
Boyle’s law is applicable for an
a) Adiabatic process
b) Isothermal process
c) Isobaric process
d) Isochoric process
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Boyle's law states that the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the pressure in the given volume. This is only possible if no gas escapes the container in which it is kept and the temperature of the container is held constant. The word iso, prefixed before any thermodynamic process implies that the process is taking place at a constant suffixed thermodynamic variable. Knowing this is enough to guess the answer to the above question.
Complete step by step answer:
Now let us understand first how Boyle's law works from a graph. Let the gas be enclosed in a container of fixed amount and held at constant temperature.
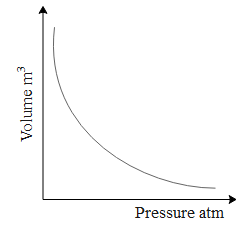
From the above graph we can comment that volume and pressure vary inversely. Mathematically written as $V\propto \dfrac{1}{P}$. Further we can write this equation as $PV=\text{k}...\text{(1), where k is constant}\text{.}$.
For an ideal gas , $PV=nRT...(2)$ where n is the amount of gas R is the gas constant and T is the temperature of the gas. Comparing equation 1 and 2 we can say that, nRT=k which is a constant.
Hence we can conclude that, only when the temperature is constant Boyle's law is obeyed. And by definition of isothermal process i.e. any thermodynamic process carried out at constant temperature is called isothermal.
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note:
It is to be noted that Boyle's law is not always obeyed at any given constant temperature. This is because of the inter conversion of the state of the substance. Hence the minimum temperature below which Boyle's law is not obeyed is called Boyle's temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Now let us understand first how Boyle's law works from a graph. Let the gas be enclosed in a container of fixed amount and held at constant temperature.

From the above graph we can comment that volume and pressure vary inversely. Mathematically written as $V\propto \dfrac{1}{P}$. Further we can write this equation as $PV=\text{k}...\text{(1), where k is constant}\text{.}$.
For an ideal gas , $PV=nRT...(2)$ where n is the amount of gas R is the gas constant and T is the temperature of the gas. Comparing equation 1 and 2 we can say that, nRT=k which is a constant.
Hence we can conclude that, only when the temperature is constant Boyle's law is obeyed. And by definition of isothermal process i.e. any thermodynamic process carried out at constant temperature is called isothermal.
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note:
It is to be noted that Boyle's law is not always obeyed at any given constant temperature. This is because of the inter conversion of the state of the substance. Hence the minimum temperature below which Boyle's law is not obeyed is called Boyle's temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




