
\[CO\] is practically non-polar since:
A: The σ-electron drift from C to O is almost nullified by the pi -electron drift from O to C
B: The σ-electron drift from O to C is almost nullified by the pi -electron drift from C to O
C: the bond moment is low
D: there is a triple bond between C and O
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: Polar molecules exist when there occurs a difference between the electronegativity of bonded atoms. On the other hand, non-polar molecules exist when electrons are shared equally between the atoms in a diatomic molecule or in case of a large molecule when polar bonds cancel out each other.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of carbon monoxide (\[CO\]) comprises one oxygen atom and one carbon atom. The both atoms are linked to each other by a triple bond consisting of two pi bonds as well as one sigma bond as shown below.
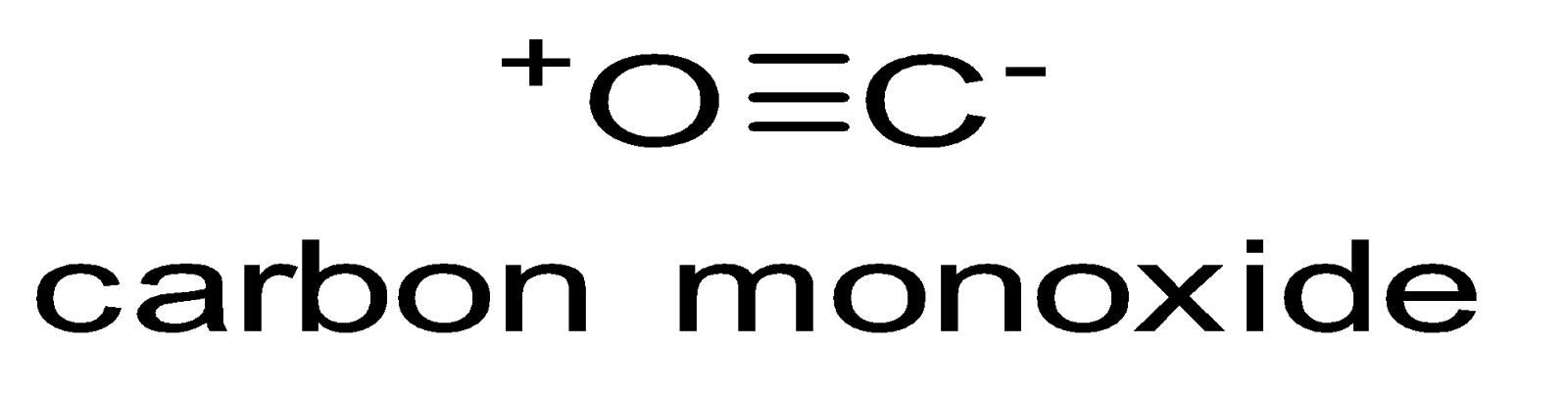
Carbon and oxygen altogether consist of 10 valence band electrons. According to octet rule in case of both oxygen and carbon, these two atoms lead to the formation of a triple bond, with six electrons being shared in the three bonding molecular orbitals. Out of which, four shared electrons are from the oxygen atom while two shared electrons are from the carbon atom. One bonding molecular orbital is being engrossed by two electrons coming from oxygen, thus, forming a dipolar bond. This leads to $C \leftarrow O$ polarization of molecules possessing a smaller negative charge over carbon and a smaller positive charge over oxygen. The remaining two bonding molecular orbitals are engrossed by one electron from oxygen and one electron from carbon, thereby forming polar covalent bonds having $C \to O$ reverse polarization owing to the oxygen being more electronegative in comparison to carbon. In \[CO\] molecules, carbon atom has a net negative charge.
Due to the presence of pi bond in \[CO\] molecule, electrons are drifted from oxygen towards carbon thus nullifying the polarity and making the molecule non-polar. We can say that in case of \[CO\] molecule, $C - O$ σ moment as well as $O - C$ pi−moment cancel out each other which makes it non-polar.
