
Biuret test is not given by:
a.) Carbohydrates
b.) Polypeptides
c.) Urea
d.) Proteins
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Amine derivatives of carboxylic acids are called amides. Amides are organic compounds that have -CONH- functional groups. This functionality is generally present in proteins. The Biuret test is the trademark test for the amide linkage.
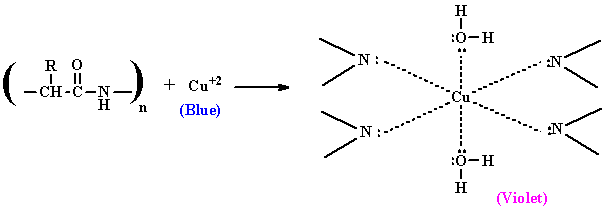
Complete answer: The biuret test is a synthetic test utilized for identifying the presence of peptide bonds. Within the sight of peptides, a copper(II) particle structures violet-colored coordination buildings in an alkaline solution. A few variations on the test have been grown, for example, the BCA test and the Modified Lowry test.
A. Carbohydrates are molecules consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are a significant food source and a key type of vitality for most creatures. At the point when consolidated together to shape polymers, sugars can work as long haul food storage molecules, as defensive layers for creatures and cells, and as the principal basic help for plants and constituents of numerous cells and their substance. Since there is no amide linkage in carbohydrates, they do not give this test.
B. The polypeptide chain is a chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. It can also be defined as the decoding of mRNA into proteins. As there is an amide linkage present in polypeptides so it will give biuret test.
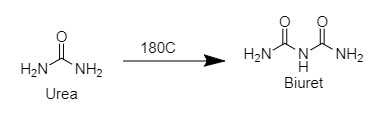
C. Urea is an organic compound with the formulae ${ CO\left[ { NH }_{ 2 } \right] _{ 2 } }$. Urea is also an important raw material for the chemical industry.
D. Proteins: Proteins are large macromolecules consisting of one or more chains of amino acids.they have functions like growth, catalytic activity, maintenance of the human body, etc
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option C. But biuret test is shown by compounds having amide linkages, not glycosidic linkages. Glycosidic linkage is a kind of covalent bond that joins a starch (carbohydrates) particle to some other gathering.
Complete answer: The biuret test is a synthetic test utilized for identifying the presence of peptide bonds. Within the sight of peptides, a copper(II) particle structures violet-colored coordination buildings in an alkaline solution. A few variations on the test have been grown, for example, the BCA test and the Modified Lowry test.
A. Carbohydrates are molecules consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are a significant food source and a key type of vitality for most creatures. At the point when consolidated together to shape polymers, sugars can work as long haul food storage molecules, as defensive layers for creatures and cells, and as the principal basic help for plants and constituents of numerous cells and their substance. Since there is no amide linkage in carbohydrates, they do not give this test.
B. The polypeptide chain is a chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. It can also be defined as the decoding of mRNA into proteins. As there is an amide linkage present in polypeptides so it will give biuret test.

C. Urea is an organic compound with the formulae ${ CO\left[ { NH }_{ 2 } \right] _{ 2 } }$. Urea is also an important raw material for the chemical industry.

D. Proteins: Proteins are large macromolecules consisting of one or more chains of amino acids.they have functions like growth, catalytic activity, maintenance of the human body, etc
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option C. But biuret test is shown by compounds having amide linkages, not glycosidic linkages. Glycosidic linkage is a kind of covalent bond that joins a starch (carbohydrates) particle to some other gathering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




