
Complete the refracted ray in the flowing ray diagram
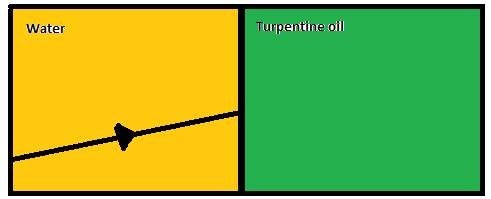

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Water has a density of 1000 \[\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}\]while the density of turpentine oil is 870\[\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}\]. According to the Snell’s law, if a ray of light passes through a optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium, the ray moves away from the normal, while if it if a ray of light passes through a optically rarer medium to an optically denser medium, the ray moves towards the normal.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, there are two mediums in the picture. One of them is water, while the other medium is turpentine oil. The incident ray for the medium of water to turpentine oil is shown in the above picture.
The speed of a wave changes when it passes from one medium to another and it bends. This bending of a wave when it enters a medium where its speed is different is called Refraction. The bending of a wave depends on the refractive index of the medium and the angle between the ray and the line perpendicular (normal) to the surface separating the two media. Now to understand how the refracted ray will behave in this case, we must first know Snell's law.
Now according to the Snell’s law,
\[{{\eta }_{i}}\centerdot \sin {{\theta }_{i}}={{\eta }_{r}}\sin {{\theta }_{r}}\]
Where,
\[{\eta _i}\] is the refractive index of the medium where the incident ray lies,
\[{\theta _i}\] is the angle between the normal and the incident ray,
\[{\eta _r}\] is the refractive index of the medium where the refracted ray lies, and
\[{\theta _r}\] is the angle between the normal and the refracted ray. Thus from the Snell’s law, we can say that when a ray passes from a denser medium to rarer medium, the ray moves away from the normal, while when the ray passes from a rarer medium to a denser medium, the ray moves towards the normal.
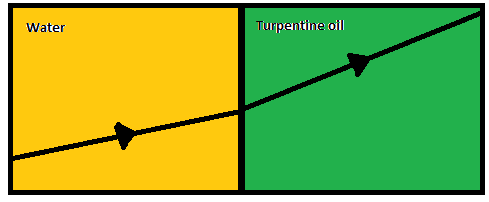
Now, water has a density of 1000\[\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}\] and turpentine oil has a density of 870\[\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}\], which is a rarer medium than water. Hence the ray moves away from the normal.
Thus the refracted ray of the following ray diagram is as follows:
Note:
Here, if the difference between the two refractive indices of the two medium is extremely high, unlike in the case as above, then the incident ray instead of refracting, it reflects. This will happen only if the angle of refraction is over 90 degrees, and the ray reflects. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection, and this angle is known as critical angle.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, there are two mediums in the picture. One of them is water, while the other medium is turpentine oil. The incident ray for the medium of water to turpentine oil is shown in the above picture.
The speed of a wave changes when it passes from one medium to another and it bends. This bending of a wave when it enters a medium where its speed is different is called Refraction. The bending of a wave depends on the refractive index of the medium and the angle between the ray and the line perpendicular (normal) to the surface separating the two media. Now to understand how the refracted ray will behave in this case, we must first know Snell's law.
Now according to the Snell’s law,
\[{{\eta }_{i}}\centerdot \sin {{\theta }_{i}}={{\eta }_{r}}\sin {{\theta }_{r}}\]
Where,
\[{\eta _i}\] is the refractive index of the medium where the incident ray lies,
\[{\theta _i}\] is the angle between the normal and the incident ray,
\[{\eta _r}\] is the refractive index of the medium where the refracted ray lies, and
\[{\theta _r}\] is the angle between the normal and the refracted ray. Thus from the Snell’s law, we can say that when a ray passes from a denser medium to rarer medium, the ray moves away from the normal, while when the ray passes from a rarer medium to a denser medium, the ray moves towards the normal.
Now, water has a density of 1000\[\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}\] and turpentine oil has a density of 870\[\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}\], which is a rarer medium than water. Hence the ray moves away from the normal.
Thus the refracted ray of the following ray diagram is as follows:

Note:
Here, if the difference between the two refractive indices of the two medium is extremely high, unlike in the case as above, then the incident ray instead of refracting, it reflects. This will happen only if the angle of refraction is over 90 degrees, and the ray reflects. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection, and this angle is known as critical angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




