
Collect information about experiments done by Faraday.
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint: Electricity and magnetism are connected in several ways. Faraday’s electromagnetic induction experiments are the examples for that. Changing magnetic fields cause the emf generation.
Complete step by step answer:
Electricity and magnetism are interrelated in many ways. That’s why electromagnetism discipline has been developed. Moving charges or currents can produce magnetic fields. Thus, it can deflect the magnetic compass needle. Faraday developed a system that showed, moving magnetic field produces electricity. He discovered that, if the number of magnetic lines of forces changes, an emf is produced in the circuit. This process is collectively known as electromagnetic induction.
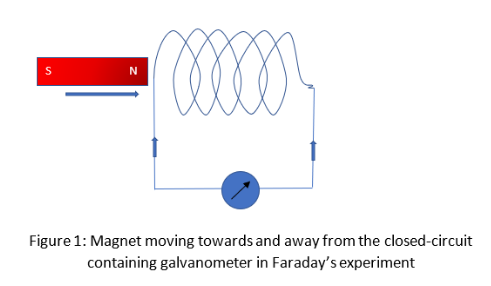
Figure above shows a closed-circuit containing coils of insulated wire. There are no sources of emf, hence it won’t show any deflections in the galvanometer. If we move the bar magnet towards the coil, a deflection will produce a galvanometer. It is not a permanent deflection. When we remove the magnet outside of the coil, the galvanometer shows an opposite deflection. We can see this deflection of a needle in the galvanometer very fast if we move the bar magnet quickly. We can observe deflection in the opposite side of observed deflection, if we change the poles of the magnet. He even tried to move the coil by fixing the magnet. Even though deflections in the galvanometer were generated. He observed that if the motion of a magnet is faster, larger is the deflection produced in the galvanometer.
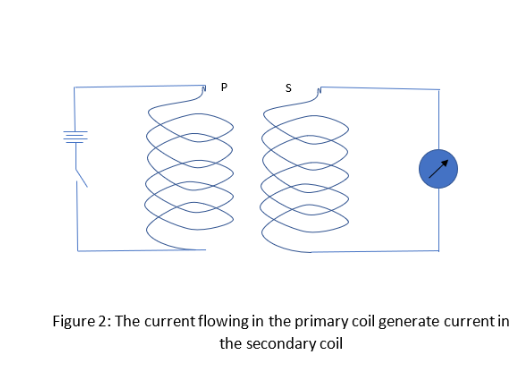
As we can see the figure 2, primary circuit consists of a switch and battery and secondary circuit have a galvanometer. If we are moving either of the coils, the galvanometer shows deflection. Here the current carrying coil produces the magnetic field. Sudden deflections in one direction can be obtained if we turn on the primary coil and in the opposite direction when the current supply turns off.
Additional information:
Faraday’s law of induction predicted how a magnetic field interacts with an electric circuit to produce emf.
\[\varepsilon =-\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}\], where \[{{\phi }_{B}}\] is the magnetic flux and \[\varepsilon \] is the induced emf. Induced emf is actually a driving force for current.
Note: Understand the effect that is generated when a conductor is placed in a changing magnetic field and how the induced current is generated. Candidates are advised to learn self induction and mutual induction also for the better understanding about electromagnetism.
Complete step by step answer:
Electricity and magnetism are interrelated in many ways. That’s why electromagnetism discipline has been developed. Moving charges or currents can produce magnetic fields. Thus, it can deflect the magnetic compass needle. Faraday developed a system that showed, moving magnetic field produces electricity. He discovered that, if the number of magnetic lines of forces changes, an emf is produced in the circuit. This process is collectively known as electromagnetic induction.

Figure above shows a closed-circuit containing coils of insulated wire. There are no sources of emf, hence it won’t show any deflections in the galvanometer. If we move the bar magnet towards the coil, a deflection will produce a galvanometer. It is not a permanent deflection. When we remove the magnet outside of the coil, the galvanometer shows an opposite deflection. We can see this deflection of a needle in the galvanometer very fast if we move the bar magnet quickly. We can observe deflection in the opposite side of observed deflection, if we change the poles of the magnet. He even tried to move the coil by fixing the magnet. Even though deflections in the galvanometer were generated. He observed that if the motion of a magnet is faster, larger is the deflection produced in the galvanometer.

As we can see the figure 2, primary circuit consists of a switch and battery and secondary circuit have a galvanometer. If we are moving either of the coils, the galvanometer shows deflection. Here the current carrying coil produces the magnetic field. Sudden deflections in one direction can be obtained if we turn on the primary coil and in the opposite direction when the current supply turns off.
Additional information:
Faraday’s law of induction predicted how a magnetic field interacts with an electric circuit to produce emf.
\[\varepsilon =-\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}\], where \[{{\phi }_{B}}\] is the magnetic flux and \[\varepsilon \] is the induced emf. Induced emf is actually a driving force for current.
Note: Understand the effect that is generated when a conductor is placed in a changing magnetic field and how the induced current is generated. Candidates are advised to learn self induction and mutual induction also for the better understanding about electromagnetism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




