present and are found in hard woody parts and in monocot hypodermis. It is the chief mechanical tissue of plants. It is of two types of fibres and sclereids. Fibres are elongated and found the xylem and phloem fibres. Sclereids have narrow lumen and are commonly found in the fruit walls of nuts, pulp of fruits like guava, pear and sapota, in seed coats of legumes and in leaves of tea.
2. Complex Tissue
Complex tissues are made up of many different types of cells that function together as a unit. Plants have complex tissues called xylem and phloem.
Xylem: It is also called ‘hydrome’ or wood. It helps in the conduction of water and minerals in unidirectional manner from roots to stem. It is more developed in xerophytes and poorly developed in hydrophytes. Xylem has four components namely, Tracheids, Vessels, Xylem fibres and Xylem parenchyma. Tracheids and vessels, together are called Tracheary elements. Gymnosperms lack vessels in their xylem. Out of these, tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres are dead due to the presence of lignin. The only living component in xylem is xylem parenchyma.
Phloem: It is also called as bast or ‘leptome’. It helps in the conduction of food in a bidirectional manner, from roots to leaves or vice-versa depending upon the need of the plant part. It also has four components viz, Sieve tube elements, Companion cells, Phloem fibres and Phloem parenchyma. Out of these, the only dead component is phloem fibre. Gymnosperms lack sieve tubes and companion cells and instead they have sieve cells and albuminous cells.
Note:
Both xylem and phloem have primary and secondary form. Secondary xylem and secondary phloem are formed during secondary growth. Primary Xylem and Phloem are differentiated into protoxylem, metaxylem and protophloem, metaphloem, respectively. The protophloem are first formed and narrow sieve tubes and metaphloem are late formed and have bigger sieve tubes. Similarly, protoxylem are initial and small; metaxylem are later and larger. When protoxylem are towards periphery, the condition is called as ‘Exarch’ and is generally found in roots while the condition when protoxylem is towards center and metaxylem at periphery, it is known as ‘Endarch’ and is found in stems.
Complete answer:
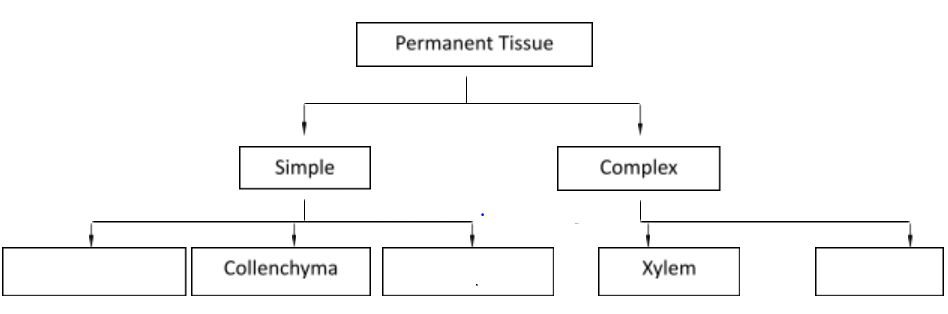
Permanent tissue cells do not usually divide any further. Permanent tissues having all cells similar in structure and function are called simple tissues while those having many different types of cells are called complex tissues.
1. Simple Tissue
Just one type of cell makes up a basic tissue. Plants include parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, which are simple tissues.
Parenchyma: These are living cells and form a thin and cellulosic primary wall. Intercellular spaces are present, and the shape may vary (spherical/oval/round/polygonal). Chloroplasts are present in parenchymatous cells. Pits are not found. Mostly found in all plant parts and is the most abundant filling tissue. Mainly performs the function of food storage.
Collenchyma: It is the living mechanical tissue and forms the primary wall and has pectin present at corners which makes it non uniformly thick. Intercellular spaces are absent, and its shape also varies. It also does not have pits. It is found in dicot hypodermis, petiole of leaves. Mainly performs the function of mechanical support.
Sclerenchyma: It is the dead tissue (without protoplast). It forms the secondary wall which is made of lignin and is uniformly thick. No intercellular spaces. These are long and narrow in shape. Pits are present and are found in hard woody parts and in monocot hypodermis. It is the chief mechanical tissue of plants. It is of two types of fibres and sclereids. Fibres are elongated and found the xylem and phloem fibres. Sclereids have narrow lumen and are commonly found in the fruit walls of nuts, pulp of fruits like guava, pear and sapota, in seed coats of legumes and in leaves of tea.
2. Complex Tissue
Complex tissues are made up of many different types of cells that function together as a unit. Plants have complex tissues called xylem and phloem.
Xylem: It is also called ‘hydrome’ or wood. It helps in the conduction of water and minerals in unidirectional manner from roots to stem. It is more developed in xerophytes and poorly developed in hydrophytes. Xylem has four components namely, Tracheids, Vessels, Xylem fibres and Xylem parenchyma. Tracheids and vessels, together are called Tracheary elements. Gymnosperms lack vessels in their xylem. Out of these, tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres are dead due to the presence of lignin. The only living component in xylem is xylem parenchyma.
Phloem: It is also called as bast or ‘leptome’. It helps in the conduction of food in a bidirectional manner, from roots to leaves or vice-versa depending upon the need of the plant part. It also has four components viz, Sieve tube elements, Companion cells, Phloem fibres and Phloem parenchyma. Out of these, the only dead component is phloem fibre. Gymnosperms lack sieve tubes and companion cells and instead they have sieve cells and albuminous cells.

Note:
Both xylem and phloem have primary and secondary form. Secondary xylem and secondary phloem are formed during secondary growth. Primary Xylem and Phloem are differentiated into protoxylem, metaxylem and protophloem, metaphloem, respectively. The protophloem are first formed and narrow sieve tubes and metaphloem are late formed and have bigger sieve tubes. Similarly, protoxylem are initial and small; metaxylem are later and larger. When protoxylem are towards periphery, the condition is called as ‘Exarch’ and is generally found in roots while the condition when protoxylem is towards center and metaxylem at periphery, it is known as ‘Endarch’ and is found in stems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




