
How many chiral centers are in (G) (L- ascorbic acid)?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4

Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: A molecule with one chiral center exhibits two mirror-image configurations, which are known as enantiomers. If any molecule should possess more than one chiral center will write to possible more configurations with different projection formulas. Those molecules are not enantiomers and not mirror images of each other.
Complete Solution :
- If a molecule exhibits an opposite R/S configuration with all chiral centers between two stereoisomers is called enantiomers.
- If at least one, but not all of the chiral centers are opposite R/S configuration between two stereoisomers which are diastereomers. The substances related to each other and which can be converted one into another only by changing the configurations at one or more chiral centers are called diastereomers.
- Let us find the numbers of chiral centers are in L-ascorbic acid.
The geometrical property of a molecule or ion which cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combinations of rotations and translations is called chirality.
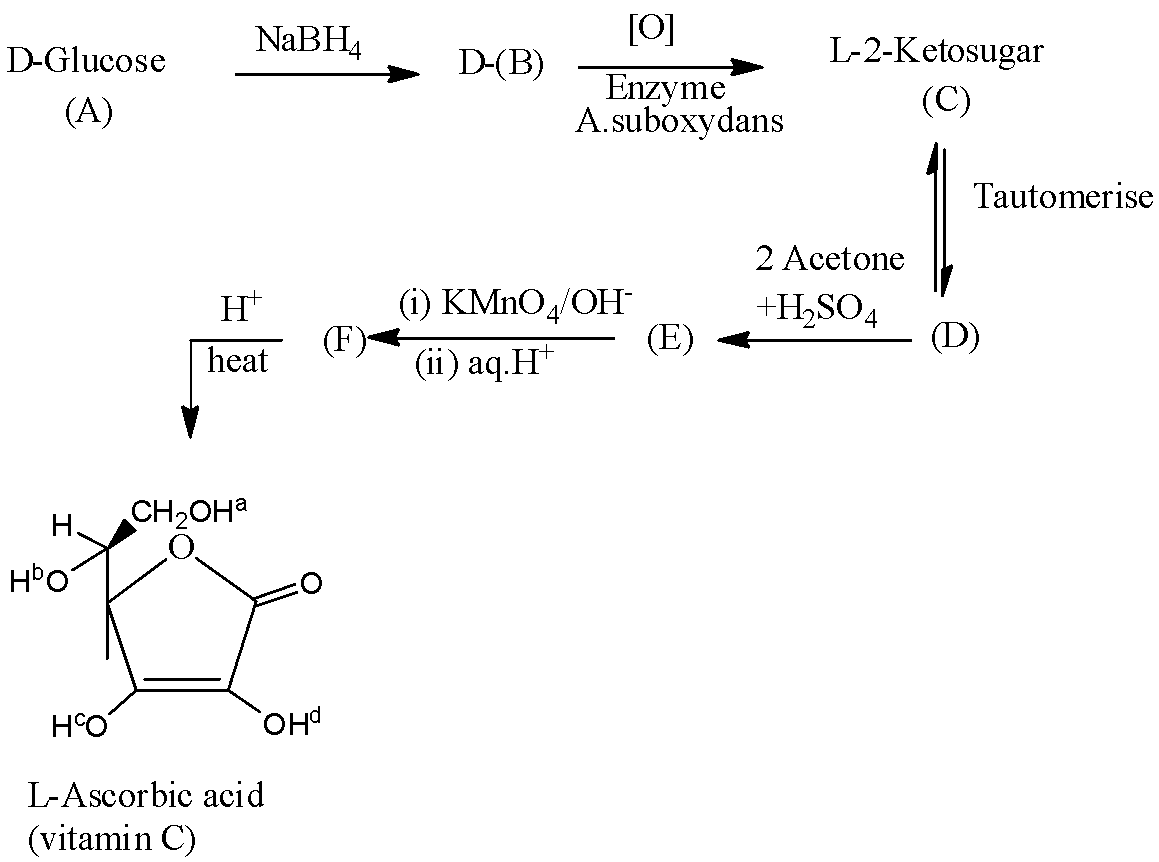
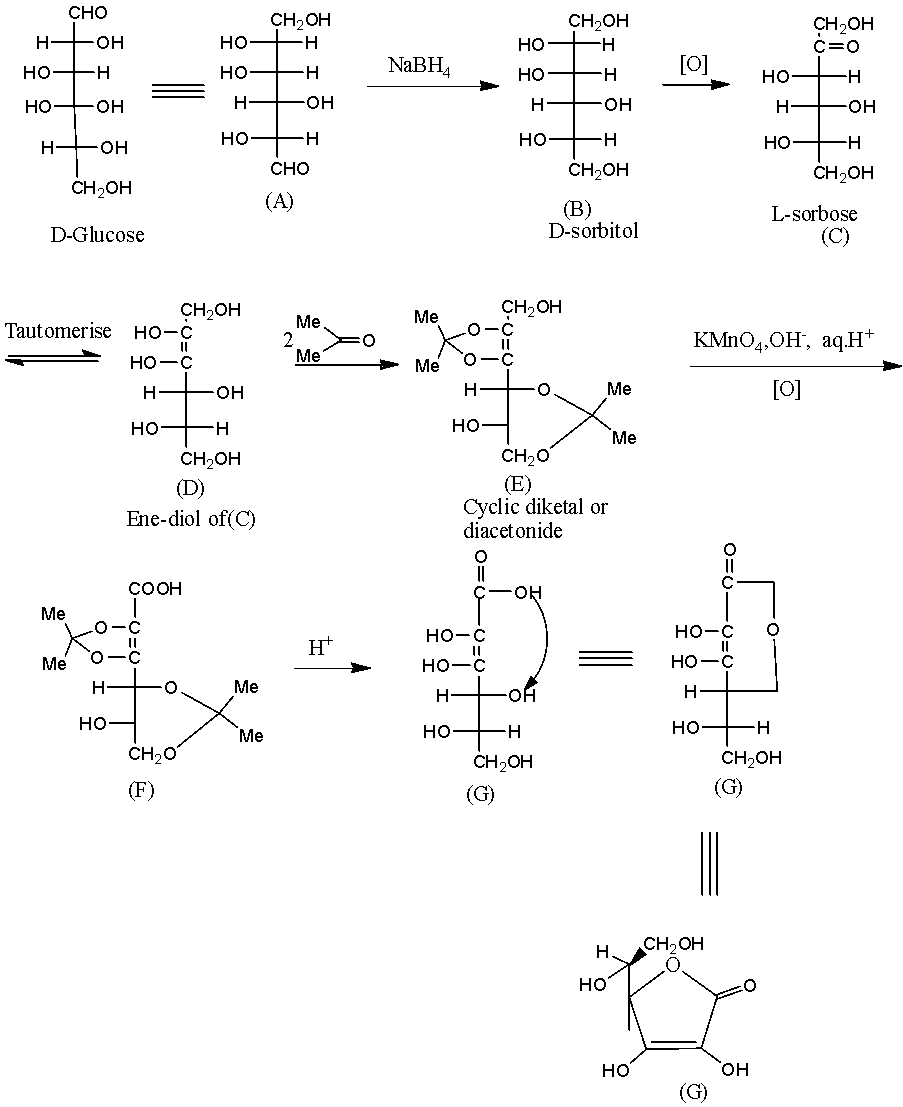
- The given L- ascorbic acid will form by the following reactions.
