
Axile placentation occurs in
(a) Asteraceae and Fabaceae
(b) Brassicaceae and Solanaceae
(c) Solanaceae and Liliaceae
(d) None of the above
Answer
545.1k+ views
Hint: Axile placentation is found in a large family, commonly called a potato family. It shows the presence of a swollen placenta. They play an important role in the production of medicines and herbs. It is a common characteristic representative of the monocotyledonous family.
Complete answer:
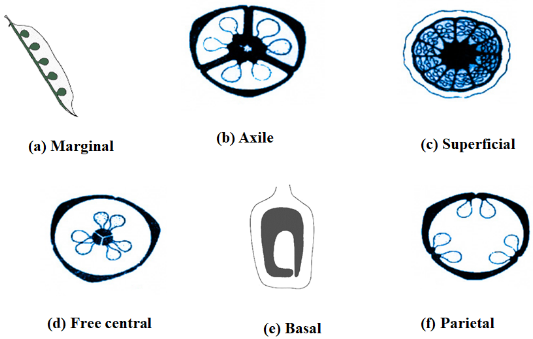
Placentation refers to the arrangement of ovules within the ovary. Ovules are attached to ovarian walls through the placenta. Axile placentation is commonly seen in Solanaceae, Rutaceae, Liliaceae. In bicarpellary to multicarpellary the axile placentation is present, syncarpous ovary, the carpels fuse to make septa forming a central axis and ovules are arranged on the axis.
-Basal: The placenta is found in mono to multicarpellary, syncarpous ovary. Usually, at the base, a single ovule is attached. E.g.: Helianthus.
-Parietal: It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The unilocular ovary becomes bilocular due to the formation of the false septum. E.g.: Cucumber.
-Free central: It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Ovules are found on the central axis in unilocular condition after the false septum degrades. E.g.: Dianthus, Primula (primroses)
-Marginal: This type of placentation is found in the monocarpellary unilocular ovary, the placenta forms a rigid along ventral side, and ovules are arranged in two vertical rows. E.g.: Pisum sativum (pea).
-In axile placentation, the carpels are folded inward with ovules placed along the central axis of the ovary. e.g., tomato, lemon.
-It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary.
-The placenta is axial and the ovules are formed at the angles where the septa join the central placenta.
So, the correct answer is “Solanaceae and Liliaceae”.
Note:
In axile placentation, the carpels are folded inward with ovules placed along the central axis of the ovary. e.g., tomato, lemon. It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The placenta is axial and the ovules are formed at the angles where the septa join the central placenta.
Complete answer:
Placentation refers to the arrangement of ovules within the ovary. Ovules are attached to ovarian walls through the placenta. Axile placentation is commonly seen in Solanaceae, Rutaceae, Liliaceae. In bicarpellary to multicarpellary the axile placentation is present, syncarpous ovary, the carpels fuse to make septa forming a central axis and ovules are arranged on the axis.
-Basal: The placenta is found in mono to multicarpellary, syncarpous ovary. Usually, at the base, a single ovule is attached. E.g.: Helianthus.
-Parietal: It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The unilocular ovary becomes bilocular due to the formation of the false septum. E.g.: Cucumber.
-Free central: It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Ovules are found on the central axis in unilocular condition after the false septum degrades. E.g.: Dianthus, Primula (primroses)
-Marginal: This type of placentation is found in the monocarpellary unilocular ovary, the placenta forms a rigid along ventral side, and ovules are arranged in two vertical rows. E.g.: Pisum sativum (pea).
-In axile placentation, the carpels are folded inward with ovules placed along the central axis of the ovary. e.g., tomato, lemon.
-It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary.
-The placenta is axial and the ovules are formed at the angles where the septa join the central placenta.
So, the correct answer is “Solanaceae and Liliaceae”.
Note:
In axile placentation, the carpels are folded inward with ovules placed along the central axis of the ovary. e.g., tomato, lemon. It is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The placenta is axial and the ovules are formed at the angles where the septa join the central placenta.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




