
Complete the following equations and name the products formed.
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow{Conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}/443K}Ethene$
(A)- True
(B)- False
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: When ethanol is heated with conc. sulphuric acid, sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent and takes up the water molecule from the reactant.
Complete step by step answer:
-The acid catalysts normally used for dehydration of alcohols are conc. sulphuric acid or conc. phosphoric acid.
-Acid in such acid-catalyzed dehydration reactions not only acts as a dehydrating agent, but it is also a strong oxidizing agent which oxidizes some of the alcohols to form carbon dioxide and the same ties are reduced to give sulphur dioxide. Both these gases are removed to get alkene as the product.
-Ethanol is heated with an excess of sulfuric acid at a temperature of 443K. Carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide produced due to the oxidation of alcohols are removed by passing through sodium hydroxide solution and ethene is collected over water.
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\xrightarrow{conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4,}}443K}C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
So, the given statement is true.So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Different forms of alcohols can be dehydrated in different ways. Following are the reactions for their conversions-
(i) One of the ways is by using aluminium oxide as a catalyst. This is the simple way of making gaseous alkenes likes ethene. In this, ethanol vapour is passed over heated aluminium oxide powder due to which dehydration takes place in the ethanol molecule and it gives ethene and water vapour.
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\xrightarrow{A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}}C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
(ii) Another way is the dehydration of secondary alcohol to give the corresponding alkene. Cyclohexanol is heated with concentrated phosphoric acid giving liquid cyclohexene after purification. Here phosphoric acid in place of sulphuric acid is a safer choice it is safer and produces a less messy reaction.
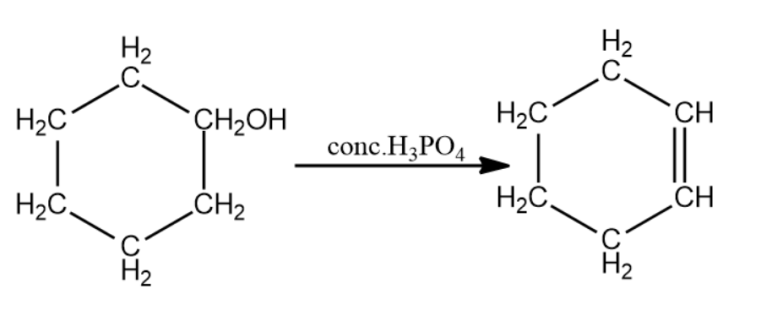
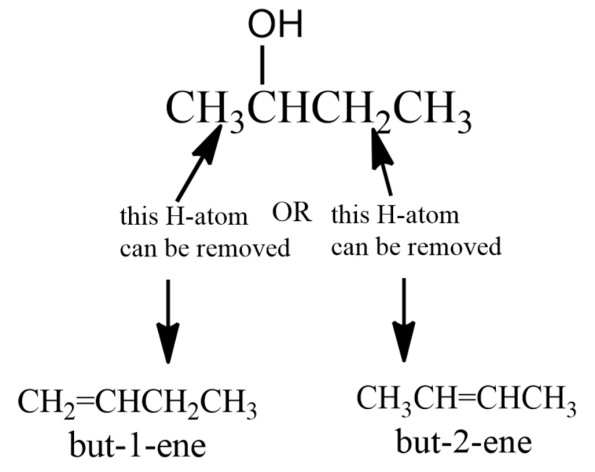
(iii) Next is the dehydration of complicated alcohol molecules. Let us consider Butan-2-ol for this conversion. When alcohol is dehydrated, the –OH group and an H-atom from the next carbon in the chain is removed in the form of water. With molecules like butan-2-ol, there are two possibilities-
Complete step by step answer:
-The acid catalysts normally used for dehydration of alcohols are conc. sulphuric acid or conc. phosphoric acid.
-Acid in such acid-catalyzed dehydration reactions not only acts as a dehydrating agent, but it is also a strong oxidizing agent which oxidizes some of the alcohols to form carbon dioxide and the same ties are reduced to give sulphur dioxide. Both these gases are removed to get alkene as the product.
-Ethanol is heated with an excess of sulfuric acid at a temperature of 443K. Carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide produced due to the oxidation of alcohols are removed by passing through sodium hydroxide solution and ethene is collected over water.
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\xrightarrow{conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4,}}443K}C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
So, the given statement is true.So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Different forms of alcohols can be dehydrated in different ways. Following are the reactions for their conversions-
(i) One of the ways is by using aluminium oxide as a catalyst. This is the simple way of making gaseous alkenes likes ethene. In this, ethanol vapour is passed over heated aluminium oxide powder due to which dehydration takes place in the ethanol molecule and it gives ethene and water vapour.
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\xrightarrow{A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}}C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
(ii) Another way is the dehydration of secondary alcohol to give the corresponding alkene. Cyclohexanol is heated with concentrated phosphoric acid giving liquid cyclohexene after purification. Here phosphoric acid in place of sulphuric acid is a safer choice it is safer and produces a less messy reaction.

(iii) Next is the dehydration of complicated alcohol molecules. Let us consider Butan-2-ol for this conversion. When alcohol is dehydrated, the –OH group and an H-atom from the next carbon in the chain is removed in the form of water. With molecules like butan-2-ol, there are two possibilities-

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




