
Choose the incorrect statement from the following:
A.Monosaccharides are optically active polyhydroxy carbonyl compounds.
B.Fructose does not reduce Fehling’s solution because it is ketose.
C.$\alpha -D(+)-glucose$ and $\beta -D(+)-glucose$ are anomers.
D.$D-glucose$ and $D-mannose$ are $C-2$ epimers.
Answer
570.3k+ views
Hint: Optical activity is the ability of a compound to rotate the plane polarised light.
Fehling’s solution is generally used to differentiate between the ketone and carbohydrates.
Anomers are the type of compounds which are epimers of each other, as in their spatial arrangement of a specific carbon (depending on the molecule), is different.
Complete answer:
Optical activity can be defined as the property of a compound or sugar, of rotating the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light. This means that the light will bend or rotate in either side after being passed through a polarimeter, which is the setup which contains the solution.
Monosaccharides are the type of simple sugars which contain an oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms for every carbon atom which is present in the molecule. Generally we can represent it by the formula \[{{\left(C{{H}_{2}}O\right)}_{n}}\] . All the monosaccharides which are known to us (except dihydroxyacetone) contain at least one asymmetric carbon atom, which are also termed as chiral carbon. As a result of this, they are optically active. So the statement in option A is true.
A ketose can be defined as a monosaccharide which contains one ketone group per molecule. Fructose, also called fruit sugar, is a simple ketonic monosaccharide, meaning they contain ketone group, is found in many plants, where it is often observed that it has a bond with glucose in order to form the disaccharide sucrose.
Fehling’s test contains a solution which is usually prepared fresh in laboratories. At first, the solution exists in the form of two separate solutions which are labelled as Fehling’s A and Fehling’s B. Fehling’s A is a solution which contains \[copper\left(II\right)sulphate\] , and is blue in colour. Whereas Fehling’s B solution is a clear liquid solution which consists of potassium sodium tartrate along with a strong alkali, generally sodium hydroxide. During the test solutions A and B are prepared individually and stored. The test is generally used in case of reducing sugars but is known to be NOT specific for aldehydes. For example, fructose gives a positive test with Fehling's solution. So the statement in option B, is false, hence it is the correct answer.
Anomers are a kind of cyclic monosaccharides that are epimers, which differs from each other in the configuration at \[C-2\] if they are ketoses or in the configuration of \[C-1\] if they are aldoses.
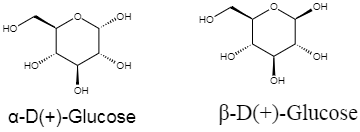
As we can see that, both the structures given in the diagram, are almost identical, except that in \[\alpha\] form, the \[OH\] group on the far right is down, that is pointing inside the plane, and, in the $\beta$ form, the \[OH\] group on the far right is up. All cyclic structures of monosaccharides show anomeric behaviour \[\alpha\] (down) and $\beta$ (up) versions. So the statement in option C, is true.
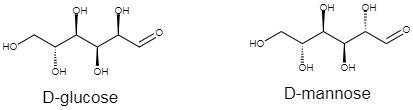
In stereochemistry, an epimer can be defined as one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers would differ in configuration at only one stereogenic center, and it would be opposite, out of at least two. Diastereomers are defined as non-mirror image non-identical stereoisomers. As we can see from the given structure, the second carbon in both the structures differ from each other as the hydroxide group has different spatial arrangements. So the statement in option D is true.
And hence option B is the correct answer.
Note:Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy carbonyl compounds which are optically active due to the presence of chiral carbons.
Fructose gives a positive fehling’s test, as it is a type of ketose. $\alpha-D(+)-glucose$ and $\beta-D(+)-glucose$ are anomers of each other as they both differ in the spatial arrangement of one hydroxyl group. $D-glucose$ and $D-mannose$ are $C-2$ epimers, as both of them differ from each other at $C-2$ , that is only one carbon.
Fehling’s solution is generally used to differentiate between the ketone and carbohydrates.
Anomers are the type of compounds which are epimers of each other, as in their spatial arrangement of a specific carbon (depending on the molecule), is different.
Complete answer:
Optical activity can be defined as the property of a compound or sugar, of rotating the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light. This means that the light will bend or rotate in either side after being passed through a polarimeter, which is the setup which contains the solution.
Monosaccharides are the type of simple sugars which contain an oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms for every carbon atom which is present in the molecule. Generally we can represent it by the formula \[{{\left(C{{H}_{2}}O\right)}_{n}}\] . All the monosaccharides which are known to us (except dihydroxyacetone) contain at least one asymmetric carbon atom, which are also termed as chiral carbon. As a result of this, they are optically active. So the statement in option A is true.
A ketose can be defined as a monosaccharide which contains one ketone group per molecule. Fructose, also called fruit sugar, is a simple ketonic monosaccharide, meaning they contain ketone group, is found in many plants, where it is often observed that it has a bond with glucose in order to form the disaccharide sucrose.
Fehling’s test contains a solution which is usually prepared fresh in laboratories. At first, the solution exists in the form of two separate solutions which are labelled as Fehling’s A and Fehling’s B. Fehling’s A is a solution which contains \[copper\left(II\right)sulphate\] , and is blue in colour. Whereas Fehling’s B solution is a clear liquid solution which consists of potassium sodium tartrate along with a strong alkali, generally sodium hydroxide. During the test solutions A and B are prepared individually and stored. The test is generally used in case of reducing sugars but is known to be NOT specific for aldehydes. For example, fructose gives a positive test with Fehling's solution. So the statement in option B, is false, hence it is the correct answer.
Anomers are a kind of cyclic monosaccharides that are epimers, which differs from each other in the configuration at \[C-2\] if they are ketoses or in the configuration of \[C-1\] if they are aldoses.

As we can see that, both the structures given in the diagram, are almost identical, except that in \[\alpha\] form, the \[OH\] group on the far right is down, that is pointing inside the plane, and, in the $\beta$ form, the \[OH\] group on the far right is up. All cyclic structures of monosaccharides show anomeric behaviour \[\alpha\] (down) and $\beta$ (up) versions. So the statement in option C, is true.

In stereochemistry, an epimer can be defined as one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers would differ in configuration at only one stereogenic center, and it would be opposite, out of at least two. Diastereomers are defined as non-mirror image non-identical stereoisomers. As we can see from the given structure, the second carbon in both the structures differ from each other as the hydroxide group has different spatial arrangements. So the statement in option D is true.
And hence option B is the correct answer.
Note:Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy carbonyl compounds which are optically active due to the presence of chiral carbons.
Fructose gives a positive fehling’s test, as it is a type of ketose. $\alpha-D(+)-glucose$ and $\beta-D(+)-glucose$ are anomers of each other as they both differ in the spatial arrangement of one hydroxyl group. $D-glucose$ and $D-mannose$ are $C-2$ epimers, as both of them differ from each other at $C-2$ , that is only one carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




