
How is average rate of change related to slope?
Answer
559.8k+ views
Hint: Slope is just a way of measuring the inclination of a line or the steepness of the line. It is defined by, change in $y$ due to the change in x. The average rate of change about a point as the interval over which the average is being taken is reduced to zero.
Average rate of change \[ = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
$({x_1},{y_1})$ - coordinates of first point in the line
\[({x_2},{y_2})\] - coordinates of second point in the line
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let’s assume the coordinates of those points as follows:
${x_1}$ coordinate is $ - 1$ and $x_2^{}$ coordinate is $3$
${y_1}$ coordinate is $ - 6$ and ${y_2}$ coordinate is $6$
Let us consider the two points ${\text{ (}} - 1, - 6{\text{) and }}(3,6){\text{ }}$
Average rate of change \[ = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
${x_1} = - 1$ and ${x_2} = 3$
${y_1} = - 6$ and ${y_2} = 6$
Now, substitute the two points in the formula of average rate of change
Average rate of change $ = \dfrac{{6 - ( - 6)}}{{3 - ( - 1)}}$
Adding the two terms,
$ = \dfrac{{6 + 6}}{{3 + 1}} = \dfrac{{12}}{4}$
Simplifying the terms,
$ = \dfrac{{12}}{4} = 3$
Average rate of change $ = 3$
Slope is calculated by finding the ratio of the vertical change to horizontal change between two distinct points on a line. The coordinates points to point a graph. And then to draw a straight line through the two points. Slope is something also referred to as the rate of change.
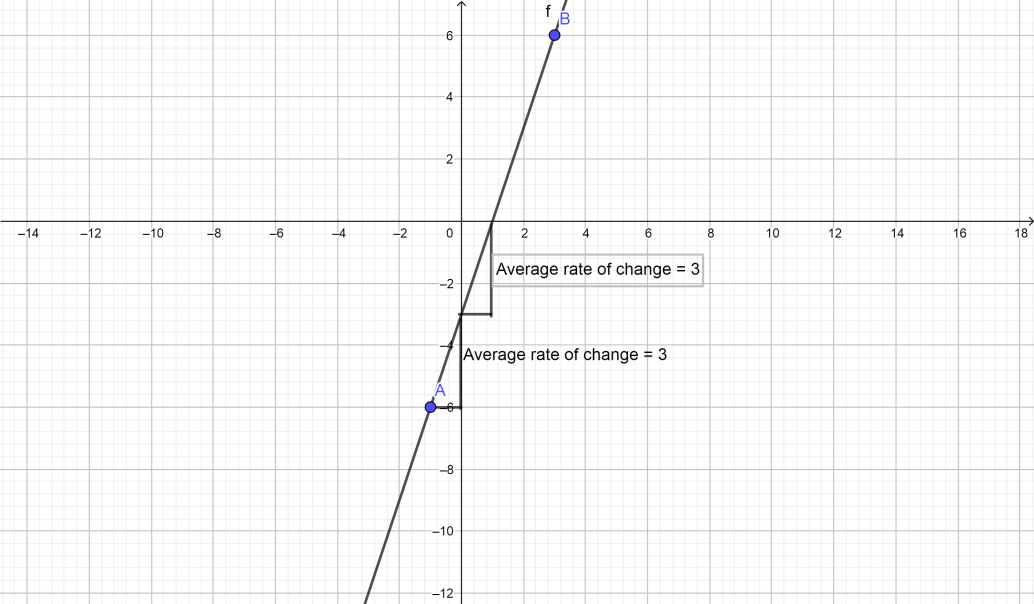
When we moved $1$ in the $x$ , we moved up $3$ in the $y$ . If you move 2 in the $x - $ direction, you’re going to move $6$ in the $y$. $6/2$ is the same thing as $3$ . This is the average rate of change between two points.
Note: The rate of change between two points on either side of x becomes closer to the slope of x as the distance between the two points is reduced. When we work with functions, the average rate of change is expressed using function notation.
For the function is,
\[\operatorname{y} = f(x)\] , where $\operatorname{x} = a$ and $\operatorname{x} = b$
Average rate of change $ = \dfrac{{{\text{change in }}y}}{{{\text{change in }}x}} = \dfrac{{f(b) - f(a)}}{{b - a}}$
Average rate of change \[ = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
$({x_1},{y_1})$ - coordinates of first point in the line
\[({x_2},{y_2})\] - coordinates of second point in the line
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let’s assume the coordinates of those points as follows:
${x_1}$ coordinate is $ - 1$ and $x_2^{}$ coordinate is $3$
${y_1}$ coordinate is $ - 6$ and ${y_2}$ coordinate is $6$
Let us consider the two points ${\text{ (}} - 1, - 6{\text{) and }}(3,6){\text{ }}$
Average rate of change \[ = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
${x_1} = - 1$ and ${x_2} = 3$
${y_1} = - 6$ and ${y_2} = 6$
Now, substitute the two points in the formula of average rate of change
Average rate of change $ = \dfrac{{6 - ( - 6)}}{{3 - ( - 1)}}$
Adding the two terms,
$ = \dfrac{{6 + 6}}{{3 + 1}} = \dfrac{{12}}{4}$
Simplifying the terms,
$ = \dfrac{{12}}{4} = 3$
Average rate of change $ = 3$
Slope is calculated by finding the ratio of the vertical change to horizontal change between two distinct points on a line. The coordinates points to point a graph. And then to draw a straight line through the two points. Slope is something also referred to as the rate of change.

When we moved $1$ in the $x$ , we moved up $3$ in the $y$ . If you move 2 in the $x - $ direction, you’re going to move $6$ in the $y$. $6/2$ is the same thing as $3$ . This is the average rate of change between two points.
Note: The rate of change between two points on either side of x becomes closer to the slope of x as the distance between the two points is reduced. When we work with functions, the average rate of change is expressed using function notation.
For the function is,
\[\operatorname{y} = f(x)\] , where $\operatorname{x} = a$ and $\operatorname{x} = b$
Average rate of change $ = \dfrac{{{\text{change in }}y}}{{{\text{change in }}x}} = \dfrac{{f(b) - f(a)}}{{b - a}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




