
ATP is composed of a nitrogenous base, a sugar and how many phosphates?
Answer
534k+ views
Hint :ATP is called the energy currency of the cell. It is generated by the metabolic activities carrying out in our body like respiration. It is used for transferring energy in the cell. It stands for Adenosine triphosphate.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To solve this question, we must know about the structure of ATP.
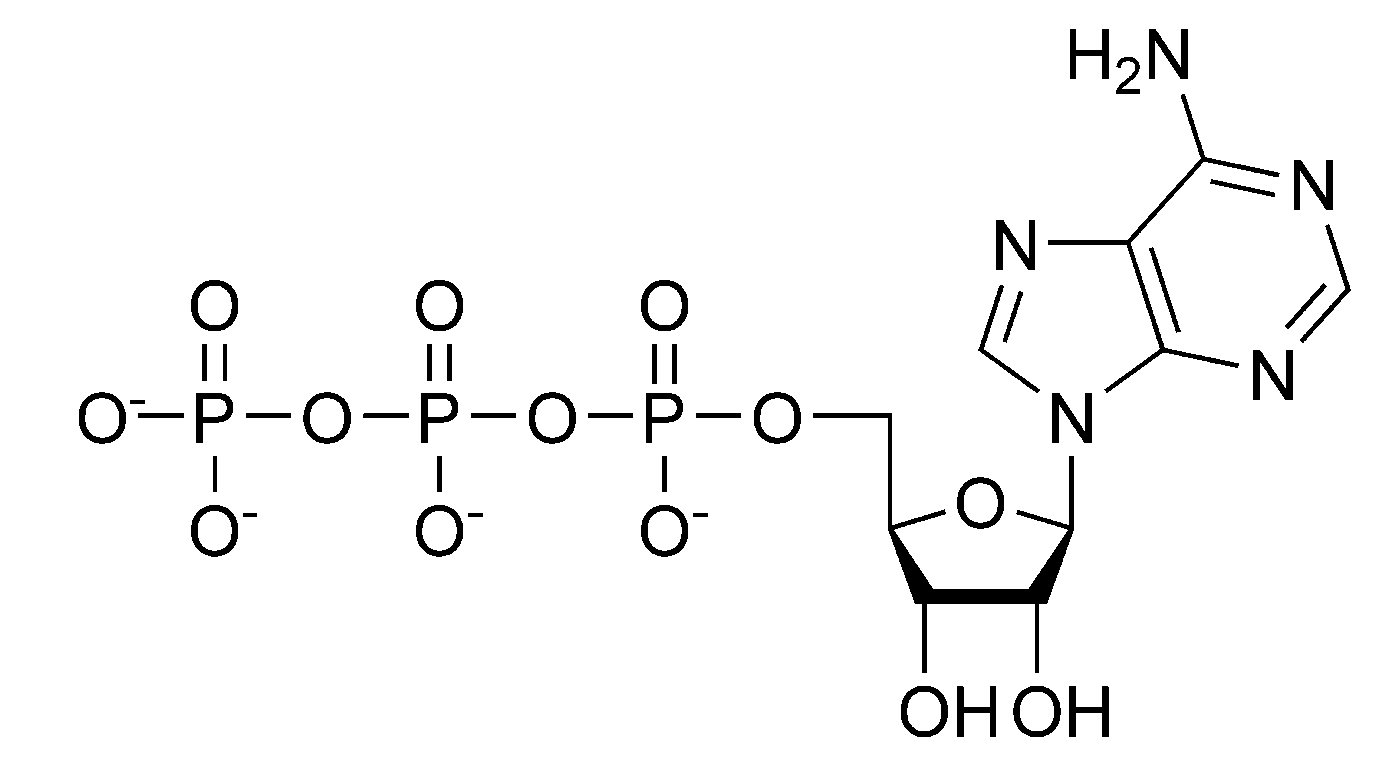
ATP or the Adenosine triphosphate is the most important energy supplying molecule in the living cell. It is made up of a nucleotide called the adenosine, a five-carbon sugar and three phosphate groups. The phosphates are connected through phosphor-anhydride bonds which have a very high energy content. The phosphate group forms the tail of ATP.
Structure of ATP- It consists of adenine which is attached by a 9-nitrogen atom to the 1’carbon atom of a ribose sugar. This is attached at the 5’ carbon atom of the ribose sugar to the three-phosphate group. The three-phosphoryl group is called alpha, beta and gamma. These tail phosphoryl groups help in the transfer of energy.
Properties of ATP:
It is stable in aqueous solution. The optimum pH under which ATP is stable is 6.8 and 7.4. Extreme pH hydrolyses ATP to ADP and phosphate. The bond P-O-P is the high energy bond.
Note :
ATP is important for carrying out various physiological functions like in signal transduction, amino acid synthesis and activation, DNA and RNA synthesis, in neurotransmission, transport of polar molecules etc. ATP also acts as a precursor to DNA and RNA. It is also used as a coenzyme.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To solve this question, we must know about the structure of ATP.
ATP or the Adenosine triphosphate is the most important energy supplying molecule in the living cell. It is made up of a nucleotide called the adenosine, a five-carbon sugar and three phosphate groups. The phosphates are connected through phosphor-anhydride bonds which have a very high energy content. The phosphate group forms the tail of ATP.
Structure of ATP- It consists of adenine which is attached by a 9-nitrogen atom to the 1’carbon atom of a ribose sugar. This is attached at the 5’ carbon atom of the ribose sugar to the three-phosphate group. The three-phosphoryl group is called alpha, beta and gamma. These tail phosphoryl groups help in the transfer of energy.

Properties of ATP:
It is stable in aqueous solution. The optimum pH under which ATP is stable is 6.8 and 7.4. Extreme pH hydrolyses ATP to ADP and phosphate. The bond P-O-P is the high energy bond.
Note :
ATP is important for carrying out various physiological functions like in signal transduction, amino acid synthesis and activation, DNA and RNA synthesis, in neurotransmission, transport of polar molecules etc. ATP also acts as a precursor to DNA and RNA. It is also used as a coenzyme.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




