
Benzene reacts with \[C{H_3}COCl\] in the presence of \[AlC{l_3}\] to give
A.\[{C_6}{H_5}Cl\]
B.\[{C_6}{H_5}COCl\]
C.\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_3}\]
D.\[{C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}\]
Answer
501.9k+ views
Hint: The Friedel–Crafts acylation is a very important organic reaction of an arene with an acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides in the presence of a strong Lewis acid catalyst like anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\] . This reaction proceeds by an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction mechanism to form a monoacetylated products.
Complete answer:
Benzene is a very popular example of an arene and it will undergo Friedel-Crafts acylation when treated with acyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid such as \[AlC{l_3}\]
The mechanism of the reaction is as shown below:
The first step in this mechanism is the activation of the electrophile by using the Lewis acid. Lewis acid coordinates to the halogen in the acyl halide, and departure of the halogen as \[AlCl_4^ - \] results in the formation of a resonance-stabilized carbocation known as the “acylium ion”.
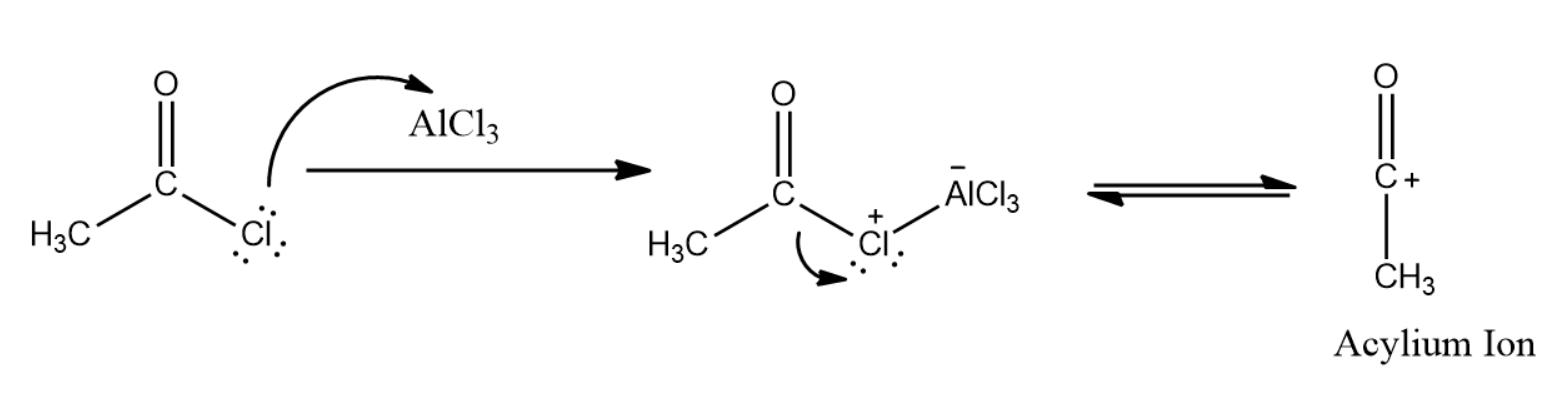
The acylium ion is the active electrophile in the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction. Once formed, the acylium ion is attacked by the aromatic ring in this case the benzene molecule. The final step of this reaction is deprotonation at carbon to regenerate the aromatic ring.
