
Complete the picture.
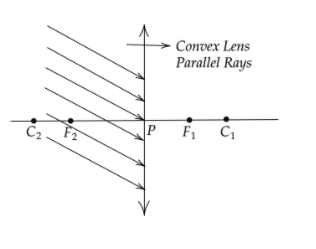

Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: We first need to know the nature and image formation of convex lenses. In case of convex lenses when a parallel line comes from infinity incidents on the lens reflected back and converge at a point that is the focus at the principal axis.
Complete step by step solution:
Convex Lens:
It is a lens that converges the rays of light that convey the parallel rays to its principal axis which is respectively thick across the middle and the thin at the lower and upper edges. Also the edges are conversed outward.
Focal length:
It is the distance between the centers of a convex lens where the parallel rays converge.
Principle Axis:
It is defined as the line that passes through the center of the surface of the convex lens and through the center of the curvature of all the segments of the lens.
As per the figure given in the problem the light rays come from infinity and are parallel to each other so after conversion it will get converse at a point on the principle axis.
Now the complete picture will look like,
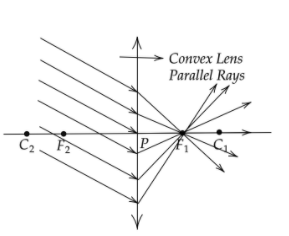
The formula of the convex lens is defined as the,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where,
Focal length of the lens = f
Final value of the image = v
Initial value of the image = u
Note:
Remember that the convex lenses are used in the microscopes, magnification glasses and the eyeglasses. And with the help of this example we can signify how these lenses are used to crest real images. Another important point to remember is that in eyeglasses the convex lenses remain closer to the eye creating a virtual image.
Complete step by step solution:
Convex Lens:
It is a lens that converges the rays of light that convey the parallel rays to its principal axis which is respectively thick across the middle and the thin at the lower and upper edges. Also the edges are conversed outward.
Focal length:
It is the distance between the centers of a convex lens where the parallel rays converge.
Principle Axis:
It is defined as the line that passes through the center of the surface of the convex lens and through the center of the curvature of all the segments of the lens.
As per the figure given in the problem the light rays come from infinity and are parallel to each other so after conversion it will get converse at a point on the principle axis.
Now the complete picture will look like,

The formula of the convex lens is defined as the,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where,
Focal length of the lens = f
Final value of the image = v
Initial value of the image = u
Note:
Remember that the convex lenses are used in the microscopes, magnification glasses and the eyeglasses. And with the help of this example we can signify how these lenses are used to crest real images. Another important point to remember is that in eyeglasses the convex lenses remain closer to the eye creating a virtual image.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




