
Complete the given reaction:
\[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\xrightarrow[2.Aq.N{{H}_{3}}]{1.B{{r}_{2}},P}\]
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The presence of alpha hydrogen makes the aliphatic carboxylic acid to react with bromine in the presence of phosphorus. This type of chemical reaction is called Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked that butanoic acid is reacting with bromine and later reacting with ammonia.
- We have to find the product in the given reaction.
- The given reaction is as follows.
\[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\xrightarrow[2.Aq.N{{H}_{3}}]{1.B{{r}_{2}},P}\]
- The reaction contains two steps.
- In the first step the butanoic acid reacts with bromine in the presence of phosphorus.
- In the second step the product formed in the step-1 reacts with ammonia.
Step-1:
- The chemical reaction butanoic acid with bromine in the presence of phosphorus is as follows.
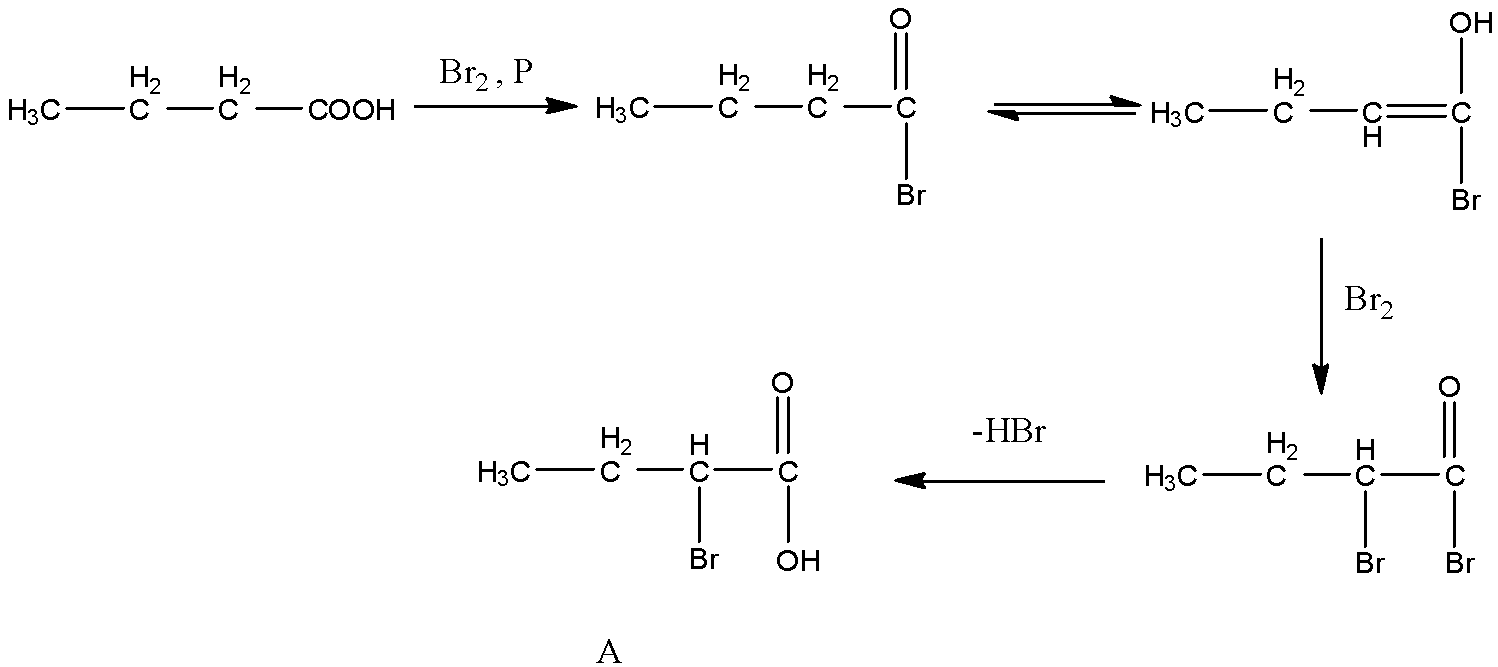
- At starting the carboxylic acid reacts with bromine and forms a bromo derivative. Later there is a generation of unsaturation in the compound due to rearrangement of hydrogen.
