
Compare the relative stability of the following resonance structure.
[p]
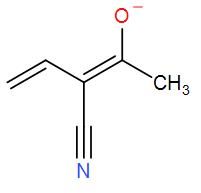
[q]
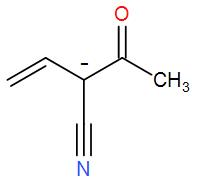
[r]
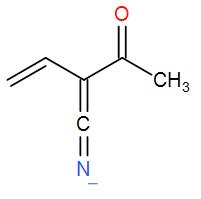
[A] p > q > r
[B] q > p > r
[C] q > r > p
[D] p > r > q



Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint: To answer this, you must remember that the phenomenon of the existence of a molecule in many structures due to the delocalization of electrons is called resonance. Here, remember that a negative charge on an electronegative atom is stabilizing whereas on an electropositive atom it is destabilizing.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that resonance is stabilizing energy. It affects the stability of a compound/ molecule and thus affects its structure and the reaction it undergoes.
The canonical forms of a molecule are also known as Resonating Structures.
Now, let us discuss the question given to us.
We can see that the parent structure is the same; it is the negative charge that is delocalizing to give us a different resonating structure.
- In the above compounds, Carbon, Nitrogen, and oxygen are present. Out of these, oxygen is the most electronegative element than nitrogen and carbon is the least electronegative element.
- We know that the presence of a negative charge on an electronegative element is more stable as compared to that of less electronegative elements.
So, we can say that the negative charge on oxygen is more stable, and hence, the stability increases.
Also, we know that $C\equiv N$ is more stable than $C=C=N$ as the negative charge is shared over nitrogen and carbon only in the former.
- In p, the negative charge is on oxygen so it is the most stable. In q, the negative charge is on carbon and thus will be the least stable structure. And in r, the negative charge is on nitrogen.
Hence, the stability order will be p > r > q.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information”.
- Resonance helps to represent the possible ion intermediates by having the extra electron or electrons delocalized within the molecules.
- A molecule that has several resonance structures is more stable than a molecule that has fewer resonance structures.
Note: Resonance is a stabilizing energy. It is a way of describing bonding by the delocalized electrons where the bonding cannot be expressed by a single Lewis structure. There are two types of resonance energy-positive resonance, known as +R, and negative resonance known as –R.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that resonance is stabilizing energy. It affects the stability of a compound/ molecule and thus affects its structure and the reaction it undergoes.
The canonical forms of a molecule are also known as Resonating Structures.
Now, let us discuss the question given to us.
We can see that the parent structure is the same; it is the negative charge that is delocalizing to give us a different resonating structure.
- In the above compounds, Carbon, Nitrogen, and oxygen are present. Out of these, oxygen is the most electronegative element than nitrogen and carbon is the least electronegative element.
- We know that the presence of a negative charge on an electronegative element is more stable as compared to that of less electronegative elements.
So, we can say that the negative charge on oxygen is more stable, and hence, the stability increases.
Also, we know that $C\equiv N$ is more stable than $C=C=N$ as the negative charge is shared over nitrogen and carbon only in the former.
- In p, the negative charge is on oxygen so it is the most stable. In q, the negative charge is on carbon and thus will be the least stable structure. And in r, the negative charge is on nitrogen.
Hence, the stability order will be p > r > q.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information”.
- Resonance helps to represent the possible ion intermediates by having the extra electron or electrons delocalized within the molecules.
- A molecule that has several resonance structures is more stable than a molecule that has fewer resonance structures.
Note: Resonance is a stabilizing energy. It is a way of describing bonding by the delocalized electrons where the bonding cannot be expressed by a single Lewis structure. There are two types of resonance energy-positive resonance, known as +R, and negative resonance known as –R.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




