
Brady’s reagent is:
A. $\left[ Cu{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{4}} \right]S{{O}_{4}}$
B. $KMn{{O}_{4}}/NaI{{O}_{4}}$
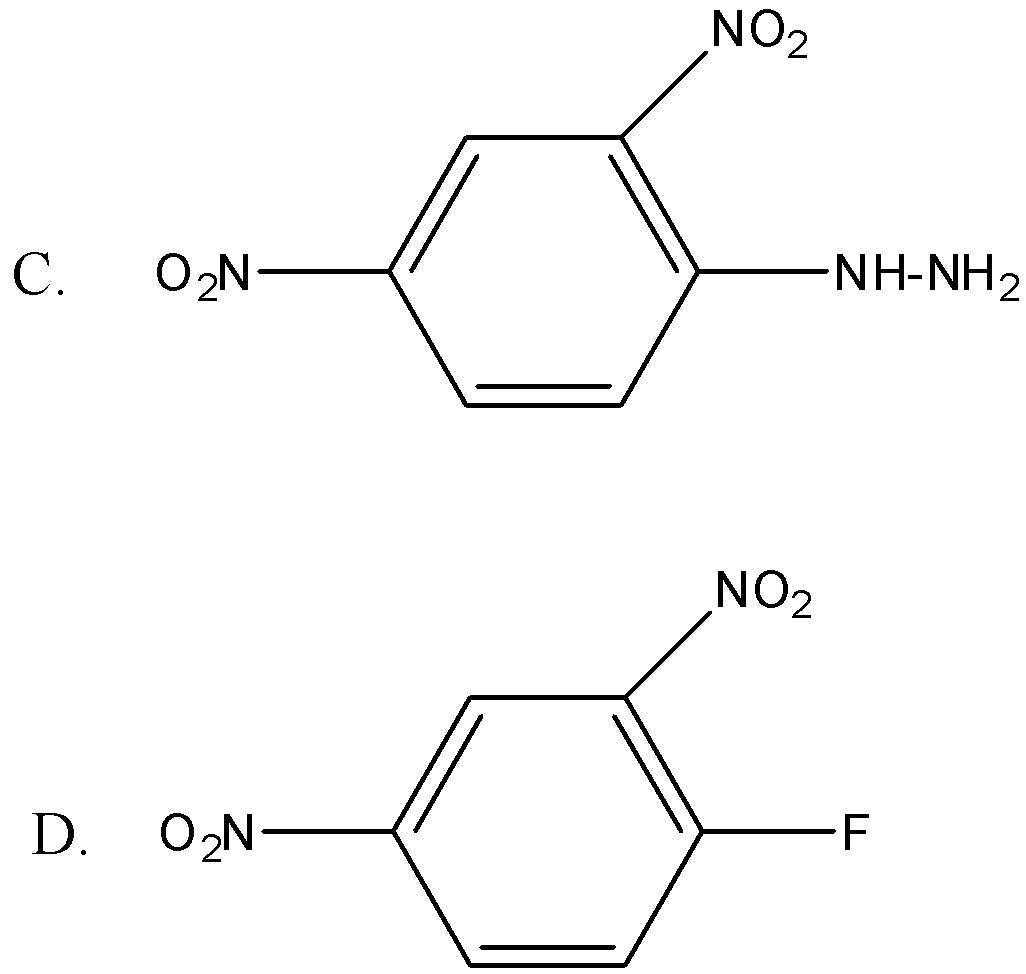

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Brady’s reagent is an important reagent in organic chemistry as it is used to test the presence of carbonyl compounds. It is also called 2,4-DNP whose IUPAC name is 2,4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine. Its chemical formula is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{3}}{{\left( N{{O}_{2}} \right)}_{2}}NHN{{H}_{2}}$. It shows positive tests with pure carbonyl compounds.
Complete step by step solution:
-Pure carbonyl compounds are aldehydes and ketones. There are many functional groups that can attach themselves with the carbon chains to form compounds which show different characteristics and behavior compared to normal compounds.
