
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Both starch and cellulose are polysaccharides, i.e., they are formed when the monosaccharide monomer molecules are joined together by glycosidic linkages.
-Both starch and cellulose have the general molecular formula of ${\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}} \right)_{\text{n}}}$ where the value of n ranges from 200 to 1000 in case of starch and from 300 to 3000 in case of cellulose.
Complete step by step answer:
Starch is actually a mixture of two components: amylose which is water soluble and amylopectin which is water insoluble. Both amylose and amylopectin are polymers of ${{\alpha }}$ -D-glucose. A molecule of amylose contains 200 to 1000 glucose units and a molecule of amylopectin contains 2000 to 3000 glucose units.
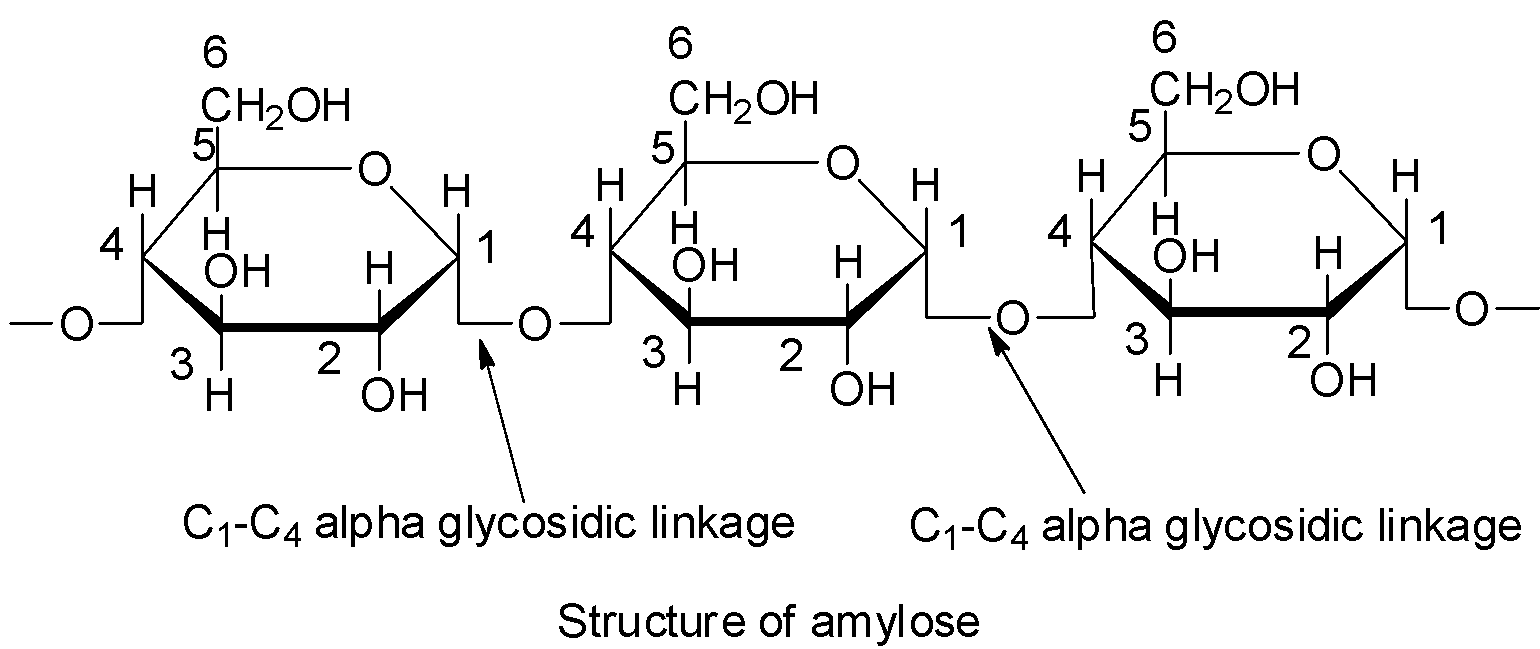
Structure of amylose: Amylose is a linear polymer of ${{\alpha }}$ -D-glucose in which ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of one glucose unit is linked to ${{\text{C}}_4}$of the other glucose unit through an ${{\alpha }}$-glycosidic linkage.
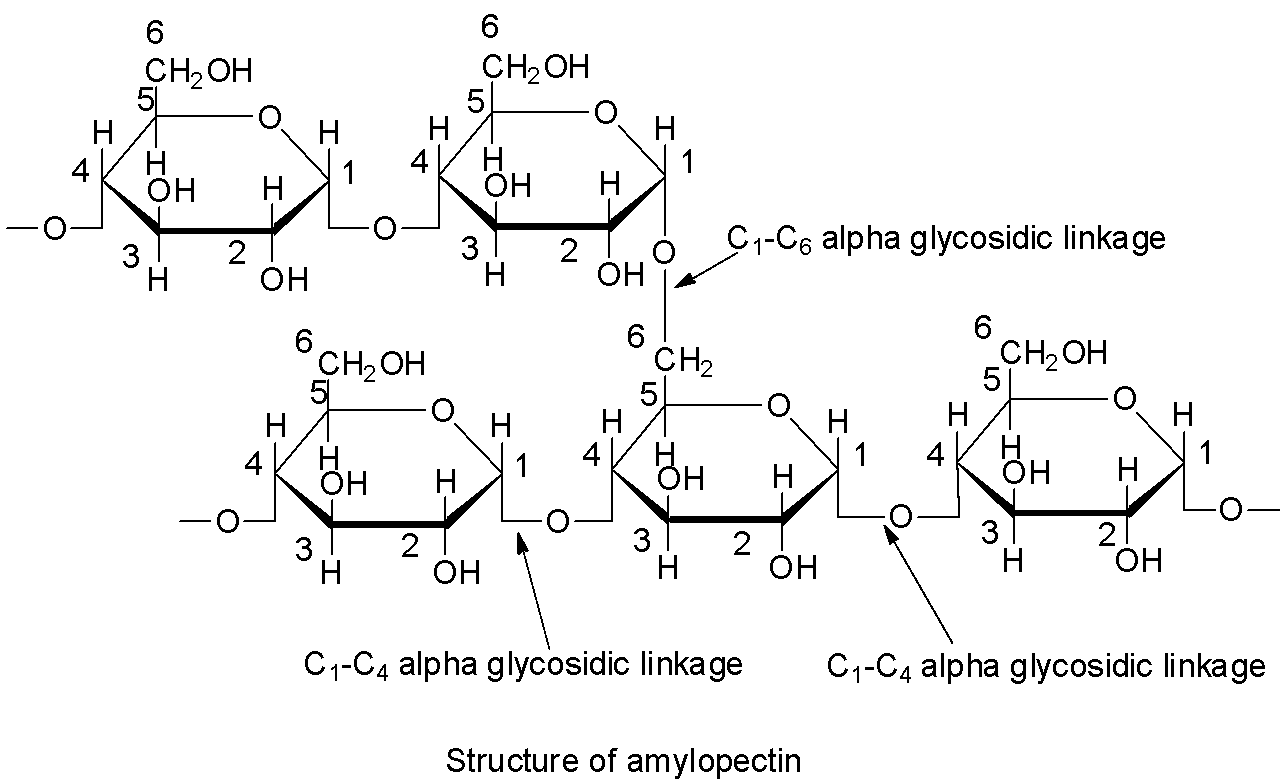
Structure of amylopectin: Amylopectin is a highly branched polymer of ${{\alpha }}$ -D-glucose. Amylopectin consists of a huge number of short chains each of which contains 20 to 25 glucose units which are joined together by ${{\alpha }}$-glycosidic linkages involving ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of one glucose unit with ${{\text{C}}_4}$of the other. The ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of terminal glucose unit of each chain is further linked to ${{\text{C}}_6}$ of some other glucose unit of the next chain by ${{\text{C}}_1}{\text{ - }}{{\text{C}}_6}$ ${{\alpha }}$-glycosidic linkage.
On the other hand, cellulose is a linear polymer of ${{\beta }}$ -D-glucose in which ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of one glucose unit is linked to ${{\text{C}}_4}$ of the other glucose unit through a ${{\beta }}$-glycosidic linkage. From X-ray analysis, it has been confirmed that cellulose is made up of several long linear chains and these chains lie side by side to form bundles held together by hydrogen bonding.