- The structure of L –ascorbic acid with two chiral centers marked as (*) shown below,
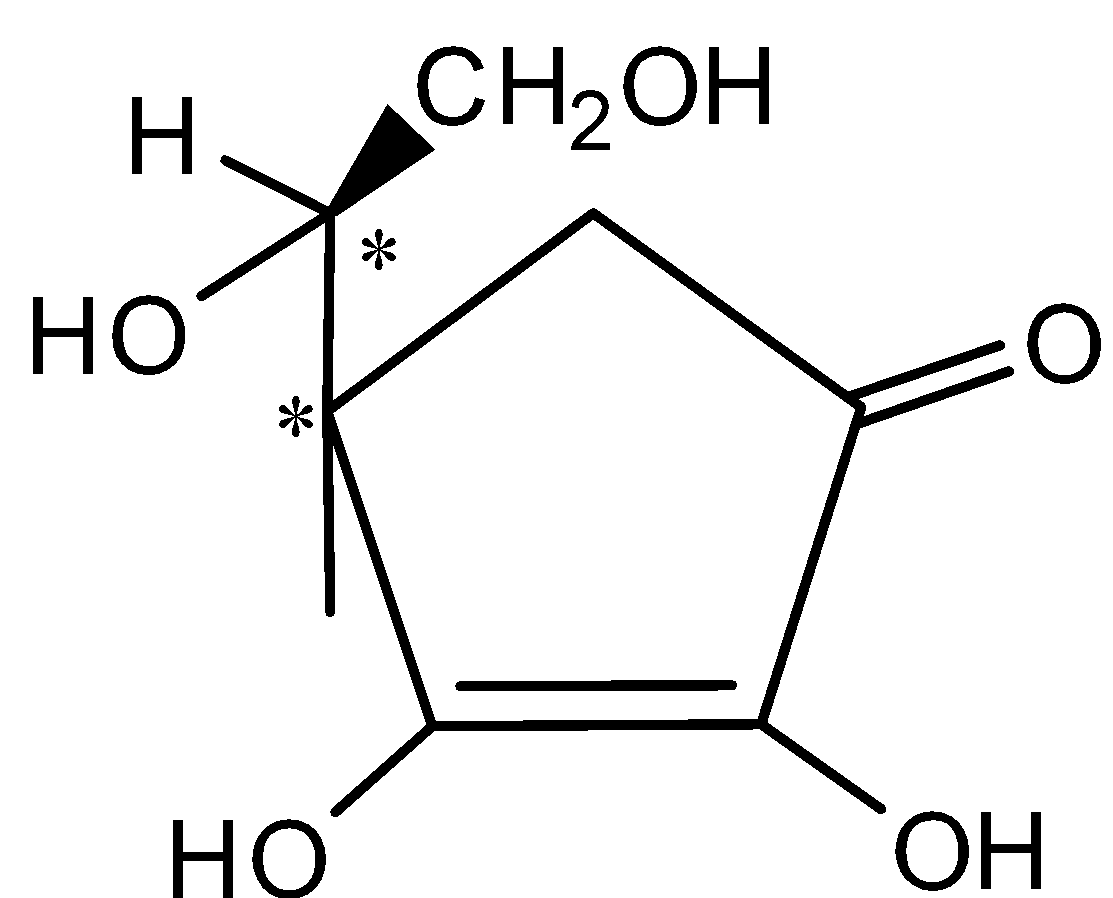
Hence, the number of chiral centers in G (L-ascorbic acid) = 2
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The difference between diastereomers and enantiomers is more than geometry. Apart from optical rotations, enantiomers have identical physical properties and diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties. Diastereomers with two chiral centers by noting with right foot (D, D) is a mirror image that has the same physical properties and left foot (L, L) has different properties due to not being a mirror image. Because of these reasons, diastereomers have different physical properties.
Complete Solution :
- If a molecule exhibits an opposite R/S configuration with all chiral centers between two stereoisomers is called enantiomers.
- If at least one, but not all of the chiral centers are opposite R/S configuration between two stereoisomers which are diastereomers. The substances related to each other and which can be converted one into another only by changing the configurations at one or more chiral centers are called diastereomers.
- Let us find the numbers of chiral centers are in L-ascorbic acid.
The geometrical property of a molecule or ion which cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combinations of rotations and translations is called chirality.
- The given L- ascorbic acid will form by the following reactions.

- The structure of L –ascorbic acid with two chiral centers marked as (*) shown below,

Hence, the number of chiral centers in G (L-ascorbic acid) = 2
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The difference between diastereomers and enantiomers is more than geometry. Apart from optical rotations, enantiomers have identical physical properties and diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties. Diastereomers with two chiral centers by noting with right foot (D, D) is a mirror image that has the same physical properties and left foot (L, L) has different properties due to not being a mirror image. Because of these reasons, diastereomers have different physical properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




