
How is boron obtained from borax? Give chemical equations with reaction conditions. Write the structure of ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ and its reaction with ${\text{HCl}}$.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know that borax is sodium tetraborate. ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is known as diborane. In the structure of diborane, there are four terminal hydrogen atoms. Two hydrogen atoms are in a ring with the two boron atoms.
Complete answer:
We know that borax is sodium tetraborate. The chemical formula for borax is ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$.
Boron is obtained from borax or sodium tetraborate using the procedure as follows:
First borax is heated with concentrated hydrochloric acid or concentrated sulphuric acid. In the reaction, boric acid $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}} \right)$ is produced.
The reaction is as follows: ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}} + {\text{2HCl}} \to {\text{2NaCl}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$
The boric acid formed then reacts with water and orthoboric acid $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ separates out.
The reaction is as follows: ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}} + {\text{5}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \to {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Orthoboric acid is strongly heated and boric anhydride $\left( {{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ is produced.
The reaction is as follows: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \to {{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{3}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
Boric anhydride is then reduced with metals like sodium or potassium or magnesium to obtain boron.
The reaction is as follows: ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{6Na}} \to {\text{2B}} + {\text{3N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
The structure of diborane $\left( {{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}} \right)$ is as follows:
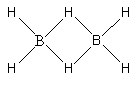
In the structure of diborane, there are four terminal hydrogen atoms. Two hydrogen atoms are in a ring with the two boron atoms. When a bond is formed between boron and the terminal hydrogen, one electron is shared by the boron atom and one electron is shared by the hydrogen atom. Thus, two atoms get bonded by sharing two electrons. Thus, the bonds formed between boron atoms and the terminal hydrogen atoms are 2-centre, 2-electron bonds.
Boron atom has three valence electrons. Two valence electrons out of these three are used in forming the bonds with the terminal hydrogen atoms.
When the ${\text{B - H - B}}$ bridge is formed, one electron is shared by the boron atom and one electron is shared by the hydrogen atom. Thus, the ${\text{B - H - B}}$ bridge forms two 3-centre, 2-electron bonds. Thus, the ${\text{B - H - B}}$ bridge is formed by the sharing of two electrons.The 2-centre, 2-electron bonds in diborane are known as banana bonds.
Diborane reacts with hydrochloric acid to form chloroborane. The molecular formula for chloric diborane is ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}$. Hydrogen gas is evolved in the reaction.
The reaction is as follows:
${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}} + {\text{HCl}} \to {{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
Note:Diborane is colourless and is highly flammable at room temperature. It has a sweet smell. Hydrolysis of diborane gives boric acid. Hydrogen gas is evolved in the reaction. Diborane is used as a reducing agent in many chemical reactions.
Complete answer:
We know that borax is sodium tetraborate. The chemical formula for borax is ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$.
Boron is obtained from borax or sodium tetraborate using the procedure as follows:
First borax is heated with concentrated hydrochloric acid or concentrated sulphuric acid. In the reaction, boric acid $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}} \right)$ is produced.
The reaction is as follows: ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}} + {\text{2HCl}} \to {\text{2NaCl}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$
The boric acid formed then reacts with water and orthoboric acid $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ separates out.
The reaction is as follows: ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}} + {\text{5}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \to {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Orthoboric acid is strongly heated and boric anhydride $\left( {{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ is produced.
The reaction is as follows: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \to {{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{3}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
Boric anhydride is then reduced with metals like sodium or potassium or magnesium to obtain boron.
The reaction is as follows: ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{6Na}} \to {\text{2B}} + {\text{3N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
The structure of diborane $\left( {{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}} \right)$ is as follows:

In the structure of diborane, there are four terminal hydrogen atoms. Two hydrogen atoms are in a ring with the two boron atoms. When a bond is formed between boron and the terminal hydrogen, one electron is shared by the boron atom and one electron is shared by the hydrogen atom. Thus, two atoms get bonded by sharing two electrons. Thus, the bonds formed between boron atoms and the terminal hydrogen atoms are 2-centre, 2-electron bonds.
Boron atom has three valence electrons. Two valence electrons out of these three are used in forming the bonds with the terminal hydrogen atoms.
When the ${\text{B - H - B}}$ bridge is formed, one electron is shared by the boron atom and one electron is shared by the hydrogen atom. Thus, the ${\text{B - H - B}}$ bridge forms two 3-centre, 2-electron bonds. Thus, the ${\text{B - H - B}}$ bridge is formed by the sharing of two electrons.The 2-centre, 2-electron bonds in diborane are known as banana bonds.
Diborane reacts with hydrochloric acid to form chloroborane. The molecular formula for chloric diborane is ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}$. Hydrogen gas is evolved in the reaction.
The reaction is as follows:
${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}} + {\text{HCl}} \to {{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
Note:Diborane is colourless and is highly flammable at room temperature. It has a sweet smell. Hydrolysis of diborane gives boric acid. Hydrogen gas is evolved in the reaction. Diborane is used as a reducing agent in many chemical reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