Note:
-Starch acts as the major source of food material for us. It is hydrolysed by the enzyme amylase in saliva. The end product of this hydrolysis is glucose which is a very essential nutrient.
-Cellulose is considered as the chief structural material of cell walls of all plants. Due to its linear structure, cellulose is easily converted into fibres.
-Both starch and cellulose have the general molecular formula of ${\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}} \right)_{\text{n}}}$ where the value of n ranges from 200 to 1000 in case of starch and from 300 to 3000 in case of cellulose.
Complete step by step answer:
Starch is actually a mixture of two components: amylose which is water soluble and amylopectin which is water insoluble. Both amylose and amylopectin are polymers of ${{\alpha }}$ -D-glucose. A molecule of amylose contains 200 to 1000 glucose units and a molecule of amylopectin contains 2000 to 3000 glucose units.
Structure of amylose: Amylose is a linear polymer of ${{\alpha }}$ -D-glucose in which ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of one glucose unit is linked to ${{\text{C}}_4}$of the other glucose unit through an ${{\alpha }}$-glycosidic linkage.

Structure of amylopectin: Amylopectin is a highly branched polymer of ${{\alpha }}$ -D-glucose. Amylopectin consists of a huge number of short chains each of which contains 20 to 25 glucose units which are joined together by ${{\alpha }}$-glycosidic linkages involving ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of one glucose unit with ${{\text{C}}_4}$of the other. The ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of terminal glucose unit of each chain is further linked to ${{\text{C}}_6}$ of some other glucose unit of the next chain by ${{\text{C}}_1}{\text{ - }}{{\text{C}}_6}$ ${{\alpha }}$-glycosidic linkage.

On the other hand, cellulose is a linear polymer of ${{\beta }}$ -D-glucose in which ${{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}$ of one glucose unit is linked to ${{\text{C}}_4}$ of the other glucose unit through a ${{\beta }}$-glycosidic linkage. From X-ray analysis, it has been confirmed that cellulose is made up of several long linear chains and these chains lie side by side to form bundles held together by hydrogen bonding.

Note:
-Starch acts as the major source of food material for us. It is hydrolysed by the enzyme amylase in saliva. The end product of this hydrolysis is glucose which is a very essential nutrient.
-Cellulose is considered as the chief structural material of cell walls of all plants. Due to its linear structure, cellulose is easily converted into fibres.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




