
$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{COC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\xrightarrow{\text{Ba}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}}?$
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: The reaction between carbonyl compounds and bases is the aldol condensation. In this reaction, the carbonyl compound reacts with the enolate ion to give a $\beta $-hydroxy aldehyde or $\beta $-hydroxy ketone. The reactant we have is acetone, a ketonic compound. It will undergo a self-condensation reaction (with itself only). Follow the mechanism and obtain the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us solve this question, step-by-step by the mechanism:
Step (1)- The acidic hydrogen of acetone deprotonates first in the presence of a strong base barium hydroxide $\left[ \text{Ba}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}} \right]$ to form an carbanion and water. The acidic hydrogen here is the alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogen of acetone. Acidic hydrogen means the hydrogen atom which deprotonates to give stability to the compound by resonance. The reaction is
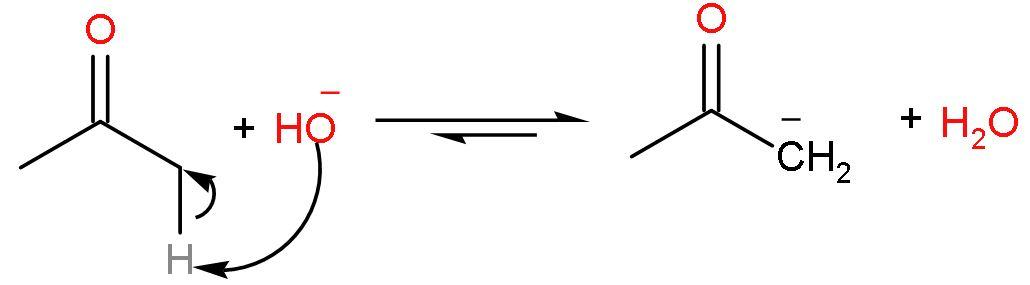
Step (2)- The carbanion or enolate ion formed will attack the new molecule of acetone. In this way, the carbon atom with negative charge will add to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group and the oxygen atom will bear the negative charge. The reaction seems like this:
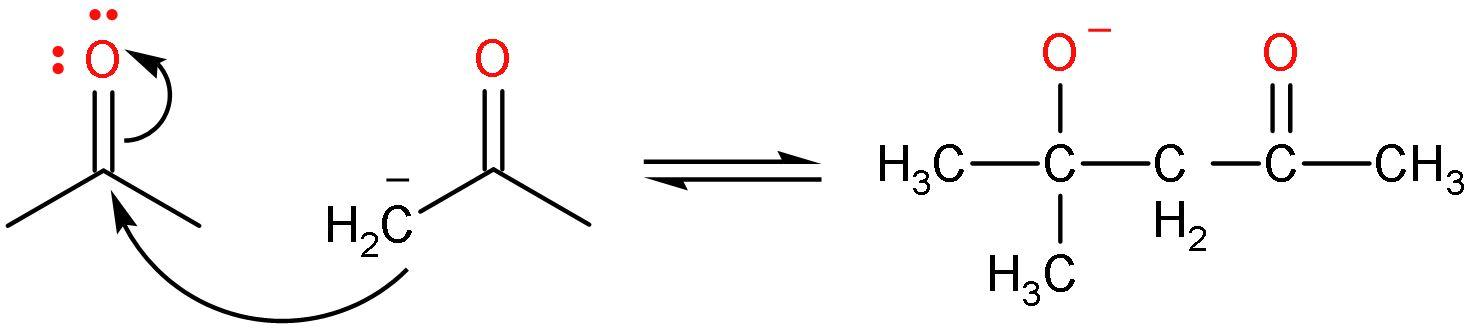
Step (3)- The negative charge on oxygen atom or the alkoxide ion will be removed by the attack of ${{\text{H}}^{+}}$ from the water to give back the base $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}$. The final product is formed. The reaction is
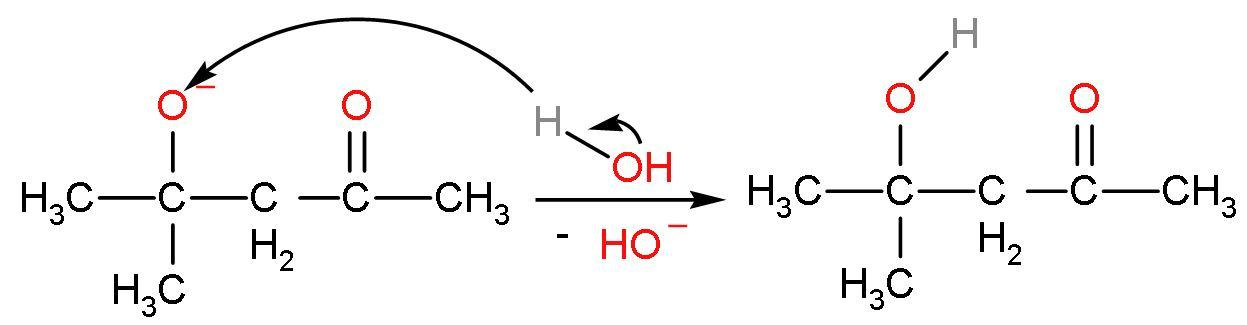
The IUPAC name of the compound is 4-hydroxy-(4,4)-dimethyl-pentan-2-one.
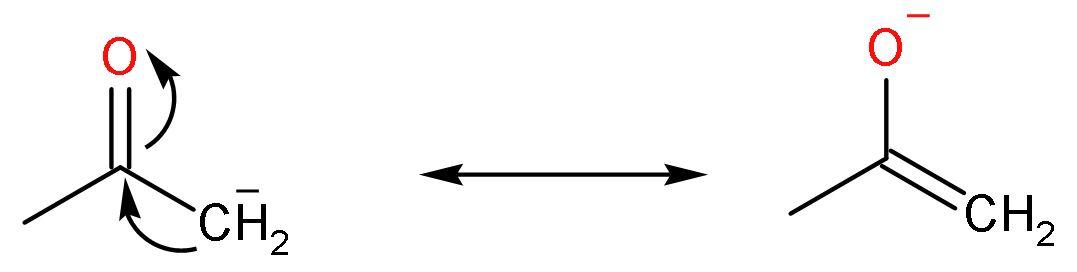
Note: After the removal of acidic hydrogen, the compound undergoes keto-enol tautomerism. This makes the compound stable due to the presence of negative charge on the electronegative oxygen atom. Like,
Complete step by step answer:
Let us solve this question, step-by-step by the mechanism:
Step (1)- The acidic hydrogen of acetone deprotonates first in the presence of a strong base barium hydroxide $\left[ \text{Ba}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}} \right]$ to form an carbanion and water. The acidic hydrogen here is the alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogen of acetone. Acidic hydrogen means the hydrogen atom which deprotonates to give stability to the compound by resonance. The reaction is

Step (2)- The carbanion or enolate ion formed will attack the new molecule of acetone. In this way, the carbon atom with negative charge will add to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group and the oxygen atom will bear the negative charge. The reaction seems like this:

Step (3)- The negative charge on oxygen atom or the alkoxide ion will be removed by the attack of ${{\text{H}}^{+}}$ from the water to give back the base $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}$. The final product is formed. The reaction is

The IUPAC name of the compound is 4-hydroxy-(4,4)-dimethyl-pentan-2-one.
Note: After the removal of acidic hydrogen, the compound undergoes keto-enol tautomerism. This makes the compound stable due to the presence of negative charge on the electronegative oxygen atom. Like,

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




