
What is the common name of the polymer obtained by the polymerization of caprolactam? Is it addition polymer or condensation polymer?
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: A polymer refers to a material or substance consisting of very huge molecules or macromolecules that are made up of many repeating subunits. Polymerization refers to the process in which many small molecules (i.e. monomers) are combined together via covalent bonds forming a chain or network.
Complete step by step answer:
Addition polymers are formed when unsaturated molecules of carbon react resulting in the long chain of polymer molecules. During the addition polymerization reaction, no atoms or molecules are eliminated or removed. On the other hand, condensation polymers are formed when bifunctional monomers react resulting in the long chain of polymer molecules. During the condensation polymerisation reaction, small molecules including water are eliminated or removed.
Nylon 6 is synthesized through condensation polymerisation by the ring-opening of caprolactam. On heating caprolactam for about 4-5 hours at about 533 K in the presence of an inert atmosphere (nitrogen), the ring decomposes and undergoes polymerization. The molten mass is then passed through spinnerets which leads to the formation of nylon 6 fibers.
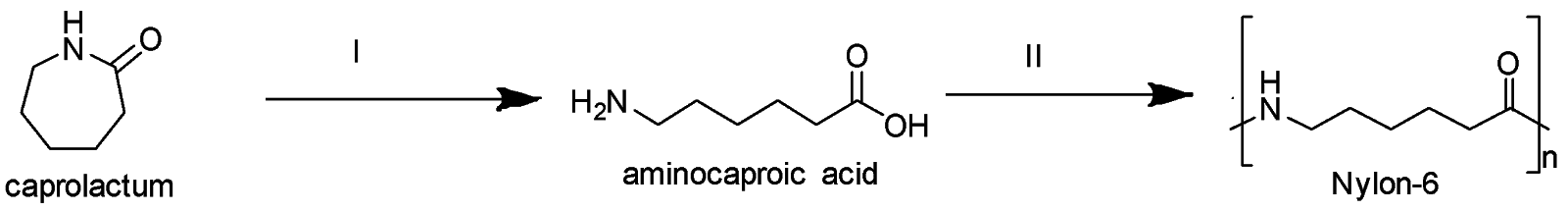
In the first step (I), ring opening of caprolactam occurs while in the second step (II), aminocaproic acid undergoes condensation polymerization to form nylon 6.
Therefore, the common name of the polymer obtained by the polymerization of caprolactam in Nylon 6. It is a condensation polymer.
Note:
The fibres of Nylon 6 are tough, having high tensile strength, elasticity and lustre. These are wrinkle-proof and also highly resistant to chemicals (acids, bases) and even abrasion. Therefore, Nylon 6 is usually applied where lubricity, toughness, and wear are the key factors to be considered, for example, gear wheels.
Complete step by step answer:
Addition polymers are formed when unsaturated molecules of carbon react resulting in the long chain of polymer molecules. During the addition polymerization reaction, no atoms or molecules are eliminated or removed. On the other hand, condensation polymers are formed when bifunctional monomers react resulting in the long chain of polymer molecules. During the condensation polymerisation reaction, small molecules including water are eliminated or removed.
Nylon 6 is synthesized through condensation polymerisation by the ring-opening of caprolactam. On heating caprolactam for about 4-5 hours at about 533 K in the presence of an inert atmosphere (nitrogen), the ring decomposes and undergoes polymerization. The molten mass is then passed through spinnerets which leads to the formation of nylon 6 fibers.

In the first step (I), ring opening of caprolactam occurs while in the second step (II), aminocaproic acid undergoes condensation polymerization to form nylon 6.
Therefore, the common name of the polymer obtained by the polymerization of caprolactam in Nylon 6. It is a condensation polymer.
Note:
The fibres of Nylon 6 are tough, having high tensile strength, elasticity and lustre. These are wrinkle-proof and also highly resistant to chemicals (acids, bases) and even abrasion. Therefore, Nylon 6 is usually applied where lubricity, toughness, and wear are the key factors to be considered, for example, gear wheels.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




