
Calculate the power delivered to each resistor in the circuit shown in the figure.
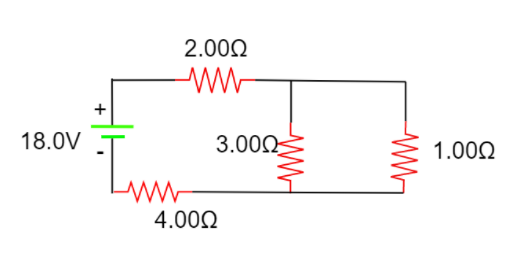

Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: Power can be calculated using the equations $P = IV$ or $P = {V^2}R$ , where $V$ is the voltage drop across the resistors (not the full voltage of the source).Whenever current goes through a resistor there will be a voltage drop. In a series circuit, the voltage drop across each resistor is exactly proportional to its size. In a parallel circuit, the voltage drop across each resistor is the same as the voltage drop across the power source. Because the current passing through each resistor is different, Ohm's Law is conserved.
Complete step by step answer:
If a current $I$ passes through a particular element in your circuit while losing voltage $V$, the power lost by that circuit element is the product of that current and voltage\[P = IV\]. Here the resistors of resistance $3\Omega $ and $1\Omega $ are in parallel. Hence their effective resistance is given by,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{1}{1} + \dfrac{1}{3} = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
$ \Rightarrow {R_p} = \dfrac{3}{4} = 0.75\Omega $
An equivalent circuit can be drawn
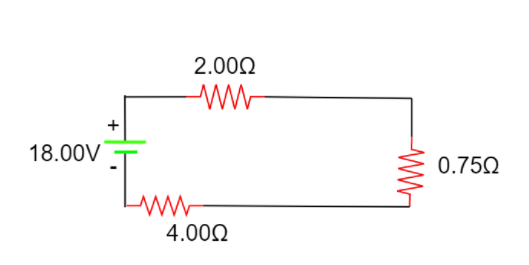
Now since these are in series connection the resistances can be simply added. Another equivalent diagram can be drawn.
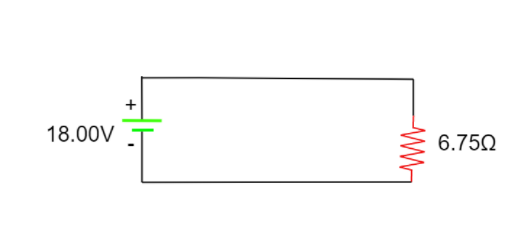
From the above figure,
Current $I = \dfrac{{18}}{{6.75}} - 2.67A$
Power across the $2\Omega $ resistor is ${P_2}$ and calculated as,
${P_2} = {I^2}R = {(2.67)^2} \times 2 = 14.2W$
Power across the $4\Omega $ resistor is ${P_4}$ and calculated as,
${P_4} = {I^2}R = {(2.67)^2} \times 4 = 28.4W$
Voltage across the $3\Omega $ and $1\Omega $ resistor is,
$\Delta V = IR = 2.67 \times 0.75 = 2V$
For $3\Omega $ resistor $I = \dfrac{{\Delta V}}{R} = \dfrac{2}{3}$
Power ${P_3} = I\Delta V = \left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) \times 2 = \dfrac{4}{3} = 1.33W$
For $1\Omega $ resistor $I = \dfrac{{\Delta V}}{R} = \dfrac{2}{1} = 2$
Power ${P_1} = I\Delta V = 2 \times 2 = 4W$
Therefore the power delivered to the resistors of resistances $1\Omega ,2\Omega ,3\Omega ,4\Omega $ are $4\,W,14.2\,W,1.33\,W,28.4\,W$ respectively.
Note:The total amount of power provided equals the entire amount of power absorbed. A resistor may absorb but not deliver power. Electrical energy is transformed into heat energy when a current flows across a resistor. The heat created in a circuit's components, all of which have some resistance, is dissipated into the air around the components.
Complete step by step answer:
If a current $I$ passes through a particular element in your circuit while losing voltage $V$, the power lost by that circuit element is the product of that current and voltage\[P = IV\]. Here the resistors of resistance $3\Omega $ and $1\Omega $ are in parallel. Hence their effective resistance is given by,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{1}{1} + \dfrac{1}{3} = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
$ \Rightarrow {R_p} = \dfrac{3}{4} = 0.75\Omega $
An equivalent circuit can be drawn

Now since these are in series connection the resistances can be simply added. Another equivalent diagram can be drawn.

From the above figure,
Current $I = \dfrac{{18}}{{6.75}} - 2.67A$
Power across the $2\Omega $ resistor is ${P_2}$ and calculated as,
${P_2} = {I^2}R = {(2.67)^2} \times 2 = 14.2W$
Power across the $4\Omega $ resistor is ${P_4}$ and calculated as,
${P_4} = {I^2}R = {(2.67)^2} \times 4 = 28.4W$
Voltage across the $3\Omega $ and $1\Omega $ resistor is,
$\Delta V = IR = 2.67 \times 0.75 = 2V$
For $3\Omega $ resistor $I = \dfrac{{\Delta V}}{R} = \dfrac{2}{3}$
Power ${P_3} = I\Delta V = \left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) \times 2 = \dfrac{4}{3} = 1.33W$
For $1\Omega $ resistor $I = \dfrac{{\Delta V}}{R} = \dfrac{2}{1} = 2$
Power ${P_1} = I\Delta V = 2 \times 2 = 4W$
Therefore the power delivered to the resistors of resistances $1\Omega ,2\Omega ,3\Omega ,4\Omega $ are $4\,W,14.2\,W,1.33\,W,28.4\,W$ respectively.
Note:The total amount of power provided equals the entire amount of power absorbed. A resistor may absorb but not deliver power. Electrical energy is transformed into heat energy when a current flows across a resistor. The heat created in a circuit's components, all of which have some resistance, is dissipated into the air around the components.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




