
Basically the product modulator is
A. An amplifier
B. A mixer
C. A frequency separator
D. A phase separator
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Carrier wave has constant frequency like sine wave and we vary characteristics of this carrier wave by overlapping modulating waves(message signal) on it. This process is called modulation and a modulated wave is produced from the transmitter and received on receiver’s side by receiver and demodulated there to get the original message signal. The device which does modulation is modulator.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand the actual meaning of modulation let us consider the simple instance which we use in our daily life. If one wants to throw a piece of paper through a very long distance it's not possible if we just throw that paper, we fold that paper to some weight, let it be a stone and throw that paper folded stone. Then that paper can reach very longer distances. Similarly in communication systems modulation plays a key role. Here the message signal which we like to transmit is analogous to paper and the carrier signal is analogous to stone and the person who throws paper is analogous to the transmitter.
Carrier wave has a constant frequency like sine wave and we vary the characteristics of this carrier wave by overlapping the modulating wave(message signal) on it. This process is called modulation and a modulated wave is produced from the transmitter and received on receiver’s side by receiver and demodulated there to get the original message signal.
Three important factors that justify the need of modulation are
a. Actual antenna/aerial size
b. Effective power which is radiated by antenna
c. Signals from different transmitters getting mixed up
a. Actual antenna size: In case of transmission systems antenna size matters. Generally bigger size antennas have big range but bigger antennas might not be always optimal while it depends on transmission frequencies too. Low frequency signal requires bigger antennas but after modulation frequency of message signal gets increased which allows us to use smaller antennas.
b. Effective power which is radiated by antenna: when frequency is increased its wavelength decreases which inturn increases the radiated power.
c. Signals from different transmitters getting mixed up: signals getting mixed up causes signal interference which causes deviation In original waveform. The process of nullification of this interference is done by modulation.
Carrier wave
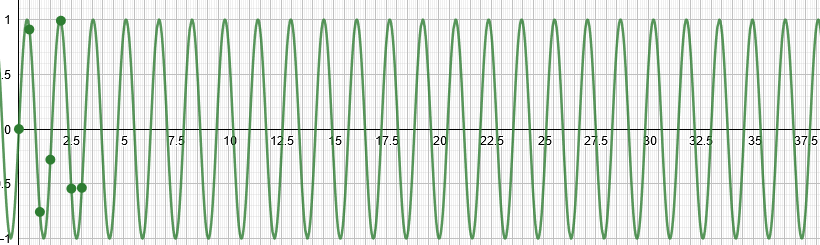
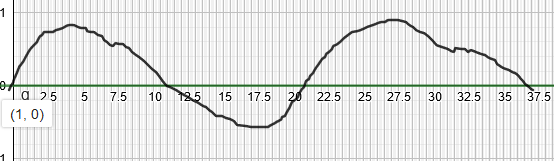
Modulator wave
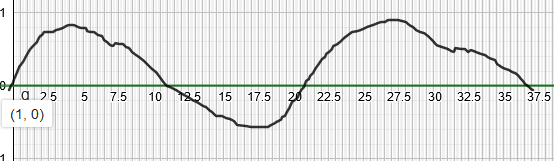
Resultant superposed EM wave
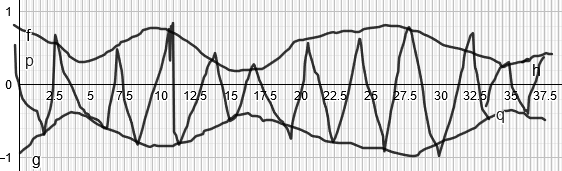
Hence a product modulator is basically a device which mixes message signal with carrier signal.
Note:
The common misconception is if we use bigger size antennas we can get bigger ranges and hence maximum optimal output. But this is not true. Bigger is not always better. Size of the antenna depends upon the frequency of the signal to be transmitted too. This mixing is necessary for long distance carrying of messages.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand the actual meaning of modulation let us consider the simple instance which we use in our daily life. If one wants to throw a piece of paper through a very long distance it's not possible if we just throw that paper, we fold that paper to some weight, let it be a stone and throw that paper folded stone. Then that paper can reach very longer distances. Similarly in communication systems modulation plays a key role. Here the message signal which we like to transmit is analogous to paper and the carrier signal is analogous to stone and the person who throws paper is analogous to the transmitter.
Carrier wave has a constant frequency like sine wave and we vary the characteristics of this carrier wave by overlapping the modulating wave(message signal) on it. This process is called modulation and a modulated wave is produced from the transmitter and received on receiver’s side by receiver and demodulated there to get the original message signal.
Three important factors that justify the need of modulation are
a. Actual antenna/aerial size
b. Effective power which is radiated by antenna
c. Signals from different transmitters getting mixed up
a. Actual antenna size: In case of transmission systems antenna size matters. Generally bigger size antennas have big range but bigger antennas might not be always optimal while it depends on transmission frequencies too. Low frequency signal requires bigger antennas but after modulation frequency of message signal gets increased which allows us to use smaller antennas.
b. Effective power which is radiated by antenna: when frequency is increased its wavelength decreases which inturn increases the radiated power.
c. Signals from different transmitters getting mixed up: signals getting mixed up causes signal interference which causes deviation In original waveform. The process of nullification of this interference is done by modulation.
Carrier wave


Modulator wave

Resultant superposed EM wave

Hence a product modulator is basically a device which mixes message signal with carrier signal.
Note:
The common misconception is if we use bigger size antennas we can get bigger ranges and hence maximum optimal output. But this is not true. Bigger is not always better. Size of the antenna depends upon the frequency of the signal to be transmitted too. This mixing is necessary for long distance carrying of messages.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




