
Both sickle cell anemia and Huntington’s chorea are
(a)Bacteria related diseases
(b)Congenital disorders
(c)Pollutant induced disorders
(d)Virus related disorders
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: An inherited medical condition that is often present from the birth caused due to a single mutation in the structure of DNA. They contain long term disability. Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s chorea are some of the examples.
Complete answer:
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited autosomal recessive disorder that is caused by mutations in the HBB gene. In chromosome 11 normal DNA sequence has an amino acid chain of Pro-Glu-Glu but in sickle cell disease, amino acid Glu is replaced with Val.
Huntington’s disease is an inherited autosomal dominant disorder, which means a person needs only one copy of defective genes to develop this disorder. In this, the altered HTT gene is passed from one generation to the next thereby the size of CAG trinucleotide repeat often increases.people with adult-onset have 40-50 CAG gene repeats in the HTT gene, people with juvenile stage have 60 CAG repeats
Both the disorders are inherited to offspring and are present since birth in offspring.
Additional Information: -Generally RCB live for 120 days but in sickle cell anemia they die within 10 to 20 days.
- Amniocentesis is done usually 14-16 weeks of pregnancy to detect sickle cell anemia.
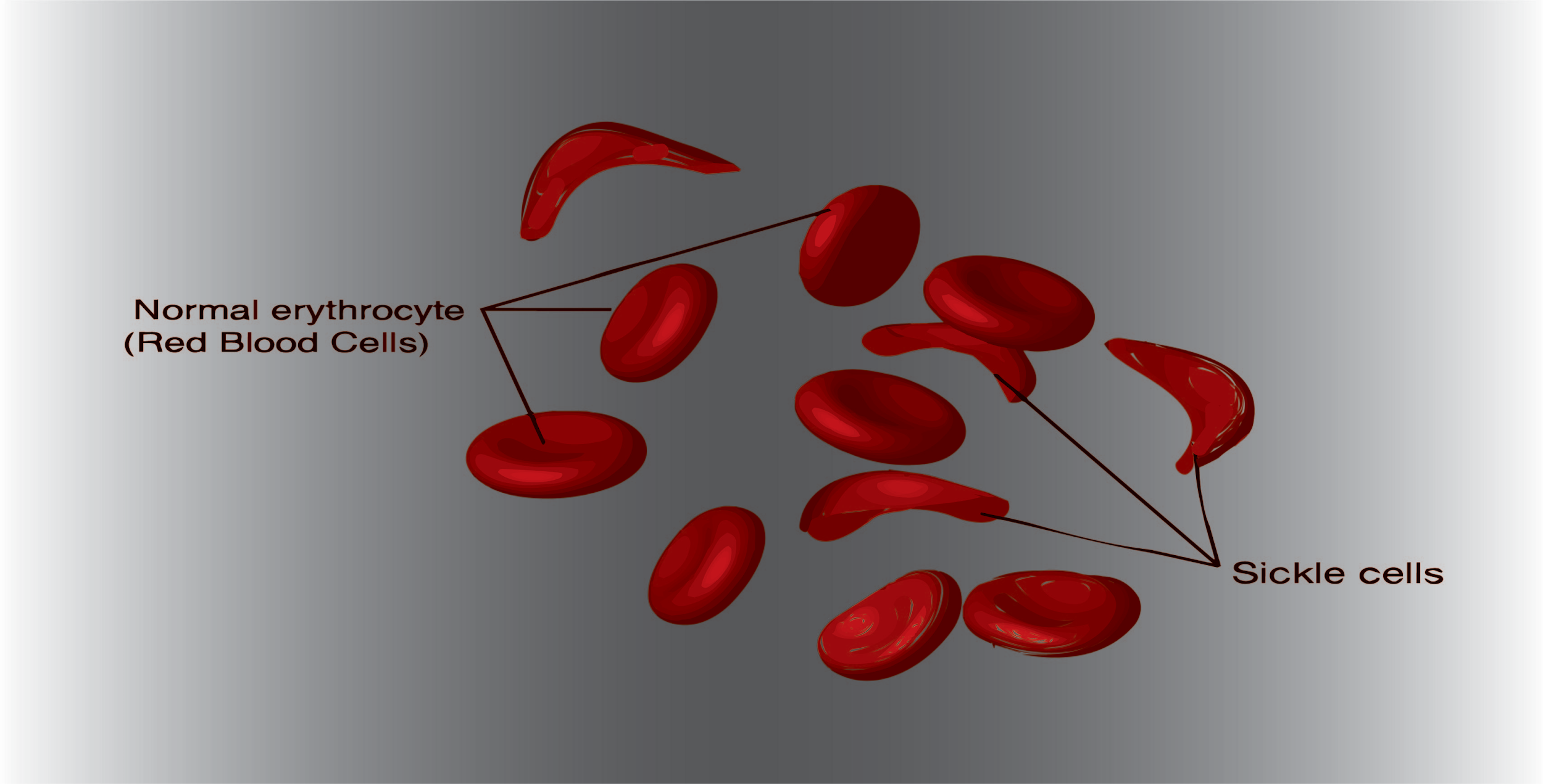
- Generally, RBC is biconcave in shape but in sickle cell anemia they’re in sickle shape.
