
At time $ t = 0 $ , terminal A in the circuit shown in the figure is connected to B by a key and an alternating current $ I\left( t \right) = {I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right) $ , with $ {I_o} = 1A $ and $ \omega = 500rad/s $ starts flowing in it with the initial direction shown in the figure. At $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ , the key is switched from B to D. Now onwards only A and D are connected. A total charge $ Q $ flows from the battery to charge the capacitor fully. If $ C = 20\mu F $ , $ R = 10\Omega $ and the battery is ideal with emf of $ 50V $ , identify the correct statement(s).

(A) Magnitude of maximum charge on the capacitor before $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ is $ 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
(B) The current in the left part of the circuit just before $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ is clockwise.
(C) Immediately after A is connected to D the current in $ R $ is $ 10A $
(D) $ Q = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint In this circuit, for the first half, the current in the circuit will be the derivative of the charge across the capacitor. From there by integrating we get the charge across the capacitor at the time $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ . The current in the left part of the circuit is found by substituting $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ in $ I\left( t \right) = {I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right) $ . Next, we can find the current in the resistor by using the Kirchhoff’s current law in the second circuit and the value of $ Q $ will be the difference between the final charge across the capacitor and the charge at $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ . From there we can find the correct statements.
Formula Used: In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow q = CV $
where $ q $ is charge across capacitors, $ V $ is the potential across the capacitor and $ C $ is the capacitance of the capacitor.
Complete step by step answer
To find the correct statements, let us first consider the initial circuit where the connection is between A and B. Here we can see that a capacitor is connected across the source. Let the current flowing in the circuit be $ I $ . So we can write this current as,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} $
where $ q $ is the charge across the capacitor.
Now in the question we are given $ I\left( t \right) = {I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right) $ . So substituting and bringing $ dt $ to the other side,
$\Rightarrow dq = \left[ {{I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right)} \right]dt $
Now we can integrate on both the sides. The limit for the charge will be from zero to $ q $ and time will be from zero to $ t $
Therefore, we get the equation as,
$\Rightarrow \int\limits_0^q {dq} = \int\limits_0^t {\left[ {{I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right)} \right]dt} $
So we get,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{{{I_o}}}{\omega }\left. {\sin \left( {\omega t} \right)} \right|_0^t $
Substituting the limits we get,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{{{I_o}}}{\omega }\sin \left( {\omega t} \right) $
Hence on substituting the values $ {I_o} = 1A $ , $ \omega = 500rad/s $ ,and for the maximum value of the charge, the value of $ \sin \left( {\omega t} \right) $ has to be 1, therefore we have,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{1}{{500}}C $
So we get the charge as, $ q = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $ .Therefore, option A is incorrect.
Now the current in the circuit will be $ I\left( t \right) = {I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right) $ . Here we substitute $ {I_o} = 1A $ and $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ . So we get,
$\Rightarrow I\left( t \right) = 1 \times \cos \left( {\omega \times \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }}} \right) $
Hence we have,
$\Rightarrow I\left( t \right) = \cos \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $
Now the value of $ \cos \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $ is $ - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} $
So the current is $ I\left( t \right) = - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} $
In the figure we are given the clockwise direction for the positive cycle of the current. So the negative sign shows that the current is moving in an anticlockwise direction. So option B is incorrect.
Now for the second circuit, the connection is made across A and D.
The capacitor is having a charge given by, $ q = CV $
We have, $ q = \dfrac{{{I_o}}}{\omega }\sin \left( {\omega t} \right) $ where $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ , $ {I_o} = 1A $ and $ \omega = 500rad/s $
Substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{1}{{500}} \times \sin \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $
The value of $ \sin \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $ is $ - \dfrac{1}{2} $
So we get,
$\Rightarrow q = - \dfrac{1}{{500 \times 2}} $
Hence the charge is $ q = - {10^{ - 3}}C $
The capacitance of the capacitor is given $ C = 20\mu F $ . So substituting in $ q = CV $ we get the potential as, $ V = - \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{20 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}} $
On calculating we get
$\Rightarrow V = - 50V $
So we have the circuit as,
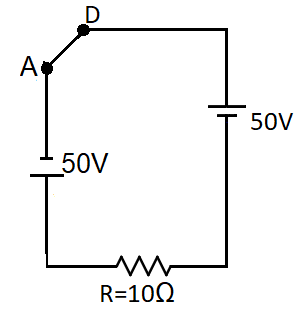
On applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law we get,
$\Rightarrow 50 + 50 = IR $
From here we get the current as,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{100}}{R} $
We are given $ R = 10\Omega $
So substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{100}}{{10}} = 10A $
So the current across the resistance is $ 10A $ . So option C is correct.
Now $ Q $ is the charge flowing from the battery to the capacitor. So the value of $ Q $ will be the final charge of the capacitor minus the charge at $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ .
