
Bicarpellary syncarpous ovary with axile placentation is found in
a. Solanaceae
b. Asteraceae
c. Malvaceae
d. Caesalpiniaceae
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: When there are two carpels present, it is known as bicarpellary. Gynoecium is termed syncarpous when carpels are fused. The placentation is said to be axile, when the placenta is axially placed and the ovules are attached to it in a multilocular ovary.
Complete answer:
As we know that bicarpellary means there are two carpels and when the carpels are fused, the gynoecium is termed as syncarpous.
Now, the placentation is said to be axile, when the placenta is axial and the ovules are attached to it in a multilocular ovary.
Now let us discuss each option one by one.
> First option is Solanaceae family which is also called ‘potato family’.
Gynoecium of solanaceae is bicarpellary, syncarpous; ovary superior, bilocular, placentation swollen with many ovules, obliquely placed ovaries, axile placentation.
Examples:- Tomato, Lemon

> The Asteraceae family is the daisy family.
Its gynoecium is bicarpellary, syncarpous, inferior, unilocular with single anatropous ovule, basal placentation, style simple, long, stigma bifid.
Examples:- Daisy, Sunflower
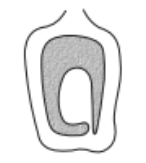
> The Malvacae family is the hibiscus family.
Its gynoecium is multicarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, multilocular with axile placentation, ovules one to many in each loculus.
Example: Hibiscus

> Caesalpiniaceae is a subfamily according to the latest classifications. It belongs to the family fabaceae. Its gynoecium is monocarpellary, ovary superior or slightly inferior, unilocular with marginal placentation.
Examples: Peacock flower, Imli
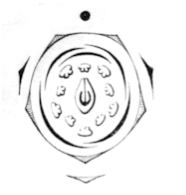
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Kindly note the slight differences among the features of gynoecium of these different families. Also the examples given are in common name so that it is more relatable. See the floral diagrams carefully to check the position of ovules and carpels.
Complete answer:
As we know that bicarpellary means there are two carpels and when the carpels are fused, the gynoecium is termed as syncarpous.
Now, the placentation is said to be axile, when the placenta is axial and the ovules are attached to it in a multilocular ovary.
Now let us discuss each option one by one.
> First option is Solanaceae family which is also called ‘potato family’.
Gynoecium of solanaceae is bicarpellary, syncarpous; ovary superior, bilocular, placentation swollen with many ovules, obliquely placed ovaries, axile placentation.
Examples:- Tomato, Lemon

> The Asteraceae family is the daisy family.
Its gynoecium is bicarpellary, syncarpous, inferior, unilocular with single anatropous ovule, basal placentation, style simple, long, stigma bifid.
Examples:- Daisy, Sunflower

> The Malvacae family is the hibiscus family.
Its gynoecium is multicarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, multilocular with axile placentation, ovules one to many in each loculus.
Example: Hibiscus

> Caesalpiniaceae is a subfamily according to the latest classifications. It belongs to the family fabaceae. Its gynoecium is monocarpellary, ovary superior or slightly inferior, unilocular with marginal placentation.
Examples: Peacock flower, Imli

Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Kindly note the slight differences among the features of gynoecium of these different families. Also the examples given are in common name so that it is more relatable. See the floral diagrams carefully to check the position of ovules and carpels.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




