
How do I calculate the angular velocity of a falling object ?
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: Angular velocity is defined as the ratio of angular displacement \[\Delta \theta \] to the time interval \[\Delta t\]. Angular velocity is a vector quantity. It is represented by ω.
It is given as:
\[\omega = \dfrac{{{\theta _2} - {\theta _1}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}} = \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}}\]
The SI unit of angular velocity is radian per second and expressed as (rad/s). Angular velocity can be defined for following three situations:
-Angular velocity of particle about any fixed point.
-Angular velocity of a rigid body performing pure rotational motion.
-Angular velocity of a rigid body performing both rotational and translational motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a rigid body rotating about a fixed line AB while falling under the influence of gravity.
Now consider a particle P. We draw a perpendicular PO to the axis of rotation.
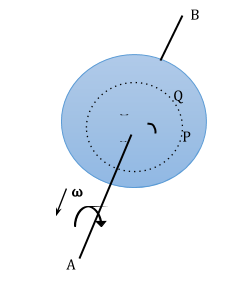
In the \[\Delta t\], this particle moves to point Q
Let \[\angle QOP = \Delta \theta \]
Then, we can say that the particle has rotated through
an angle\[\Delta \theta \].
In fact all the particles of the rigid body have rotated with
the same angle \[\Delta \theta \]or we can say that
the whole body has rotated
through an angle \[\Delta \theta \].
The average angular velocity of the rigid body
during the time interval \[\Delta t\] is:-
\[\omega = \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}}\]
The instantaneous angular velocity of rigid body is
\[\omega = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{\Delta t \to 0} \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}} = \dfrac{{d\theta }}{{dt}}\]
Note:
Direction of angular is predicted by right hand rule. It is defined to be the direction in which the thumb of your right hand points when you curl your fingers in the direction of rotation.
For example, the direction of ω in the above figure is along the axis of rotation B to A. The magnitude of angular velocity is also called angular speed. However students should continue to use the word angular velocity.
It is given as:
\[\omega = \dfrac{{{\theta _2} - {\theta _1}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}} = \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}}\]
The SI unit of angular velocity is radian per second and expressed as (rad/s). Angular velocity can be defined for following three situations:
-Angular velocity of particle about any fixed point.
-Angular velocity of a rigid body performing pure rotational motion.
-Angular velocity of a rigid body performing both rotational and translational motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a rigid body rotating about a fixed line AB while falling under the influence of gravity.
Now consider a particle P. We draw a perpendicular PO to the axis of rotation.

In the \[\Delta t\], this particle moves to point Q
Let \[\angle QOP = \Delta \theta \]
Then, we can say that the particle has rotated through
an angle\[\Delta \theta \].
In fact all the particles of the rigid body have rotated with
the same angle \[\Delta \theta \]or we can say that
the whole body has rotated
through an angle \[\Delta \theta \].
The average angular velocity of the rigid body
during the time interval \[\Delta t\] is:-
\[\omega = \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}}\]
The instantaneous angular velocity of rigid body is
\[\omega = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{\Delta t \to 0} \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}} = \dfrac{{d\theta }}{{dt}}\]
Note:
Direction of angular is predicted by right hand rule. It is defined to be the direction in which the thumb of your right hand points when you curl your fingers in the direction of rotation.
For example, the direction of ω in the above figure is along the axis of rotation B to A. The magnitude of angular velocity is also called angular speed. However students should continue to use the word angular velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