-The functional groups are differentiated with one another through different reagents. Brady’s reagent shows positive test with the aldehydes and the ketones. They are said to be pure carbonyl compounds.
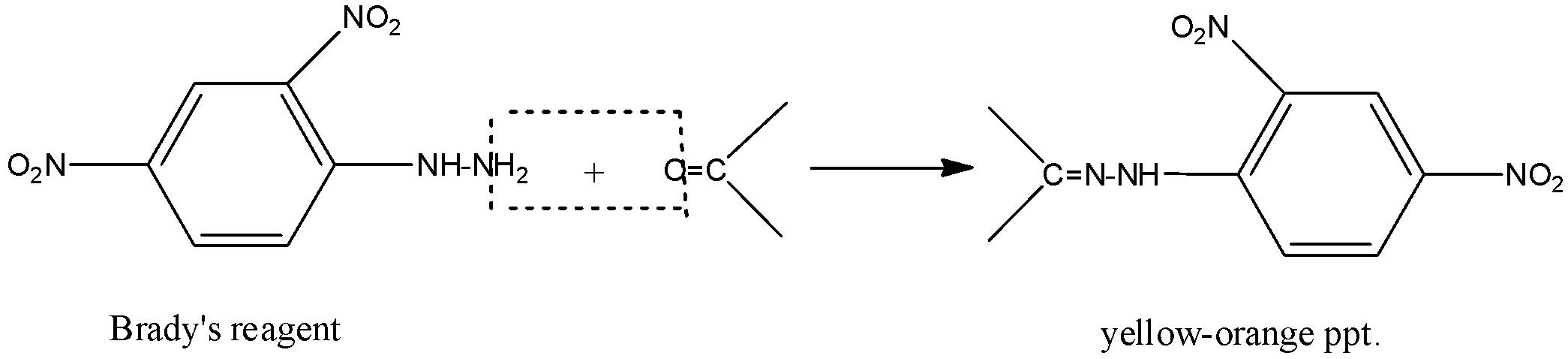
-When Brady’s reagent is reacted with pure carbonyls, it forms precipitate which is yellow-orange in colour. This colour shows the presence of the carbonyl compounds. It does not give this colour when any other compounds react with it. Brady’s reagent is red to orange in colour in pure form. The reaction can be shown as
-Observing the options, we can also solve the question by seeing the colour of the compounds given in the options. The colour of the first option is dark blue and it appears as crystals. The second option is purple in colour. The third option is red to orange in colour. The last option is colourless. So, we can directly conclude what the correct answer is.
Therefore the correct option is C.
Note: Brady’s reagent only reacts with pure carbonyls which are aldehydes and ketones. It does not react with the impure carbonyls like acid halides, esters, anhydrides, etc to give the yellow-orange precipitate. It gives elimination reactions with the aldehydes and ketones.
Complete step by step solution:
-Pure carbonyl compounds are aldehydes and ketones. There are many functional groups that can attach themselves with the carbon chains to form compounds which show different characteristics and behavior compared to normal compounds.
-The functional groups are differentiated with one another through different reagents. Brady’s reagent shows positive test with the aldehydes and the ketones. They are said to be pure carbonyl compounds.
-When Brady’s reagent is reacted with pure carbonyls, it forms precipitate which is yellow-orange in colour. This colour shows the presence of the carbonyl compounds. It does not give this colour when any other compounds react with it. Brady’s reagent is red to orange in colour in pure form. The reaction can be shown as

-Observing the options, we can also solve the question by seeing the colour of the compounds given in the options. The colour of the first option is dark blue and it appears as crystals. The second option is purple in colour. The third option is red to orange in colour. The last option is colourless. So, we can directly conclude what the correct answer is.
Therefore the correct option is C.
Note: Brady’s reagent only reacts with pure carbonyls which are aldehydes and ketones. It does not react with the impure carbonyls like acid halides, esters, anhydrides, etc to give the yellow-orange precipitate. It gives elimination reactions with the aldehydes and ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




