
Why is benzene extraordinarily stable though it contains three double bonds?
Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint: In this question we'll have to explain the stability of benzene as it contains three double bonds. As well known benzene is an organic compound and it has a molecular formula ${C_6}{H_6}$. Though it contains three double bonds and its pi electron oscillates all the time.
Complete step by step answer:
As we all know that benzene is an aromatic compound, moreover in benzene the structure represents as follows.
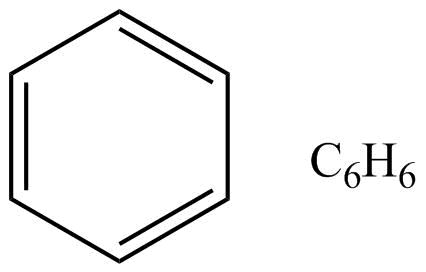
The stability in benzene is due to delocalization of electrons and its resonance effect also. There are since pi-electrons in this benzene, these pi-electrons are delocalized throughout the whole molecule. So well can draw the structure like this also,
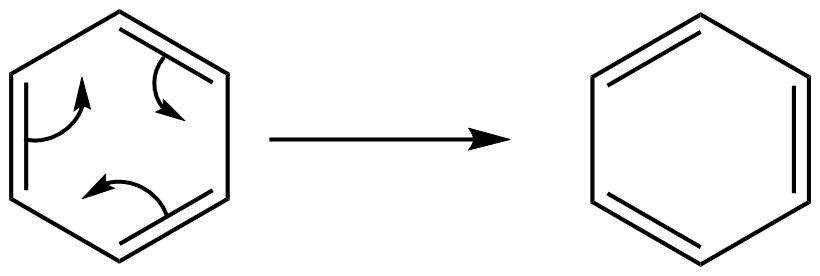
That’s why sometime we draw the structure of benzene as follows:
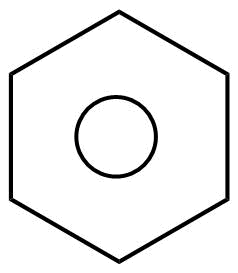
So, basically benzene is more stable due to the resonance effect as it is a resonance hybrid of two canonical forms. Therefore, all the six electrons are completely delocalized. This results in resonance stabilization as they are completely delocalized just to form one lowest energy molecular orbital which then surrounds all the carbon atoms of the ring.
The presence of three double bonds does not make the benzene stable, it is stable because of the three double bonds that are actually delocalized pi-electrons that are found to be in resonance. The bonds are not fixed like a normal double bond, they move around the structure to create several resonating structures. As you know, more the number of resonating structures, more will be the stability.
Note: Benzene is more stable than cyclohexane. The reason is (alternative single and double bonds) cyclic conjugated dienes are more stable due to resonance whereas cyclohexane is not stabilized by resonance due to which it is less stable. Moreover, with two benzene, the resulting molecule is aromatic.
Complete step by step answer:
As we all know that benzene is an aromatic compound, moreover in benzene the structure represents as follows.

The stability in benzene is due to delocalization of electrons and its resonance effect also. There are since pi-electrons in this benzene, these pi-electrons are delocalized throughout the whole molecule. So well can draw the structure like this also,

That’s why sometime we draw the structure of benzene as follows:

So, basically benzene is more stable due to the resonance effect as it is a resonance hybrid of two canonical forms. Therefore, all the six electrons are completely delocalized. This results in resonance stabilization as they are completely delocalized just to form one lowest energy molecular orbital which then surrounds all the carbon atoms of the ring.
The presence of three double bonds does not make the benzene stable, it is stable because of the three double bonds that are actually delocalized pi-electrons that are found to be in resonance. The bonds are not fixed like a normal double bond, they move around the structure to create several resonating structures. As you know, more the number of resonating structures, more will be the stability.
Note: Benzene is more stable than cyclohexane. The reason is (alternative single and double bonds) cyclic conjugated dienes are more stable due to resonance whereas cyclohexane is not stabilized by resonance due to which it is less stable. Moreover, with two benzene, the resulting molecule is aromatic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




