
Benzyne intermediate is not observed in:


Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Before solving the problem we should know the exact structure of Benzyne. So, Benzyne is basically an unstable intermediate. It has a structure almost similar to benzene with an exception that it possesses an additional pi bond.
Complete Step by step answer:
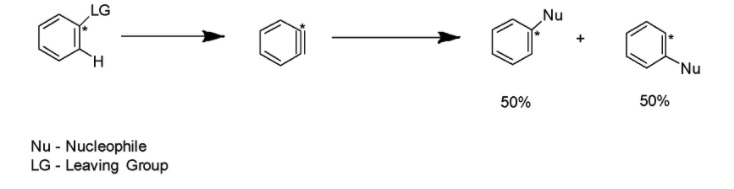
Benzyne, a very unstable intermediate, is generally attacked by the nucleophiles followed by the protonation to yield the final product. Benzyne intermediate may be attacked at any end. Thus, the characteristic loss of region-chemistry can result in the substitution. The mechanism has been mentioned below:
Now, let us discuss the occurrence of Benzyne intermediate one by one in each option given in the question. We will try to write down the possible reaction in each case.
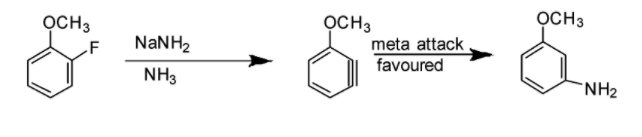
Option A: Benzyne intermediate is observed in this case as shown in the reaction below:
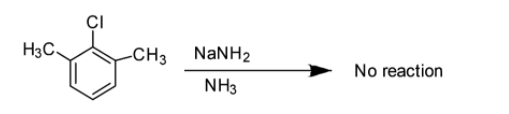
Option B: Benzyne intermediate is not observed in this case. Actually in this case ortho- positions are attached with the alkyl groups so no reaction takes place under these conditions. A hydrogen is necessarily required at least at one of these places for the reaction to take place. So, after leaving the \[Cl - \]group, Benzyne does not form owing to the absence of hydrogen atom at next carbon.
Option C: Benzyne intermediate is observed in this case as shown in the reaction below:
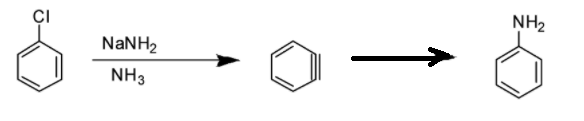
Option D: Benzyne intermediate is observed in this case as shown in the reaction below:
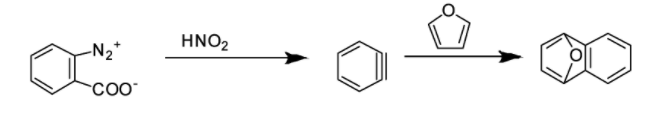
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Benzyne possesses an unstable sp2–sp2 π bent bond. It is mainly formed from the benzene and it is highly reactive. Therefore, it can never be the first or last step of the reaction. Hence, benzyne is rarely observed as a product in any reaction.

Complete Step by step answer:
Benzyne, a very unstable intermediate, is generally attacked by the nucleophiles followed by the protonation to yield the final product. Benzyne intermediate may be attacked at any end. Thus, the characteristic loss of region-chemistry can result in the substitution. The mechanism has been mentioned below:

Now, let us discuss the occurrence of Benzyne intermediate one by one in each option given in the question. We will try to write down the possible reaction in each case.
Option A: Benzyne intermediate is observed in this case as shown in the reaction below:

Option B: Benzyne intermediate is not observed in this case. Actually in this case ortho- positions are attached with the alkyl groups so no reaction takes place under these conditions. A hydrogen is necessarily required at least at one of these places for the reaction to take place. So, after leaving the \[Cl - \]group, Benzyne does not form owing to the absence of hydrogen atom at next carbon.

Option C: Benzyne intermediate is observed in this case as shown in the reaction below:

Option D: Benzyne intermediate is observed in this case as shown in the reaction below:

Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Benzyne possesses an unstable sp2–sp2 π bent bond. It is mainly formed from the benzene and it is highly reactive. Therefore, it can never be the first or last step of the reaction. Hence, benzyne is rarely observed as a product in any reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




