
How many chiral compounds are possible on the monochlorination of 2-Methyl butane?
(a) 8
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: If all the atoms or groups attached to the carbon atom are not similar, such carbon is called asymmetric carbon or chiral carbon. If any of the atoms or groups is repeated then the carbon is achiral. Monochlorination means one hydrogen atom from the compound is replaced with one chlorine atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Compounds which are non-superimposable on their mirror image are called chiral compounds and the carbon should have all the groups or atoms attached to it differently.
2-Methyl butane is an organic chemical compound that has a chain of four carbon atoms and the second carbon atom has a methyl group attached.
Monochlorination means one hydrogen atom from the compound is replaced with one chlorine atom. So, the monochlorination of 2-Methyl butane will produce 4 different products. These are 1-chloro-3-methyl butane, 2-chloro-3-methyl butane, 2-chloro-2-methyl butane, and 1-chloro-2-methyl butane.
1-chloro-3-methyl butane: It doesn’t have any carbon atom which has four different groups hence it is achiral. The structure is given below:
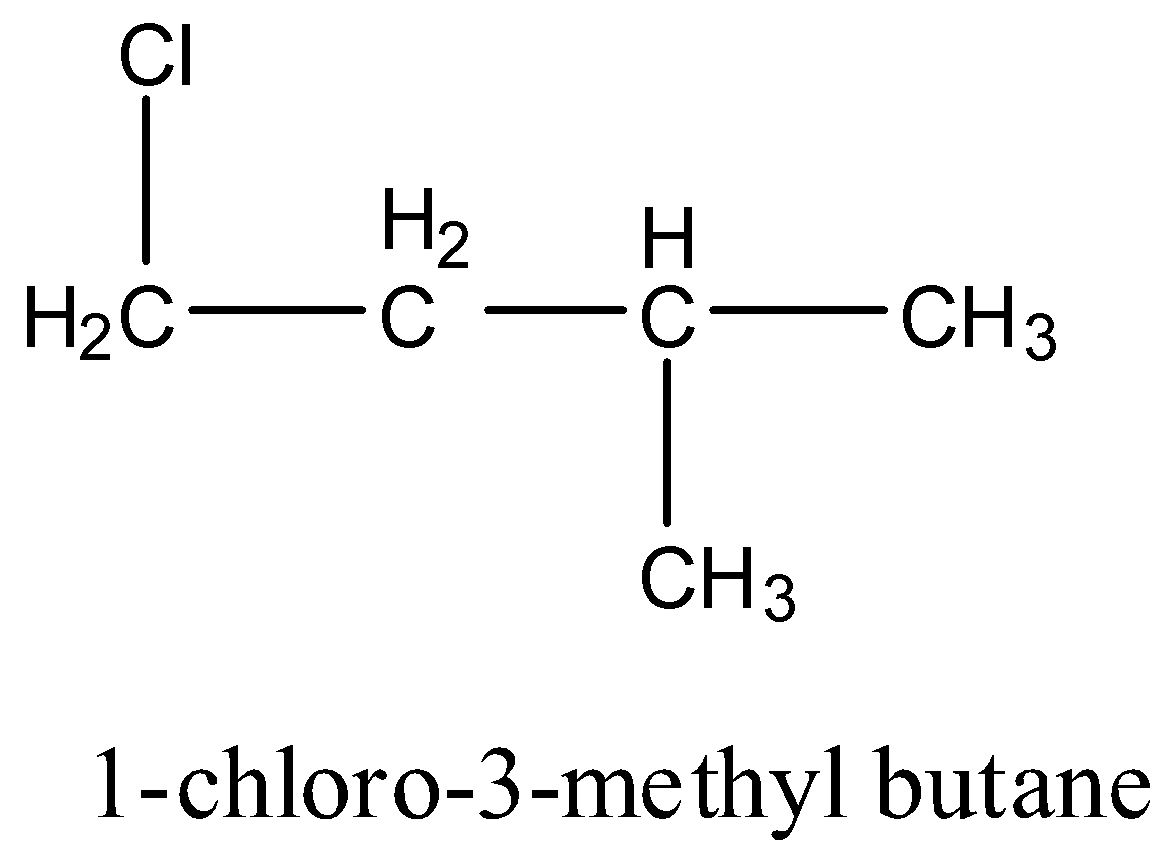
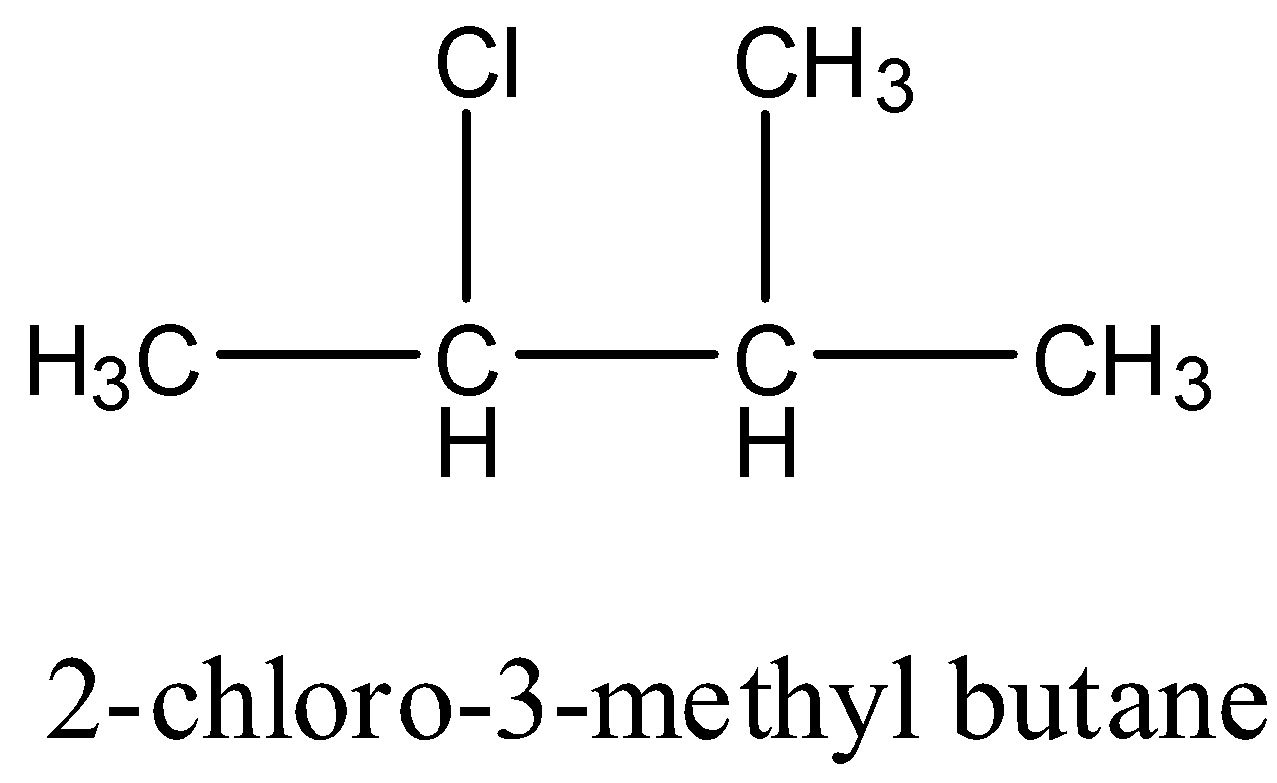
2-chloro-3-methyl butane: It has one carbon atom that has four different groups. Hence this compound is chiral. The structure is given below:
2-chloro-2-methyl butane: It doesn’t have any carbon atom which has four different groups hence it is achiral. The structure is given below:
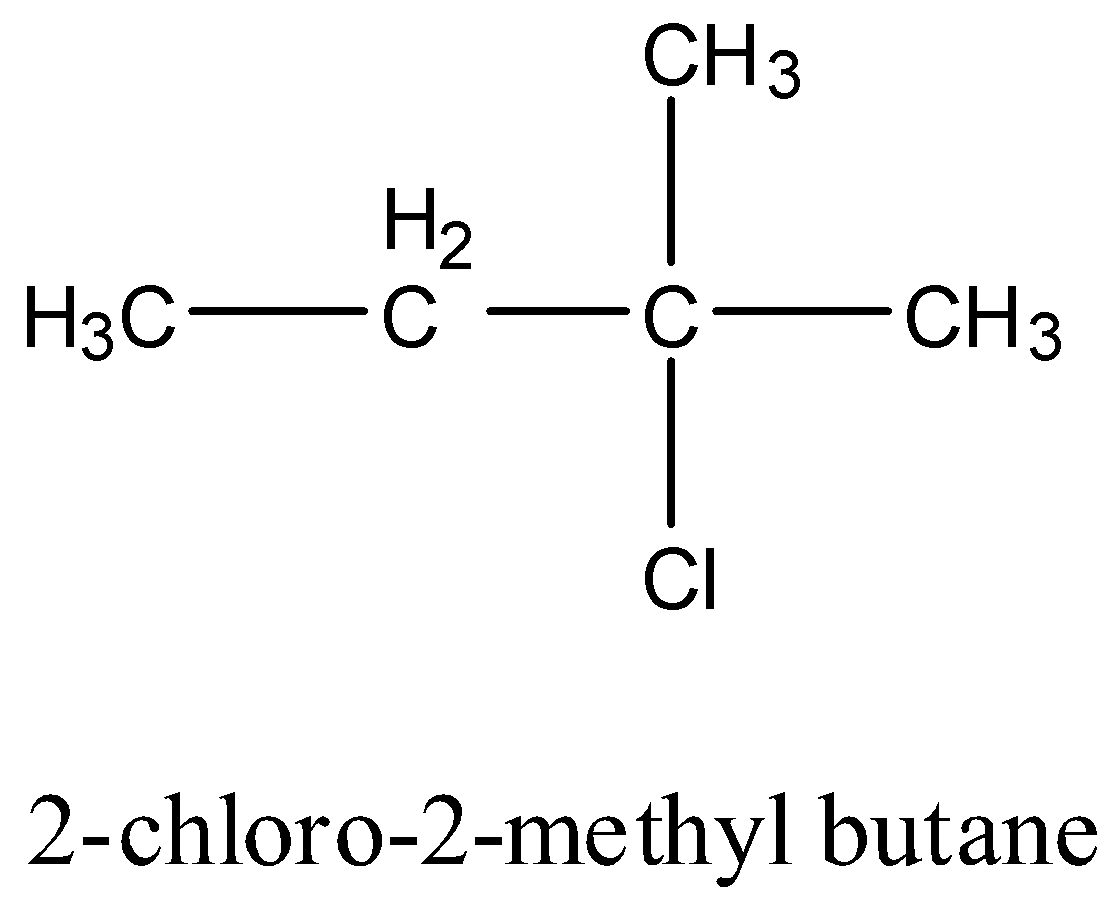
1-chloro-2-methyl butane: It has one carbon atom that has four different groups. Hence this compound is chiral. The structure is given below:
