
Boron trifluoride $(B{F_3})$ has no dipole moment $(\mu = 0D)$. Explain how this observation confirms the geometry of $B{F_3}$ predicted by VSEPR theory.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: A dipole moment of a molecule is a term that describes the two opposite charges that are separated by a distance within that molecule. One can draw the structure for the molecule $B{F_3}$ which will give the idea of the dipole moment value present in the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all let's learn about the concept of dipole moment where it is a quantity that is measured in a molecule for the determination of the partial charges present in between the two atoms or groups that are present in that molecule.
2) When there are two equal and opposite charges present in that molecule then the net dipole moment of that molecule is zero.
3) Now let's analyze the structure $B{F_3}$ and its geometry according to the VSEPR theory as below,
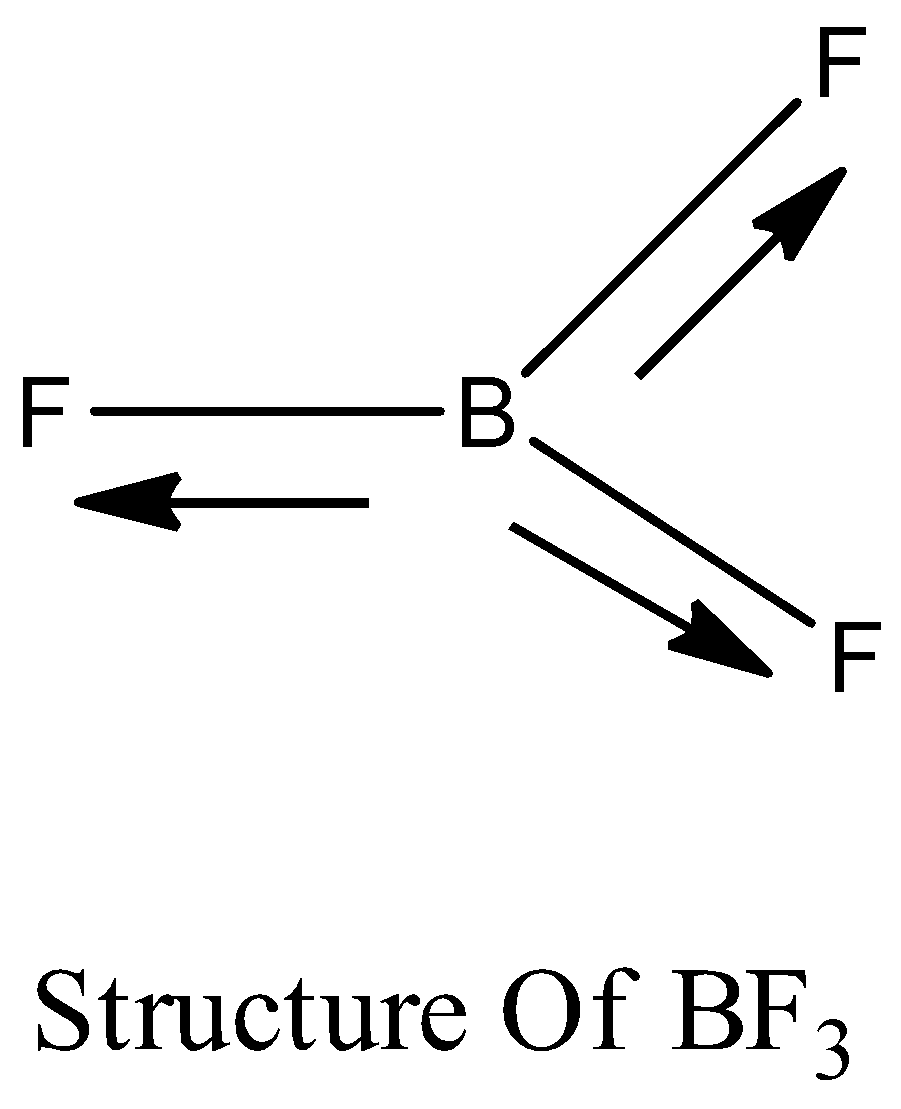
The structure $B{F_3}$ shows the trigonal planar geometry which means all the elements present in the molecule are in one plane.
4) In the molecular structure of $B{F_3}$ the resultant moment present between any two ${\text{B - F}}$ dipoles is the same in magnitude but they are present in the opposite direction to the moment of the third ${\text{B - F}}$.
5) The two opposite magnitude of forces cancel each other out. Therefore, the resultant net dipole moment of the $B{F_3}$ molecule is zero which means the Boron trifluoride $(B{F_3})$ has no dipole moment $(\mu = 0D)$.
Note:
When there is no dipole moment i.e. $(\mu = 0D)$ present in a molecule then a molecule is said to be a nonpolar molecule. The boron trifluoride is a non-polar molecule. Boron trifluoride molecule has the same geometry as the sulfur trioxide $(S{O_3})$ molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all let's learn about the concept of dipole moment where it is a quantity that is measured in a molecule for the determination of the partial charges present in between the two atoms or groups that are present in that molecule.
2) When there are two equal and opposite charges present in that molecule then the net dipole moment of that molecule is zero.
3) Now let's analyze the structure $B{F_3}$ and its geometry according to the VSEPR theory as below,

The structure $B{F_3}$ shows the trigonal planar geometry which means all the elements present in the molecule are in one plane.
4) In the molecular structure of $B{F_3}$ the resultant moment present between any two ${\text{B - F}}$ dipoles is the same in magnitude but they are present in the opposite direction to the moment of the third ${\text{B - F}}$.
5) The two opposite magnitude of forces cancel each other out. Therefore, the resultant net dipole moment of the $B{F_3}$ molecule is zero which means the Boron trifluoride $(B{F_3})$ has no dipole moment $(\mu = 0D)$.
Note:
When there is no dipole moment i.e. $(\mu = 0D)$ present in a molecule then a molecule is said to be a nonpolar molecule. The boron trifluoride is a non-polar molecule. Boron trifluoride molecule has the same geometry as the sulfur trioxide $(S{O_3})$ molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




