
At stopping potential, the photoelectric current becomes-
A. Minimum
B. Maximum
C. Zero
D. Infinity
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Stopping potential is the potential that must be applied in the photoelectric circuit to stop the ejection of electrons from the metal. It is directed opposite to the direction of flow of current and reduces down the kinetic energy of electrons to a point where they can’t leave the metal surface.
Complete answer:
In photoelectric effect, when the light with a frequency greater than the threshold frequency strikes the metal, electrons are ejected out of the metal plate.
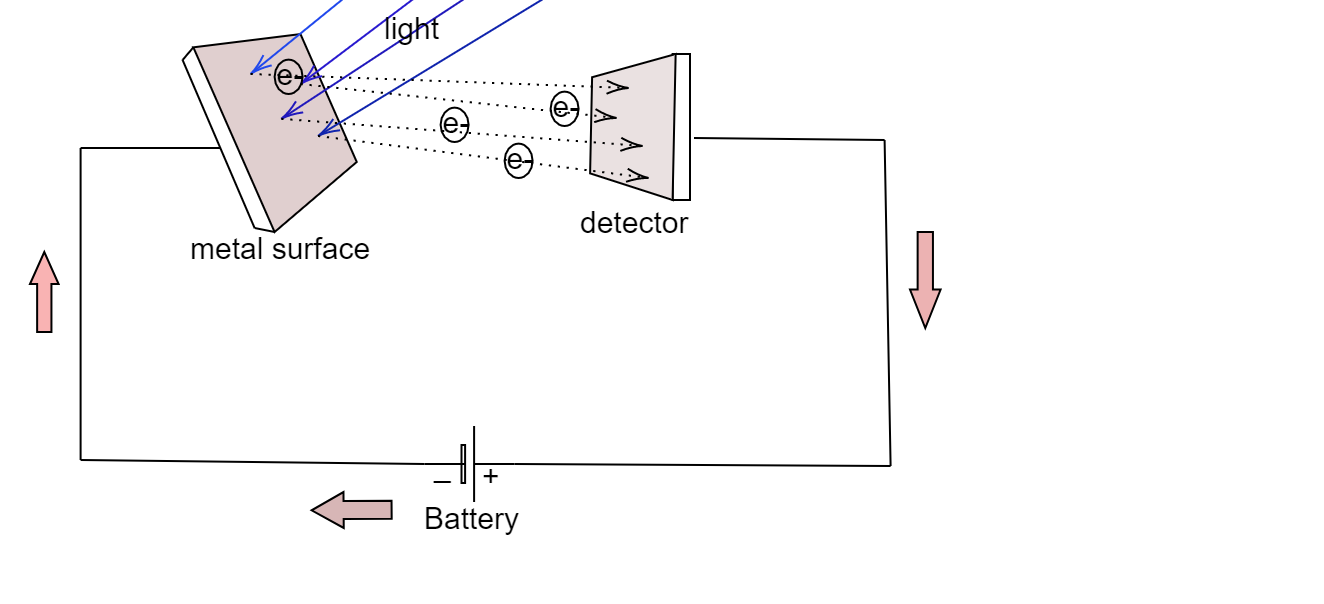
To favour the flow of electrons and to direct them in the same direction, another non photoactive metal plate connected to the battery is attached to the photoelectric metal. This creates a positive charge on the receiving end, which prompts the electrons to strike the receiver (detector) ; this also completes the circuit and the electrons can flow continuously till the light strikes the metal.