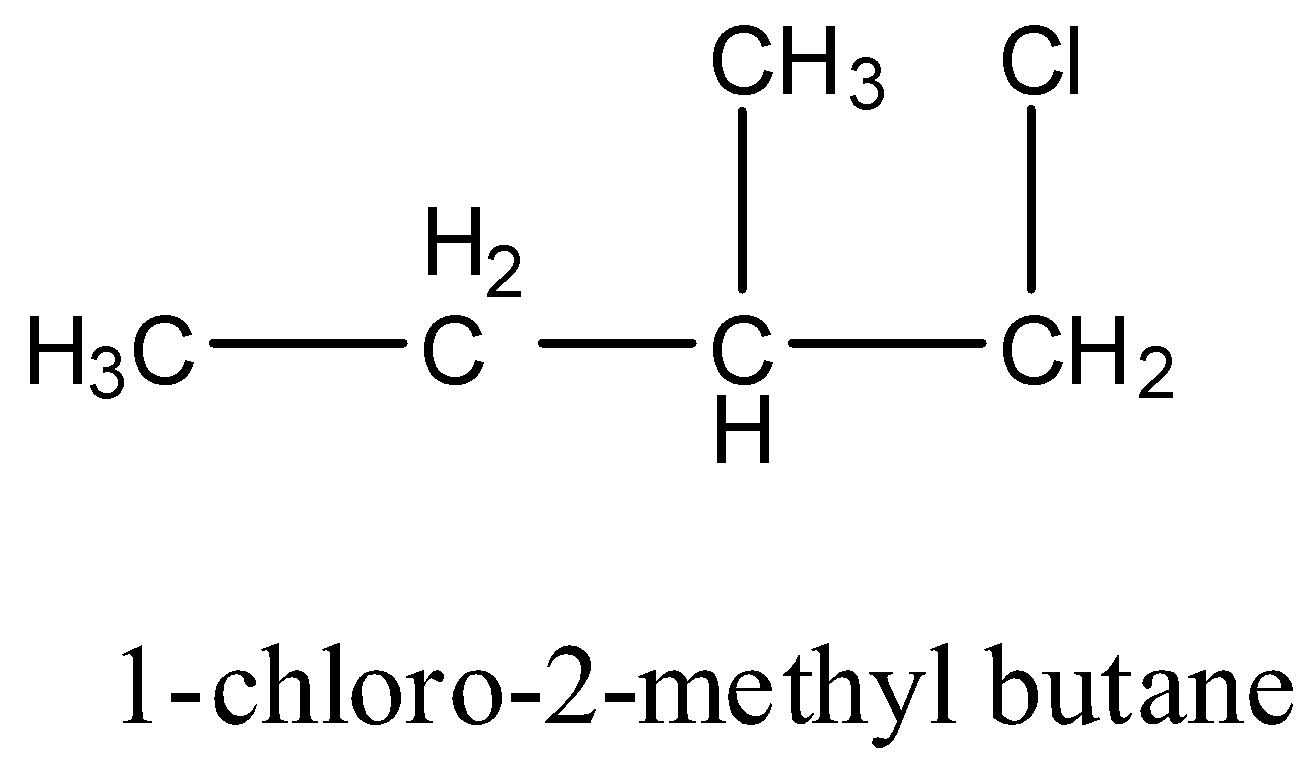
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: If the compound at least has a chiral carbon atom, that compound should be considered as a chiral compound. The chiral carbon of the compound is also known as the stereocenter of that compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Compounds which are non-superimposable on their mirror image are called chiral compounds and the carbon should have all the groups or atoms attached to it differently.
2-Methyl butane is an organic chemical compound that has a chain of four carbon atoms and the second carbon atom has a methyl group attached.
Monochlorination means one hydrogen atom from the compound is replaced with one chlorine atom. So, the monochlorination of 2-Methyl butane will produce 4 different products. These are 1-chloro-3-methyl butane, 2-chloro-3-methyl butane, 2-chloro-2-methyl butane, and 1-chloro-2-methyl butane.
1-chloro-3-methyl butane: It doesn’t have any carbon atom which has four different groups hence it is achiral. The structure is given below:

2-chloro-3-methyl butane: It has one carbon atom that has four different groups. Hence this compound is chiral. The structure is given below:

2-chloro-2-methyl butane: It doesn’t have any carbon atom which has four different groups hence it is achiral. The structure is given below:

1-chloro-2-methyl butane: It has one carbon atom that has four different groups. Hence this compound is chiral. The structure is given below:

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: If the compound at least has a chiral carbon atom, that compound should be considered as a chiral compound. The chiral carbon of the compound is also known as the stereocenter of that compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




