
Briefly explain the concept of reflection of light.
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: The property of light by which it bounces back when it strikes any object in its path is known as reflection of light. The ray which struck the surface of an object or body is known as incident ray while the one which gets bounced back is known as reflected ray.
Complete answer:
The phenomenon by which a light ray bounces back when it falls on a surface is known as reflection. It is the only phenomenon which is the reason we are able to see objects.
There are three types of reflection mainly:
A. Regular or specular reflection:
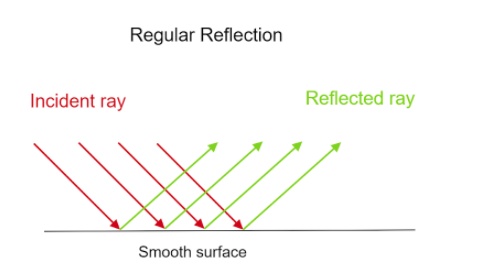
The reflection which occurs when a light ray falls on a smooth, shiny surface and gets bounced back is known as regular or specular reflection. In this particular reflection the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. There is no haziness or blurring in the image that forms after regular or specular reflection.
B. Irregular reflection:
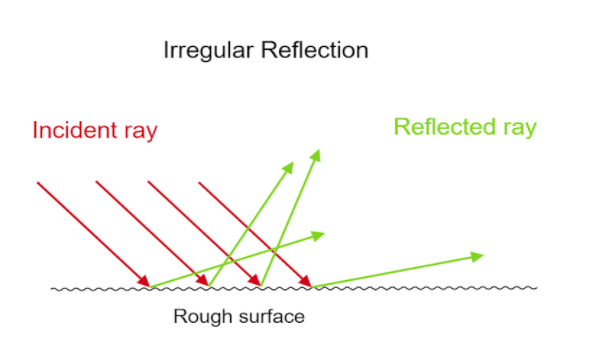
When a light ray falls into an abrupt or rough surface and gets reflected is known as irregular reflection. It occurs when the reflecting surface is not smooth, there is wear and tear on the surface. But it also helps us to see non-shiny objects.
C. Multiple reflection:
Multiple reflection is actually a subsidiary part of regular reflection. It occurs when two mirrors are placed face to face or tilted to each other. The light rays get bounced back many times and hence causes many images.
Note: The multiple angle reflection depends upon the angle of the mirror. If we increase the angle of the mirror the number of images decreases, while if we decrease the angle of the mirror the number of images increases. At a stage when the mirrors are parallel then infinite images form. It stops gradually when the intensity of light becomes zero after continuous reflection.
Complete answer:
The phenomenon by which a light ray bounces back when it falls on a surface is known as reflection. It is the only phenomenon which is the reason we are able to see objects.
There are three types of reflection mainly:
A. Regular or specular reflection:

The reflection which occurs when a light ray falls on a smooth, shiny surface and gets bounced back is known as regular or specular reflection. In this particular reflection the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. There is no haziness or blurring in the image that forms after regular or specular reflection.
B. Irregular reflection:

When a light ray falls into an abrupt or rough surface and gets reflected is known as irregular reflection. It occurs when the reflecting surface is not smooth, there is wear and tear on the surface. But it also helps us to see non-shiny objects.
C. Multiple reflection:
Multiple reflection is actually a subsidiary part of regular reflection. It occurs when two mirrors are placed face to face or tilted to each other. The light rays get bounced back many times and hence causes many images.
Note: The multiple angle reflection depends upon the angle of the mirror. If we increase the angle of the mirror the number of images decreases, while if we decrease the angle of the mirror the number of images increases. At a stage when the mirrors are parallel then infinite images form. It stops gradually when the intensity of light becomes zero after continuous reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




