
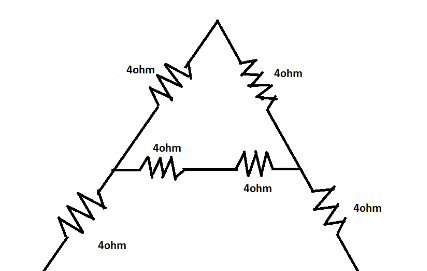
Calculate the equivalent resistance:

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:In this question, we have to find the equivalent resistance for the circuit. After viewing the circuit, we observed that there are resistances connected in series as well as in parallel. We can solve the circuit step by step by solving each branch of the circuit by using series and parallel resistances formula.
Formula used:
Equivalent resistance for the resistors connected in series is given by simply adding the values of resistance $R = {R_1} + {R_2} + \ldots $
Equivalent resistance for the resistors connected in parallel is given by adding the reciprocals of resistances $\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \ldots $
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Firstly, finding resistance for the triangle. In the triangle two resistances in the two sides is connected end to end then these two resistances are in series then the resistance be,
${R_0} = 4 + 4 = 8\Omega $
Now the base of the triangle and the equivalent resistance i.e., ${R_0}$ are in parallel then the resistance be given by,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{8} + \dfrac{1}{8}$
Now the resistance becomes $4\Omega $
Then the circuit becomes:
Above circuit is left with only three resistances connected in series:
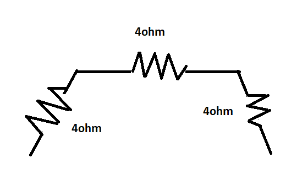
The equivalent resistance of the question is given by
$R = {R_1} + R{}_2 + {R_3}$
$ \Rightarrow R = 4 + 4 + 4$
$\therefore R = 12\Omega $
Hence, the equivalent resistance is found to be $12\Omega $.
Additional information:
Current through each resistor is equal as current is flowing through the same path.
The resistances are connected in series when the resistances are connected end to end and same current is flowing through each resistance, when a potential difference is applied across the combination.The resistances are connected in parallel when each resistance is connected to one point and another is connected to another. Potential difference across each resistor is the same and the current and current divides through each resistor.
Note:In a parallel resistance, net resistance decreases as more components are added as there are more paths for the current to pass through. More resistances mean less current is following through it. In series combination, equivalent resistance is greater than the greatest resistances connected while in parallel, equivalent is lesser than the least in the combination.
Formula used:
Equivalent resistance for the resistors connected in series is given by simply adding the values of resistance $R = {R_1} + {R_2} + \ldots $
Equivalent resistance for the resistors connected in parallel is given by adding the reciprocals of resistances $\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \ldots $
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Firstly, finding resistance for the triangle. In the triangle two resistances in the two sides is connected end to end then these two resistances are in series then the resistance be,
${R_0} = 4 + 4 = 8\Omega $
Now the base of the triangle and the equivalent resistance i.e., ${R_0}$ are in parallel then the resistance be given by,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{8} + \dfrac{1}{8}$
Now the resistance becomes $4\Omega $
Then the circuit becomes:
Above circuit is left with only three resistances connected in series:

The equivalent resistance of the question is given by
$R = {R_1} + R{}_2 + {R_3}$
$ \Rightarrow R = 4 + 4 + 4$
$\therefore R = 12\Omega $
Hence, the equivalent resistance is found to be $12\Omega $.
Additional information:
Current through each resistor is equal as current is flowing through the same path.
The resistances are connected in series when the resistances are connected end to end and same current is flowing through each resistance, when a potential difference is applied across the combination.The resistances are connected in parallel when each resistance is connected to one point and another is connected to another. Potential difference across each resistor is the same and the current and current divides through each resistor.
Note:In a parallel resistance, net resistance decreases as more components are added as there are more paths for the current to pass through. More resistances mean less current is following through it. In series combination, equivalent resistance is greater than the greatest resistances connected while in parallel, equivalent is lesser than the least in the combination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




