
When bromoethane is treated with potassium sulfide, the main product formed is:
A) Ethanethiol
B) Ethanol
C) Mustard gas
C)Thio ethyl ethane
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: When a mixture of haloalkanes is heated with the aqueous-alcoholic sodium or potassium sulfides, thioethers are formed. The sulfide acts as a nucleophile and its attack on the haloalkane.
Complete answer:
In haloalkanes, the carbon is bonded to the halogen atom ($\text{X=F,Cl,Br,I}$) which is more electronegative than carbon. The $\text{C-X}$bond is polar. As a result, the carbon acquires the partial positive charge and halogen gets a partial negative charge. This polar nature makes them highly reactive molecules. The positive charge on the carbon atom is attacked by the nucleophile. Some of the examples of nucleophiles are \[\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}\text{,C}{{\text{N}}^{\text{-}}}\text{,}\overset{\text{}}{\mathop{\text{N}}}\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{,}{{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}\text{,etc}\text{.}\]
The alkyl halide \[\text{R-X}\] was treated with sodium sulfide $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}$or potassium sulfide${{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}$. The reaction of alkyl halide is converted into the thioether or sulfides$\text{R-S-R}$.
The general reaction of the formation of thioether is
$\text{2RX+N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}\xrightarrow[\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }]{{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{OH/}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}}\text{R-S-R+2NaX}$
Let's take an example of bromoethane $\text{(CH3-CH2-Br)}$ treated with potassium sulfide ${{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}$
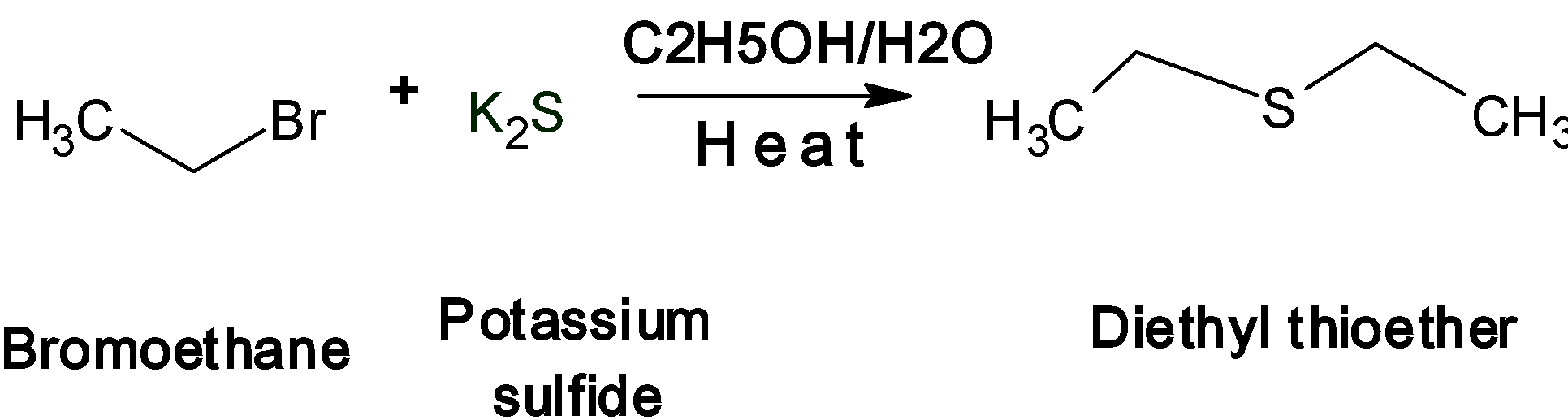
Sulfur analogs of ether are named as the thioether. This is one of the important nucleophilic substitution reactions of halogens. Here sulfide ion ${{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}$acts as a nucleophile. During the reaction, the two bromoethane molecules react with the potassium or sodium sulfide. The two $\text{B}{{\text{r}}^{\text{-}}}$ions from the bromoethane are removed as the two molecules of the$\text{HBr}$. The sulfide ion ${{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}$acts as a nucleophile and attacks simultaneously on the ethyl cation $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{-C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{+}}$to form a thioether.
The dimethyl thioether is also called thio ethyl ethane.
Hence, (D) is the correct option.
Additional information:
The sulfur analogs of ethers are called as the thioethers or sulfides as in alkyl ether nomenclature.
The general nomenclature for thioether is Alkyl thioether or Alkyl sulfide.
Note:
The sulfide ion ${{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}$ is an electron-rich species therefore it attacks the electron-deficient species like carbocation. Pay extra attention to the flow of the electron.
Complete answer:
In haloalkanes, the carbon is bonded to the halogen atom ($\text{X=F,Cl,Br,I}$) which is more electronegative than carbon. The $\text{C-X}$bond is polar. As a result, the carbon acquires the partial positive charge and halogen gets a partial negative charge. This polar nature makes them highly reactive molecules. The positive charge on the carbon atom is attacked by the nucleophile. Some of the examples of nucleophiles are \[\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}\text{,C}{{\text{N}}^{\text{-}}}\text{,}\overset{\text{}}{\mathop{\text{N}}}\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{,}{{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}\text{,etc}\text{.}\]
The alkyl halide \[\text{R-X}\] was treated with sodium sulfide $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}$or potassium sulfide${{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}$. The reaction of alkyl halide is converted into the thioether or sulfides$\text{R-S-R}$.
The general reaction of the formation of thioether is
$\text{2RX+N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}\xrightarrow[\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }]{{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{OH/}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}}\text{R-S-R+2NaX}$
Let's take an example of bromoethane $\text{(CH3-CH2-Br)}$ treated with potassium sulfide ${{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}$

Sulfur analogs of ether are named as the thioether. This is one of the important nucleophilic substitution reactions of halogens. Here sulfide ion ${{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}$acts as a nucleophile. During the reaction, the two bromoethane molecules react with the potassium or sodium sulfide. The two $\text{B}{{\text{r}}^{\text{-}}}$ions from the bromoethane are removed as the two molecules of the$\text{HBr}$. The sulfide ion ${{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}$acts as a nucleophile and attacks simultaneously on the ethyl cation $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{-C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{+}}$to form a thioether.
The dimethyl thioether is also called thio ethyl ethane.
Hence, (D) is the correct option.
Additional information:
The sulfur analogs of ethers are called as the thioethers or sulfides as in alkyl ether nomenclature.
The general nomenclature for thioether is Alkyl thioether or Alkyl sulfide.
Note:
The sulfide ion ${{\text{S}}^{\text{2-}}}$ is an electron-rich species therefore it attacks the electron-deficient species like carbocation. Pay extra attention to the flow of the electron.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