- After rearrangement the molecule again reacts with one more bromine and forms a dibromo derivative and later loses hydrogen bromide and gives a product which has bromine at alpha position.
Step-2 - The product formed in step -1 (A) is going to react with Ammonia and forms a product which contains both amine and carboxylic acid functional groups in its structure.
- The chemical reaction of step-2 is as follows.
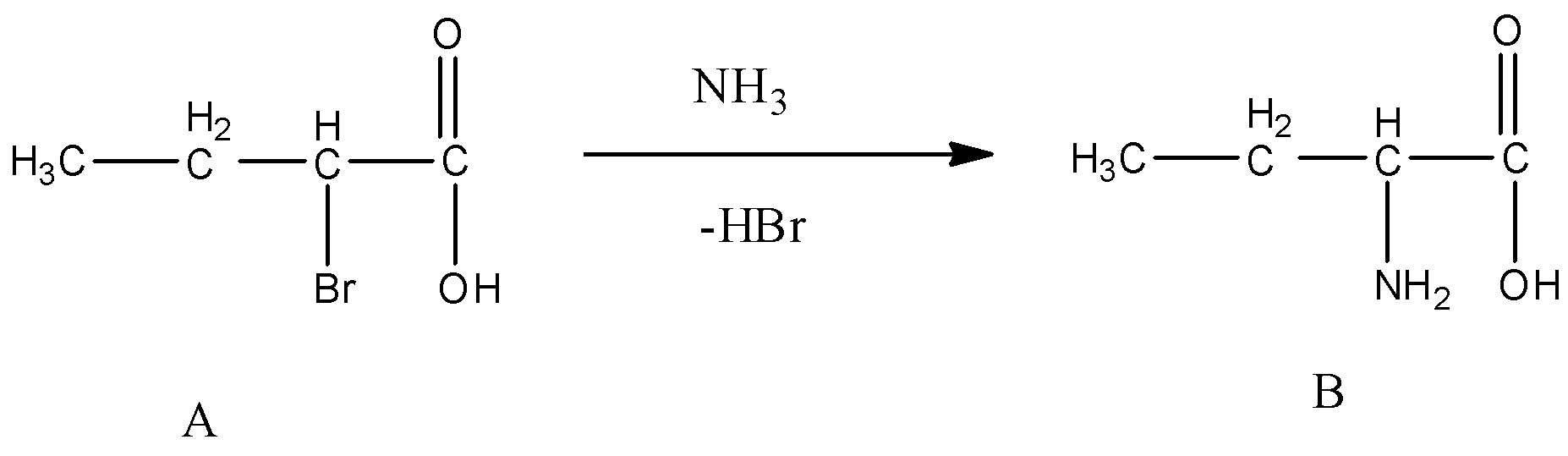
- Finally the product formed contains a amino group at alpha position.
Note: Generally Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction is used to prepare amino acids. Alanine is an amino acid which can be prepared from propionic acid by using Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked that butanoic acid is reacting with bromine and later reacting with ammonia.
- We have to find the product in the given reaction.
- The given reaction is as follows.
\[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\xrightarrow[2.Aq.N{{H}_{3}}]{1.B{{r}_{2}},P}\]
- The reaction contains two steps.
- In the first step the butanoic acid reacts with bromine in the presence of phosphorus.
- In the second step the product formed in the step-1 reacts with ammonia.
Step-1:
- The chemical reaction butanoic acid with bromine in the presence of phosphorus is as follows.

- At starting the carboxylic acid reacts with bromine and forms a bromo derivative. Later there is a generation of unsaturation in the compound due to rearrangement of hydrogen.
- After rearrangement the molecule again reacts with one more bromine and forms a dibromo derivative and later loses hydrogen bromide and gives a product which has bromine at alpha position.
Step-2 - The product formed in step -1 (A) is going to react with Ammonia and forms a product which contains both amine and carboxylic acid functional groups in its structure.
- The chemical reaction of step-2 is as follows.

- Finally the product formed contains a amino group at alpha position.
Note: Generally Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction is used to prepare amino acids. Alanine is an amino acid which can be prepared from propionic acid by using Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




