
Why budding, fragmentation, and regeneration all are considered as asexual types of reproduction?
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Asexual reproduction refers to the production of offspring from single parent without undergoing fusion of gametes. The offspring are genetically identical to that of parent and hence, commonly referred to as a clone. Since the new organisms formed through budding, fragmentation and regeneration all takes place from single parent without fusion of gamete, they all are considered as asexual type of reproduction.
Complete answer:Asexual reproduction, formation of offspring from a single parent is common in all unicellular organisms. It is common in all three domains of life such as: Archaea, Eubacteria and eukarya. In eukarya, asexual mode of reproduction takes place in protists. Somatic cells are involved in this division and not the gametes, hence this type of reproduction is also called Agamogenesis or somatogenic reproduction.
Budding: Daughter is formed as a small outgrowth on the parent's body. There are two types of budding:
1. Exogenous or external budding:. Ex: Hydra
2.Endogenous or internal budding: Buds are formed within the parent's body as in case of freshwater sponges (spongilla) and some marine sponges. They are called gemmule or internal buds.

Fragmentation: The parent’s body breaks up into several pieces and each piece later develops into a new individual. Ex: Flatworm, coelenterates and sponges.
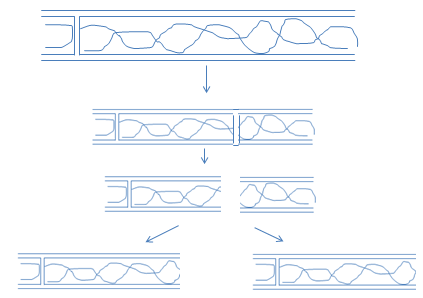
Regeneration: Regeneration is the process of renewal, restoration and regrowth of the injured region. It can occur at the level of cells, tissues and even organs.
It is of two types:
1. Morphallaxis: Formation of the whole body from a small fragment. Ex: Hydra, planaria
2. Epimorphosis: It is the replacement of lost body parts. Ex: Lizard.
Note:Few general examples of organism undergoing asexual reproduction: protozoans (Amoeaba, paramecium, euglena), sponger (sycon), coelenterates (hydra), Platyhelminthes (Planaria), annelids (Syllis), echinoderms (Starfish), tunicates (salpa), such as monera and protista. It also occurs in some lower animals such as sponges, coelenterates, worms and tunicates.
Complete answer:Asexual reproduction, formation of offspring from a single parent is common in all unicellular organisms. It is common in all three domains of life such as: Archaea, Eubacteria and eukarya. In eukarya, asexual mode of reproduction takes place in protists. Somatic cells are involved in this division and not the gametes, hence this type of reproduction is also called Agamogenesis or somatogenic reproduction.
Budding: Daughter is formed as a small outgrowth on the parent's body. There are two types of budding:
1. Exogenous or external budding:. Ex: Hydra
2.Endogenous or internal budding: Buds are formed within the parent's body as in case of freshwater sponges (spongilla) and some marine sponges. They are called gemmule or internal buds.

Fragmentation: The parent’s body breaks up into several pieces and each piece later develops into a new individual. Ex: Flatworm, coelenterates and sponges.

Regeneration: Regeneration is the process of renewal, restoration and regrowth of the injured region. It can occur at the level of cells, tissues and even organs.
It is of two types:
1. Morphallaxis: Formation of the whole body from a small fragment. Ex: Hydra, planaria
2. Epimorphosis: It is the replacement of lost body parts. Ex: Lizard.
Note:Few general examples of organism undergoing asexual reproduction: protozoans (Amoeaba, paramecium, euglena), sponger (sycon), coelenterates (hydra), Platyhelminthes (Planaria), annelids (Syllis), echinoderms (Starfish), tunicates (salpa), such as monera and protista. It also occurs in some lower animals such as sponges, coelenterates, worms and tunicates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




