
How many \[C - C\] bonds are there in hexene? What is the structural formula of hexene?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: The structural formula of hexene can be determined by decoding the information contained by its IUPAC name. It is a straight chain organic compound with no substituents and is unsaturated in nature. The number of \[C - C\] bonds present in it can be determined with the help of its structure.
Complete answer:
The structural formula of any hydrocarbon gives us information about the type of bonds present in it. It is necessary to know the structural formula of an organic compound in order to identify the functional groups present in and to also determine the position at which various substituents, functional groups and double or triple bonds are present.
The IUPAC name ‘Hexene’ gives us important information about the structure of the molecule. The prefix ‘Hex’ indicates the fact that the parent chain of this organic compound contains six carbon atoms attached to one another. The suffix ‘ene’ suggests that the compound contains one \[C = C\] double bond. The position of the double bond is automatically assumed to be between the first and the second carbon atom of the parent chain as there are no numbers written before the ‘ene’ suffix.
Since, carbon is a tetravalent atom, the remaining valencies are satisfied by connecting hydrogen atoms to it. There are no substituents or functional groups attached.
Thus there are five single \[C - C\] bonds and one double \[C = C\] bond present in Hexene.
The structure of Hexene is as follows:
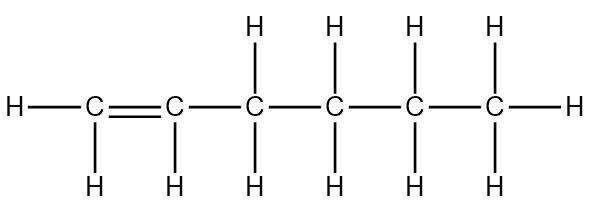
Note:
The molecular formula is never enough to identify any structure. More than one carbon compound can have the same molecular formula yet different structures, these are known as structural isomers.
Complete answer:
The structural formula of any hydrocarbon gives us information about the type of bonds present in it. It is necessary to know the structural formula of an organic compound in order to identify the functional groups present in and to also determine the position at which various substituents, functional groups and double or triple bonds are present.
The IUPAC name ‘Hexene’ gives us important information about the structure of the molecule. The prefix ‘Hex’ indicates the fact that the parent chain of this organic compound contains six carbon atoms attached to one another. The suffix ‘ene’ suggests that the compound contains one \[C = C\] double bond. The position of the double bond is automatically assumed to be between the first and the second carbon atom of the parent chain as there are no numbers written before the ‘ene’ suffix.
Since, carbon is a tetravalent atom, the remaining valencies are satisfied by connecting hydrogen atoms to it. There are no substituents or functional groups attached.
Thus there are five single \[C - C\] bonds and one double \[C = C\] bond present in Hexene.
The structure of Hexene is as follows:

Note:
The molecular formula is never enough to identify any structure. More than one carbon compound can have the same molecular formula yet different structures, these are known as structural isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