Thus the reaction can be written in general as:
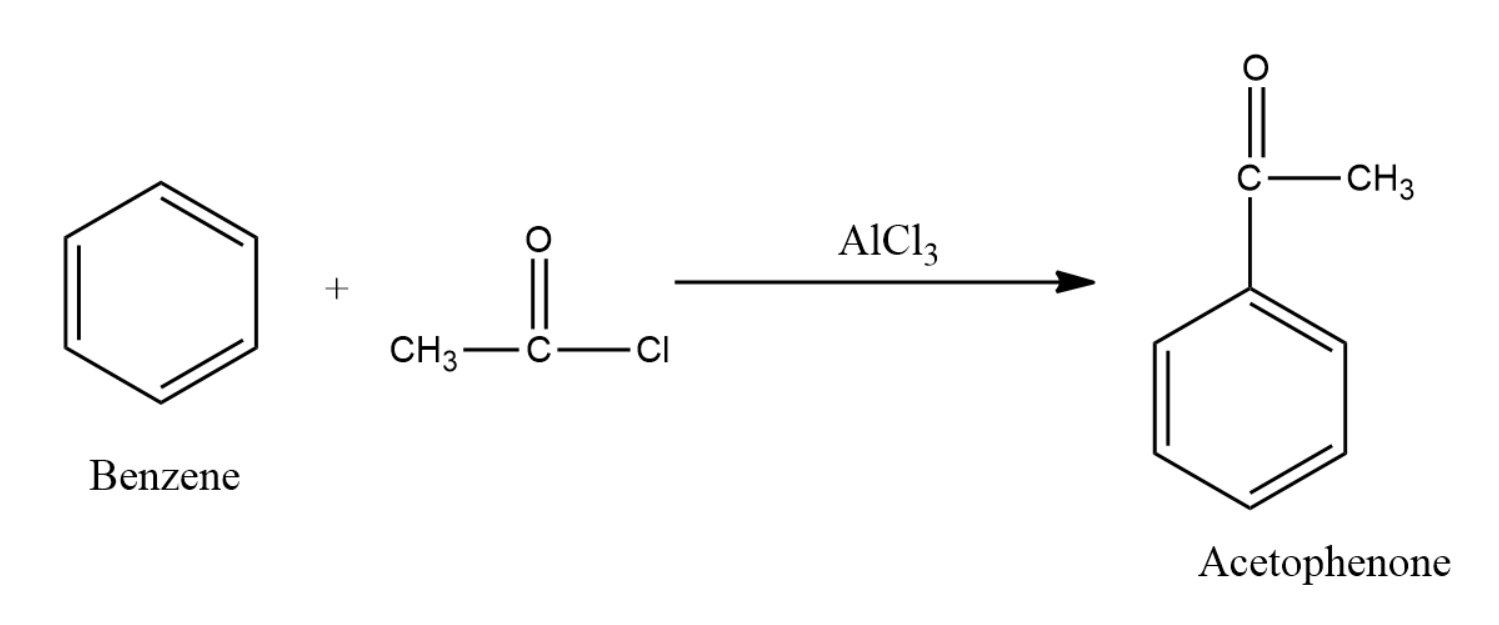
Thus the correct option is option (D) .
Note:
There is a similar reaction to acylation known as the Friedel-Crafts Alkylation. Friedel-Crafts Alkylation reaction refers to the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group by using an alkyl halide. This reaction is done through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring by the help of an alkyl carbocation. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a very useful method for generating alkyl benzenes by using alkyl halides as reactants.
Complete answer:
Benzene is a very popular example of an arene and it will undergo Friedel-Crafts acylation when treated with acyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid such as \[AlC{l_3}\]
The mechanism of the reaction is as shown below:
The first step in this mechanism is the activation of the electrophile by using the Lewis acid. Lewis acid coordinates to the halogen in the acyl halide, and departure of the halogen as \[AlCl_4^ - \] results in the formation of a resonance-stabilized carbocation known as the “acylium ion”.

The acylium ion is the active electrophile in the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction. Once formed, the acylium ion is attacked by the aromatic ring in this case the benzene molecule. The final step of this reaction is deprotonation at carbon to regenerate the aromatic ring.
Thus the reaction can be written in general as:

Thus the correct option is option (D) .
Note:
There is a similar reaction to acylation known as the Friedel-Crafts Alkylation. Friedel-Crafts Alkylation reaction refers to the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group by using an alkyl halide. This reaction is done through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring by the help of an alkyl carbocation. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a very useful method for generating alkyl benzenes by using alkyl halides as reactants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