-The most common psychiatric disorder associated with Huntington’s chorea is depression.
- Mutation in the HTT gene causes Huntington’s chorea. The HTT gene provides instructions for making a protein called ‘huntingtin’ which plays an important role in neuron function in the brain.
- Due to a lack of huntingtin protein, people with this disorder have psychological problems.
- Symptoms of sickle cell anemia are anemia, pale skin or nail bed, fever, abnormal swelling, yellow tint to the skin, or whites of the eyes.
-Symptoms of Huntington’s chorea include irritability, depression, small involuntary movements, fasciculation, poor coordination.
So, the answer is 'congenital disorders'.
Note: The onset of Huntington’s chorea usually appears in a person’s 30s or 40s. A less common form of Huntington’s chorea is called juvenile Huntington begins in childhood or adolescence.
People with 27 to 35 CAG repeats in the HTT gene do not develop Huntington’s disease but are at risk of inheriting this disease to their offspring.
Complete answer:
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited autosomal recessive disorder that is caused by mutations in the HBB gene. In chromosome 11 normal DNA sequence has an amino acid chain of Pro-Glu-Glu but in sickle cell disease, amino acid Glu is replaced with Val.
Huntington’s disease is an inherited autosomal dominant disorder, which means a person needs only one copy of defective genes to develop this disorder. In this, the altered HTT gene is passed from one generation to the next thereby the size of CAG trinucleotide repeat often increases.people with adult-onset have 40-50 CAG gene repeats in the HTT gene, people with juvenile stage have 60 CAG repeats
Both the disorders are inherited to offspring and are present since birth in offspring.
Additional Information: -Generally RCB live for 120 days but in sickle cell anemia they die within 10 to 20 days.
- Amniocentesis is done usually 14-16 weeks of pregnancy to detect sickle cell anemia.
- Generally, RBC is biconcave in shape but in sickle cell anemia they’re in sickle shape.
-The most common psychiatric disorder associated with Huntington’s chorea is depression.
- Mutation in the HTT gene causes Huntington’s chorea. The HTT gene provides instructions for making a protein called ‘huntingtin’ which plays an important role in neuron function in the brain.
- Due to a lack of huntingtin protein, people with this disorder have psychological problems.
- Symptoms of sickle cell anemia are anemia, pale skin or nail bed, fever, abnormal swelling, yellow tint to the skin, or whites of the eyes.
-Symptoms of Huntington’s chorea include irritability, depression, small involuntary movements, fasciculation, poor coordination.
So, the answer is 'congenital disorders'.
Note: The onset of Huntington’s chorea usually appears in a person’s 30s or 40s. A less common form of Huntington’s chorea is called juvenile Huntington begins in childhood or adolescence.
People with 27 to 35 CAG repeats in the HTT gene do not develop Huntington’s disease but are at risk of inheriting this disease to their offspring.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