CO is practically non-polar since the σ-electron drift from C to O is almost nullified by the π -electron drift from O to C.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
\[CO\] molecule is considered to be asymmetric as oxygen possesses more electron density compared to carbon, and thus, is slightly positive than carbon being negative. If \[CO\] behaves as a ligand, dipole moment will reverse by imparting a net negative charge towards oxygen, depending upon the structure of the coordination complex.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of carbon monoxide (\[CO\]) comprises one oxygen atom and one carbon atom. The both atoms are linked to each other by a triple bond consisting of two pi bonds as well as one sigma bond as shown below.
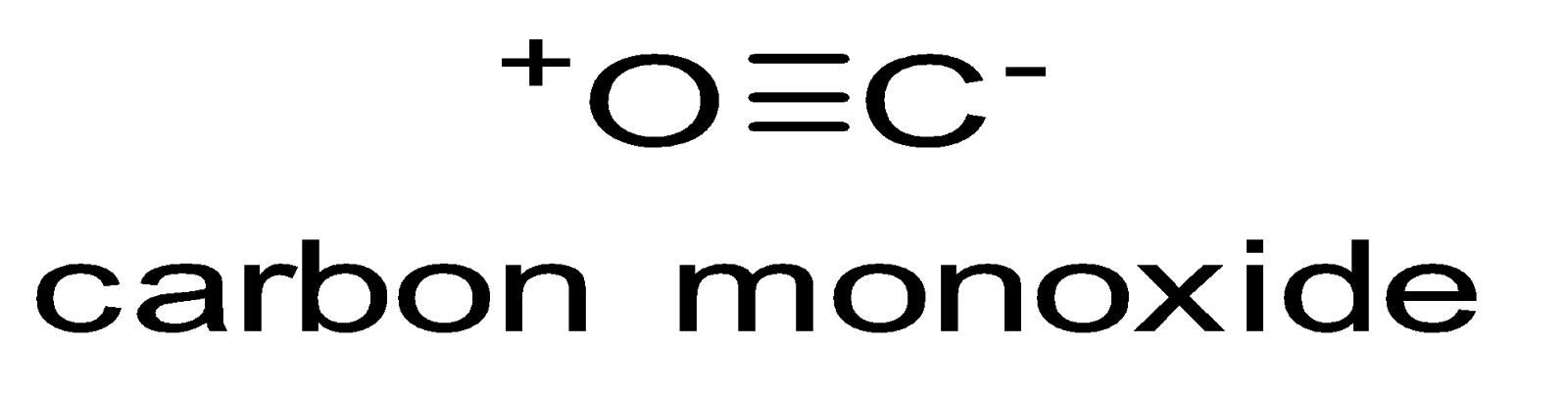
Carbon and oxygen altogether consist of 10 valence band electrons. According to octet rule in case of both oxygen and carbon, these two atoms lead to the formation of a triple bond, with six electrons being shared in the three bonding molecular orbitals. Out of which, four shared electrons are from the oxygen atom while two shared electrons are from the carbon atom. One bonding molecular orbital is being engrossed by two electrons coming from oxygen, thus, forming a dipolar bond. This leads to $C \leftarrow O$ polarization of molecules possessing a smaller negative charge over carbon and a smaller positive charge over oxygen. The remaining two bonding molecular orbitals are engrossed by one electron from oxygen and one electron from carbon, thereby forming polar covalent bonds having $C \to O$ reverse polarization owing to the oxygen being more electronegative in comparison to carbon. In \[CO\] molecules, carbon atom has a net negative charge.
Due to the presence of pi bond in \[CO\] molecule, electrons are drifted from oxygen towards carbon thus nullifying the polarity and making the molecule non-polar. We can say that in case of \[CO\] molecule, $C - O$ σ moment as well as $O - C$ pi−moment cancel out each other which makes it non-polar.
CO is practically non-polar since the σ-electron drift from C to O is almost nullified by the π -electron drift from O to C.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
\[CO\] molecule is considered to be asymmetric as oxygen possesses more electron density compared to carbon, and thus, is slightly positive than carbon being negative. If \[CO\] behaves as a ligand, dipole moment will reverse by imparting a net negative charge towards oxygen, depending upon the structure of the coordination complex.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




