
How do you calculate $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13} \right)$ ?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: We recall the range of tangent inverse, sine inverse function. We take $A={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3},B={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13}$ and use the cosine difference of angle formula $\cos \left( A-B \right)=\cos A\cos B+\sin A\sin B$. We find $s\cos A,\cos B,\sin A,\sin B$ using the ratios of right angled triangles.
Complete step by step answer:
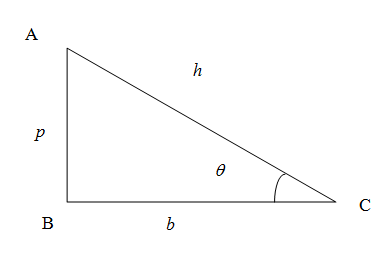
We know that in the right angled triangle the side opposite to the right angled triangle is called hypotenuse denoted as $h$, the vertical side is called perpendicular denoted as $p$ and the horizontal side is called the base denoted as $b$.
We know from the trigonometric ratios in a right angled triangle the sine of any angle is given by the ratio of side opposite to the angle to the hypotenuse, cosine of an angle is the ratio of side adjacent to the angle (excluding hypotenuse) to the hypotenuse and tangent of the angle is the ratio of opposite side to the adjacent side (excluding hypotenuse) . So we have
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{p}{h},\cos \theta =\dfrac{b}{h},\tan \theta =\dfrac{p}{b}\]
We use Pythagoras thrum to have theorem to have;
\[{{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}\]
We know that range of tangent inverse function is $\left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ and range of sine inverse function is $\left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$.We are asked to evaluate the following expression
\[\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13} \right)\]
Let us assume$A={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3},B={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13}$.So we have
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( A-B \right)\]
We use cosine difference of angle formula to have;
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( A-B \right)=\cos A\cos B+\sin A\sin B.......\left( 1 \right)\]
We take tangent both sides of $A={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3}$to have $\tan A=\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3} \right)=\dfrac{4}{3}$. If we take $p=4,b=3$ in right angled triangle to have $h=\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{4}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}}=5$. So we have
\[\sin A=\dfrac{p}{h}=\dfrac{4}{5},\cos A=\dfrac{b}{h}=\dfrac{3}{5}\]
We take sine of both sides $B={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13}$ to have $\sin B=\dfrac{12}{13}$. If we take $p=12,h=13$ we have $b=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}-{{p}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{13}^{2}}-{{12}^{2}}}=5$ to have
\[\cos B=\dfrac{b}{h}=\dfrac{5}{13}\]
We put $\sin A=\dfrac{4}{5},\cos A=\dfrac{3}{5},\sin B=\dfrac{12}{13},\cos B=\dfrac{5}{13}$ in (1) to have the required value
\[\cos \left( A-B \right)=\dfrac{3}{5}\cdot \dfrac{5}{13}+\dfrac{4}{5}\cdot \dfrac{12}{13}=\dfrac{15}{65}+\dfrac{48}{65}=\dfrac{63}{65}\]
Note:
We note that the domain of sine inverse function is $\left[ -1,1 \right]$ and since $\dfrac{12}{13}\in \left[ -1,1 \right]$ the value ${{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13}$ is well defined. The domain of tangent inverse function is real number set and hence ${{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3}$ is well defined. We can alternatively use Pythagorean trigonometric identities $\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta },\sin \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }$ and $\sin \theta =\tan \theta \cos \theta $ to find the values of $\cos B,\sin B,\sin A$,
Complete step by step answer:

We know that in the right angled triangle the side opposite to the right angled triangle is called hypotenuse denoted as $h$, the vertical side is called perpendicular denoted as $p$ and the horizontal side is called the base denoted as $b$.
We know from the trigonometric ratios in a right angled triangle the sine of any angle is given by the ratio of side opposite to the angle to the hypotenuse, cosine of an angle is the ratio of side adjacent to the angle (excluding hypotenuse) to the hypotenuse and tangent of the angle is the ratio of opposite side to the adjacent side (excluding hypotenuse) . So we have
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{p}{h},\cos \theta =\dfrac{b}{h},\tan \theta =\dfrac{p}{b}\]
We use Pythagoras thrum to have theorem to have;
\[{{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}\]
We know that range of tangent inverse function is $\left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ and range of sine inverse function is $\left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$.We are asked to evaluate the following expression
\[\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13} \right)\]
Let us assume$A={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3},B={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13}$.So we have
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( A-B \right)\]
We use cosine difference of angle formula to have;
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( A-B \right)=\cos A\cos B+\sin A\sin B.......\left( 1 \right)\]
We take tangent both sides of $A={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3}$to have $\tan A=\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3} \right)=\dfrac{4}{3}$. If we take $p=4,b=3$ in right angled triangle to have $h=\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{4}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}}=5$. So we have
\[\sin A=\dfrac{p}{h}=\dfrac{4}{5},\cos A=\dfrac{b}{h}=\dfrac{3}{5}\]
We take sine of both sides $B={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13}$ to have $\sin B=\dfrac{12}{13}$. If we take $p=12,h=13$ we have $b=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}-{{p}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{13}^{2}}-{{12}^{2}}}=5$ to have
\[\cos B=\dfrac{b}{h}=\dfrac{5}{13}\]
We put $\sin A=\dfrac{4}{5},\cos A=\dfrac{3}{5},\sin B=\dfrac{12}{13},\cos B=\dfrac{5}{13}$ in (1) to have the required value
\[\cos \left( A-B \right)=\dfrac{3}{5}\cdot \dfrac{5}{13}+\dfrac{4}{5}\cdot \dfrac{12}{13}=\dfrac{15}{65}+\dfrac{48}{65}=\dfrac{63}{65}\]
Note:
We note that the domain of sine inverse function is $\left[ -1,1 \right]$ and since $\dfrac{12}{13}\in \left[ -1,1 \right]$ the value ${{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{12}{13}$ is well defined. The domain of tangent inverse function is real number set and hence ${{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{4}{3}$ is well defined. We can alternatively use Pythagorean trigonometric identities $\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta },\sin \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }$ and $\sin \theta =\tan \theta \cos \theta $ to find the values of $\cos B,\sin B,\sin A$,
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