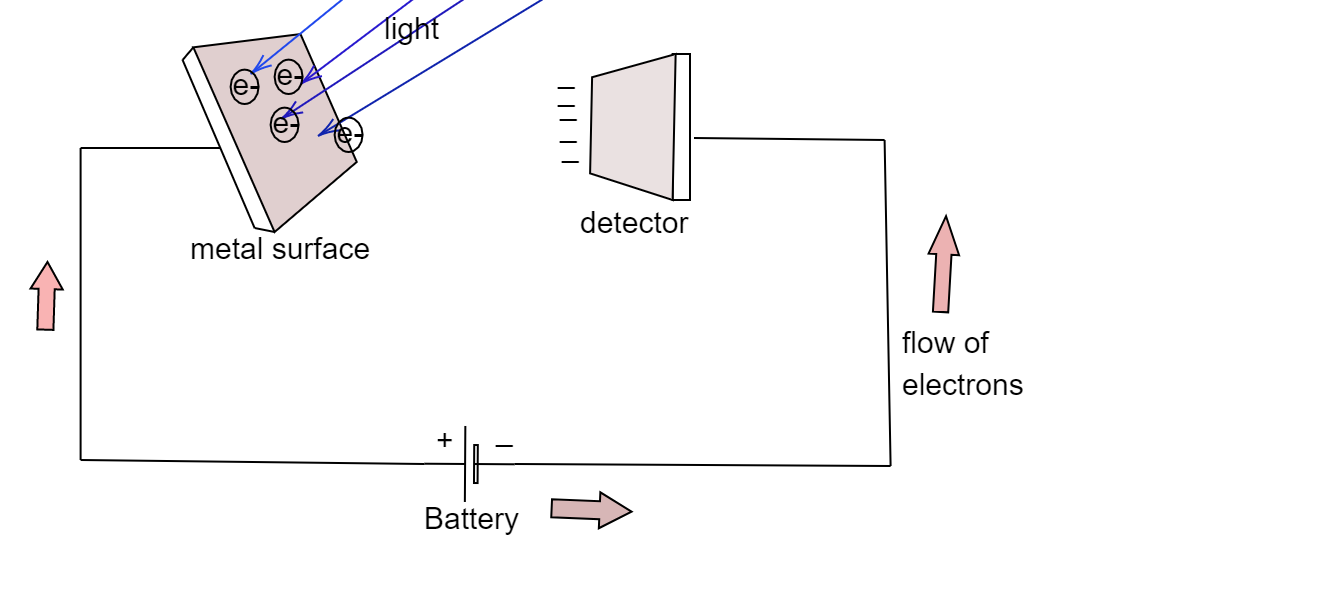
But if the direction of the battery is reversed, the detector plate will have a negative charge which will repel the electrons which get ejected from the metal surface. This lowers the kinetic energy of the electrons and as this voltage is increased, the number of electrons that strike the detector plates becomes lower. At a particular voltage the flow of electrons stops altogether, and the photocurrent becomes zero. The potential (Voltage) at which the flow of electrons stops altogether is known as the Stopping potential (${V_0}$)
Thus at the stopping potential photoelectric current becomes zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
At the stopping potential the kinetic energy of the electrons becomes zero. Thus, at the stopping potential, the electron with the highest value of Kinetic energy will also stop, this is used to calculate the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron.
Complete answer:
In photoelectric effect, when the light with a frequency greater than the threshold frequency strikes the metal, electrons are ejected out of the metal plate.

To favour the flow of electrons and to direct them in the same direction, another non photoactive metal plate connected to the battery is attached to the photoelectric metal. This creates a positive charge on the receiving end, which prompts the electrons to strike the receiver (detector) ; this also completes the circuit and the electrons can flow continuously till the light strikes the metal.

But if the direction of the battery is reversed, the detector plate will have a negative charge which will repel the electrons which get ejected from the metal surface. This lowers the kinetic energy of the electrons and as this voltage is increased, the number of electrons that strike the detector plates becomes lower. At a particular voltage the flow of electrons stops altogether, and the photocurrent becomes zero. The potential (Voltage) at which the flow of electrons stops altogether is known as the Stopping potential (${V_0}$)
Thus at the stopping potential photoelectric current becomes zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
At the stopping potential the kinetic energy of the electrons becomes zero. Thus, at the stopping potential, the electron with the highest value of Kinetic energy will also stop, this is used to calculate the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




