
Why is ATP called the energy currency of cells?
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint:- All living beings need energy to carry out physiological processes of the body, to move and to carry out daily tasks. Energy is the fuel required by the body. Living organisms derive energy for their regular energy expense from a compound called ATP.
Complete step-by-step solution:-
Adenosine Triphosphate, abbreviated as ATP, is an organic compound. It is composed of three phosphate bonds, a sugar called ribose and a base called adenine. The three phosphate bonds are connected to one another by two phosphoanhydride bonds. The bonds are very high energy bonds. ATP is formed when Adenosine Diphosphate reacts with inorganic phosphate in presence of an enzyme ATP Synthase. The formation of ATP takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. ATP can also be formed when Adenosine Monophosphate or AMP reacts with two molecules of inorganic phosphate. ATP, ADP and AMP are constantly working either to make or break phosphate bonds. In this process, energy is either stored or released in a cell.
When ATP combines with any phosphate group, energy is stored within the bonds. The reaction is an endothermic one. On the other hand, when a phosphate bond in ATP energy is liberated and the reaction involved is exothermic.
ATP is used in various functions of the body. Every biochemical or physiological process of the body requires involvement of ATP. For example, transportation cell division, respiration, photosynthesis are a few processes that require ATP. It is required for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Physical movements of the body also need ATP derived energy.
Therefore, to conclude ATP is the primary molecule involved with storage and transfer of energy. It can be used to store energy for future use or can be used in terms of energy need. Therefore, it can be compared to the function of a bank. Hence, ATP is known as the ‘energy currency’ of cells.
Adenosine Triphosphate, abbreviated as ATP, is an organic compound. It is composed of three phosphate bonds, a sugar called ribose and a base called adenine. The three phosphate bonds are connected to one another by two phosphoanhydride bonds. The bonds are very high energy bonds. ATP is formed when Adenosine Diphosphate reacts with inorganic phosphate in presence of an enzyme ATP Synthase. The formation of ATP takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. ATP can also be formed when Adenosine Monophosphate or AMP reacts with two molecules of inorganic phosphate. ATP, ADP and AMP are constantly working either to make or break phosphate bonds. In this process, energy is either stored or released in a cell.
When ATP combines with any phosphate group, energy is stored within the bonds. The reaction is an endothermic one. On the other hand, when a phosphate bond in ATP energy is liberated and the reaction involved is exothermic.
ATP is used in various functions of the body. Every biochemical or physiological process of the body requires involvement of ATP. For example, transportation cell division, respiration, photosynthesis are a few processes that require ATP. It is required for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Physical movements of the body also need ATP derived energy.
Therefore, to conclude ATP is the primary molecule involved with storage and transfer of energy. It can be used to store energy for future use or can be used in terms of energy need. Therefore, it can be compared to the function of a bank. Hence, ATP is known as the ‘energy currency’ of cells.
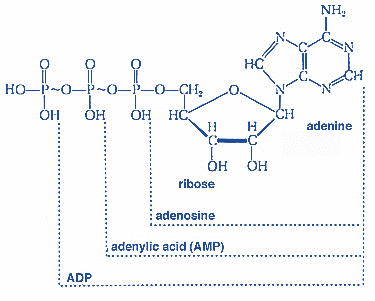
Fig: Structure of ATP, ADP and AMP
Fig: Structure of ATP, ADP and AMP
Note:- ATP is the primary source of energy in our body. ATP can be recycled. It can be used for both endothermic and exothermic processes. Microorganisms also use ATP for their energy needs. In animals, plants and humans ATP is produced in the mitochondria and is indispensable to bodily functions. Thus, ATP is rightly known as the ’energy currency’ of the cell.
Complete step-by-step solution:-
Adenosine Triphosphate, abbreviated as ATP, is an organic compound. It is composed of three phosphate bonds, a sugar called ribose and a base called adenine. The three phosphate bonds are connected to one another by two phosphoanhydride bonds. The bonds are very high energy bonds. ATP is formed when Adenosine Diphosphate reacts with inorganic phosphate in presence of an enzyme ATP Synthase. The formation of ATP takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. ATP can also be formed when Adenosine Monophosphate or AMP reacts with two molecules of inorganic phosphate. ATP, ADP and AMP are constantly working either to make or break phosphate bonds. In this process, energy is either stored or released in a cell.
When ATP combines with any phosphate group, energy is stored within the bonds. The reaction is an endothermic one. On the other hand, when a phosphate bond in ATP energy is liberated and the reaction involved is exothermic.
ATP is used in various functions of the body. Every biochemical or physiological process of the body requires involvement of ATP. For example, transportation cell division, respiration, photosynthesis are a few processes that require ATP. It is required for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Physical movements of the body also need ATP derived energy.
Therefore, to conclude ATP is the primary molecule involved with storage and transfer of energy. It can be used to store energy for future use or can be used in terms of energy need. Therefore, it can be compared to the function of a bank. Hence, ATP is known as the ‘energy currency’ of cells.
Adenosine Triphosphate, abbreviated as ATP, is an organic compound. It is composed of three phosphate bonds, a sugar called ribose and a base called adenine. The three phosphate bonds are connected to one another by two phosphoanhydride bonds. The bonds are very high energy bonds. ATP is formed when Adenosine Diphosphate reacts with inorganic phosphate in presence of an enzyme ATP Synthase. The formation of ATP takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. ATP can also be formed when Adenosine Monophosphate or AMP reacts with two molecules of inorganic phosphate. ATP, ADP and AMP are constantly working either to make or break phosphate bonds. In this process, energy is either stored or released in a cell.
When ATP combines with any phosphate group, energy is stored within the bonds. The reaction is an endothermic one. On the other hand, when a phosphate bond in ATP energy is liberated and the reaction involved is exothermic.
ATP is used in various functions of the body. Every biochemical or physiological process of the body requires involvement of ATP. For example, transportation cell division, respiration, photosynthesis are a few processes that require ATP. It is required for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Physical movements of the body also need ATP derived energy.
Therefore, to conclude ATP is the primary molecule involved with storage and transfer of energy. It can be used to store energy for future use or can be used in terms of energy need. Therefore, it can be compared to the function of a bank. Hence, ATP is known as the ‘energy currency’ of cells.

Fig: Structure of ATP, ADP and AMP
Fig: Structure of ATP, ADP and AMP
Note:- ATP is the primary source of energy in our body. ATP can be recycled. It can be used for both endothermic and exothermic processes. Microorganisms also use ATP for their energy needs. In animals, plants and humans ATP is produced in the mitochondria and is indispensable to bodily functions. Thus, ATP is rightly known as the ’energy currency’ of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