The final charge will be,
$\Rightarrow q = CV $ , by substituting $ V = 50V $ and $ C = 20\mu F $ we get,
$\Rightarrow {q_{final}} = 20 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 50C $
On calculating we get,
$\Rightarrow {q_{final}} = {10^{ - 3}}C $
And the charge at $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ we already calculated as $ q = - {10^{ - 3}}C $
So, $ Q = {q_{final}} - q $
Substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow Q = \left( {{{10}^{ - 3}} + {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right)C $ , that is,
$\Rightarrow Q = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $ , hence option D is correct.
Therefore we can conclude the options C and D are correct.
Note
A capacitor is a device that stores electric charge when it is placed in an electric field. The effect of a capacitor is called capacitance. Most capacitors contain 2 metallic plates or surfaces which are separated by a dielectric.
Formula Used: In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow q = CV $
where $ q $ is charge across capacitors, $ V $ is the potential across the capacitor and $ C $ is the capacitance of the capacitor.
Complete step by step answer
To find the correct statements, let us first consider the initial circuit where the connection is between A and B. Here we can see that a capacitor is connected across the source. Let the current flowing in the circuit be $ I $ . So we can write this current as,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} $
where $ q $ is the charge across the capacitor.
Now in the question we are given $ I\left( t \right) = {I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right) $ . So substituting and bringing $ dt $ to the other side,
$\Rightarrow dq = \left[ {{I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right)} \right]dt $
Now we can integrate on both the sides. The limit for the charge will be from zero to $ q $ and time will be from zero to $ t $
Therefore, we get the equation as,
$\Rightarrow \int\limits_0^q {dq} = \int\limits_0^t {\left[ {{I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right)} \right]dt} $
So we get,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{{{I_o}}}{\omega }\left. {\sin \left( {\omega t} \right)} \right|_0^t $
Substituting the limits we get,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{{{I_o}}}{\omega }\sin \left( {\omega t} \right) $
Hence on substituting the values $ {I_o} = 1A $ , $ \omega = 500rad/s $ ,and for the maximum value of the charge, the value of $ \sin \left( {\omega t} \right) $ has to be 1, therefore we have,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{1}{{500}}C $
So we get the charge as, $ q = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $ .Therefore, option A is incorrect.
Now the current in the circuit will be $ I\left( t \right) = {I_o}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right) $ . Here we substitute $ {I_o} = 1A $ and $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ . So we get,
$\Rightarrow I\left( t \right) = 1 \times \cos \left( {\omega \times \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }}} \right) $
Hence we have,
$\Rightarrow I\left( t \right) = \cos \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $
Now the value of $ \cos \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $ is $ - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} $
So the current is $ I\left( t \right) = - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} $
In the figure we are given the clockwise direction for the positive cycle of the current. So the negative sign shows that the current is moving in an anticlockwise direction. So option B is incorrect.
Now for the second circuit, the connection is made across A and D.
The capacitor is having a charge given by, $ q = CV $
We have, $ q = \dfrac{{{I_o}}}{\omega }\sin \left( {\omega t} \right) $ where $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ , $ {I_o} = 1A $ and $ \omega = 500rad/s $
Substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow q = \dfrac{1}{{500}} \times \sin \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $
The value of $ \sin \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}} \right) $ is $ - \dfrac{1}{2} $
So we get,
$\Rightarrow q = - \dfrac{1}{{500 \times 2}} $
Hence the charge is $ q = - {10^{ - 3}}C $
The capacitance of the capacitor is given $ C = 20\mu F $ . So substituting in $ q = CV $ we get the potential as, $ V = - \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{20 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}} $
On calculating we get
$\Rightarrow V = - 50V $
So we have the circuit as,

On applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law we get,
$\Rightarrow 50 + 50 = IR $
From here we get the current as,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{100}}{R} $
We are given $ R = 10\Omega $
So substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{100}}{{10}} = 10A $
So the current across the resistance is $ 10A $ . So option C is correct.
Now $ Q $ is the charge flowing from the battery to the capacitor. So the value of $ Q $ will be the final charge of the capacitor minus the charge at $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ .
The final charge will be,
$\Rightarrow q = CV $ , by substituting $ V = 50V $ and $ C = 20\mu F $ we get,
$\Rightarrow {q_{final}} = 20 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 50C $
On calculating we get,
$\Rightarrow {q_{final}} = {10^{ - 3}}C $
And the charge at $ t = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{{6\omega }} $ we already calculated as $ q = - {10^{ - 3}}C $
So, $ Q = {q_{final}} - q $
Substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow Q = \left( {{{10}^{ - 3}} + {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right)C $ , that is,
$\Rightarrow Q = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $ , hence option D is correct.
Therefore we can conclude the options C and D are correct.
Note
A capacitor is a device that stores electric charge when it is placed in an electric field. The effect of a capacitor is called capacitance. Most capacitors contain 2 metallic plates or surfaces which are separated by a dielectric.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




