
Briefly describe the following:
(a) Transcription
(b) Polymorphism
(c) Translation
(d) Bioinformatics
Answer
585k+ views
Hint:Transcription is the conversion of DNA information to the mRNA information. The translation is the conversion of mRNA information into protein information (amino acid sequence). Polymorphism genetic variation leading to the formation of different forms of individuals within a single species. Bioinformatics is the study involving science, mathematics, physics, and computer science.
Complete answer:Transcription is the process of synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA sequence. During this process, the DNA sequence is converted to RNA sequence and the mRNA is transferred to the cytoplasm from the nucleus of the cell. The copy of information from DNA involves four steps: Initiation, Elongation, Termination, and processing.
Figure 1: Transcription and translation
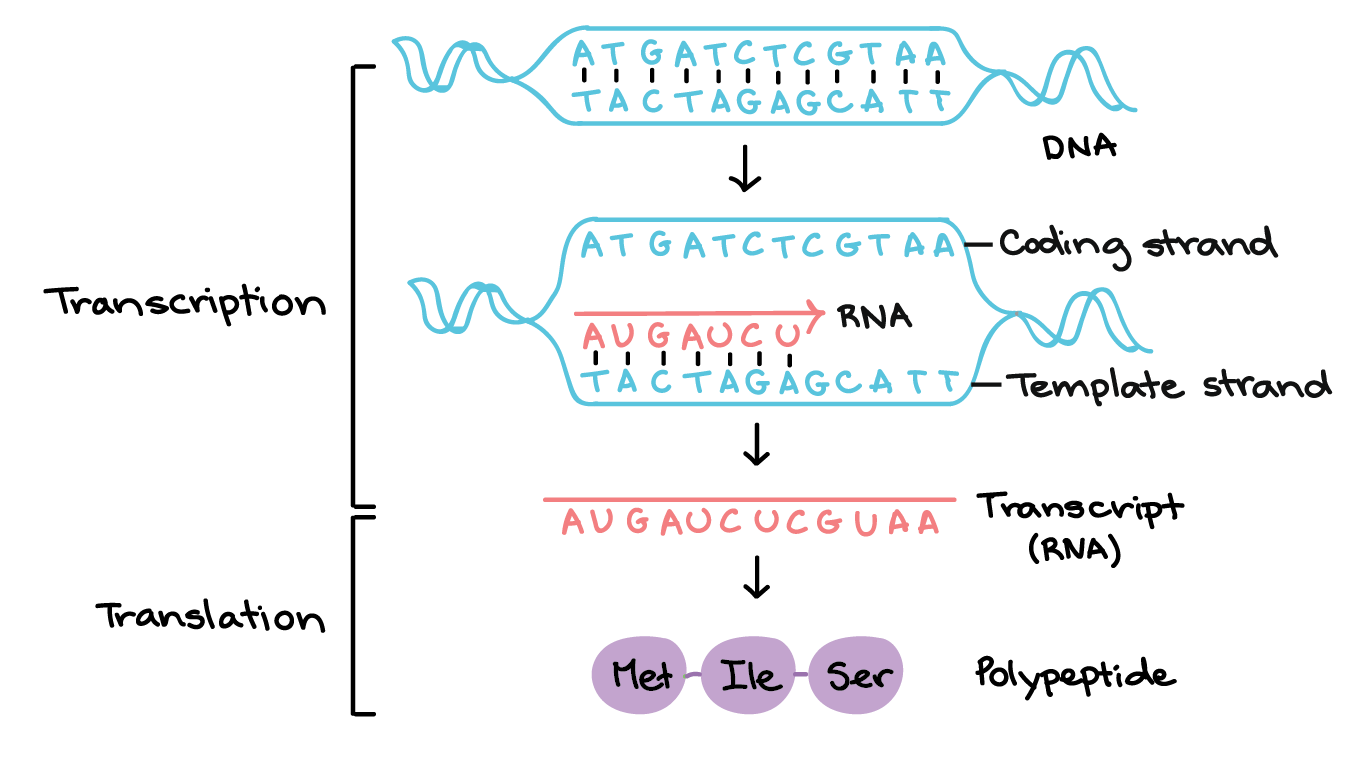
The translation is a process of conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acid sequence forming the polypeptide chain for the synthesis of proteins. The translation of mRNA takes place in the ribosome, the cell’s protein-synthesizing factory. Translation involves the assistance of tRNA for the conversion of mRNA sequence information to the amino acid sequence.
Polymorphism is the existence of more than two different forms in a particular group. In biology, polymorphism is a result of genetic variation that leads to the development of organisms with different physical characters. It divides the organism of a population into more than two different forms. For example, Humans show sex polymorphism (male, female, and transgender), polymorphism in blood type of human (A+/-, B+/-, AB+/-, and O+/-), and mimetic forms of butterflies.
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary subject of science that combines different fields of study like biology, computer science, information technology, physics, statistics, and mathematics for working with biological data. It can be used to compile, analyze, interpret, and correlate different biological data.
Note:Polymorphism in human sex is known as sexual polymorphism and the polymorphism in the blood is a form of allelic polymorphism. Transcription and translation process is a part of central dogma involving replication of DNA, followed by transcription of DNA to mRNA the mRNA is then translated to protein (a long chain of amino acids).
Complete answer:Transcription is the process of synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA sequence. During this process, the DNA sequence is converted to RNA sequence and the mRNA is transferred to the cytoplasm from the nucleus of the cell. The copy of information from DNA involves four steps: Initiation, Elongation, Termination, and processing.
Figure 1: Transcription and translation

The translation is a process of conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acid sequence forming the polypeptide chain for the synthesis of proteins. The translation of mRNA takes place in the ribosome, the cell’s protein-synthesizing factory. Translation involves the assistance of tRNA for the conversion of mRNA sequence information to the amino acid sequence.
Polymorphism is the existence of more than two different forms in a particular group. In biology, polymorphism is a result of genetic variation that leads to the development of organisms with different physical characters. It divides the organism of a population into more than two different forms. For example, Humans show sex polymorphism (male, female, and transgender), polymorphism in blood type of human (A+/-, B+/-, AB+/-, and O+/-), and mimetic forms of butterflies.
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary subject of science that combines different fields of study like biology, computer science, information technology, physics, statistics, and mathematics for working with biological data. It can be used to compile, analyze, interpret, and correlate different biological data.
Note:Polymorphism in human sex is known as sexual polymorphism and the polymorphism in the blood is a form of allelic polymorphism. Transcription and translation process is a part of central dogma involving replication of DNA, followed by transcription of DNA to mRNA the mRNA is then translated to protein (a long chain of amino acids).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




