
At room temperature, sodium crystallises in a body centred cubic lattice with $a=4.24{{A}^{\circ }}$ . Calculate the theoretical density of sodium. ( atomic mass of $Na=23.0$ )
A.$1.002gc{{m}^{-3}}$
B.$2.002gc{{m}^{-3}}$
C.$3.003gc{{m}^{-3}}$
D.None
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Body centred cubic lattice have lattice point at the centre of the cube and also to the eight corners of the cube. Body centred cubic lattice is a three dimensional lattice.
Formula used: $Density=\dfrac{Z\times M}{{{N}_{\circ }}\times V}$
Where, $Z$ Denotes as the no. of atom in a unit cell
$M$ denotes as the molar mass
${{N}_{A}}$ Denotes as the avogadro number
$V$ denotes as the volume of the unit cell
Complete step by step answer:
Body centred cube has eight corners which is shared by eight cells and has one lattice at its centre.
Therefore, the no of atoms in a unit cell$\left( N \right)=8\times \dfrac{1}{8}+1=2$
Here the atomic mass of sodium is $23$
Volume of the unit cell $={{a}^{3}}={{\left( 4.24\times {{10}^{-8}} \right)}^{3}}c{{m}^{3}}$
$\rho =\dfrac{z\times M}{{{N}_{A}}\times V}$
Where, $\rho $ is the density
$Z$ Is the number of atoms
${{N}_{A}}$ Denotes as the Avogadro number
$V$ denotes the volume of the unit cell
On substituting the values in the above given formula we get,
Hence, Density$=\dfrac{2\times 23}{\left( 6.023\times {{10}^{23}} \right){{\left( 4.24\times {{10}^{-8}} \right)}^{3}}}$
Density $=1.002gc{{m}^{-3}}$
Therefore, the correct option is $\left( A \right)$
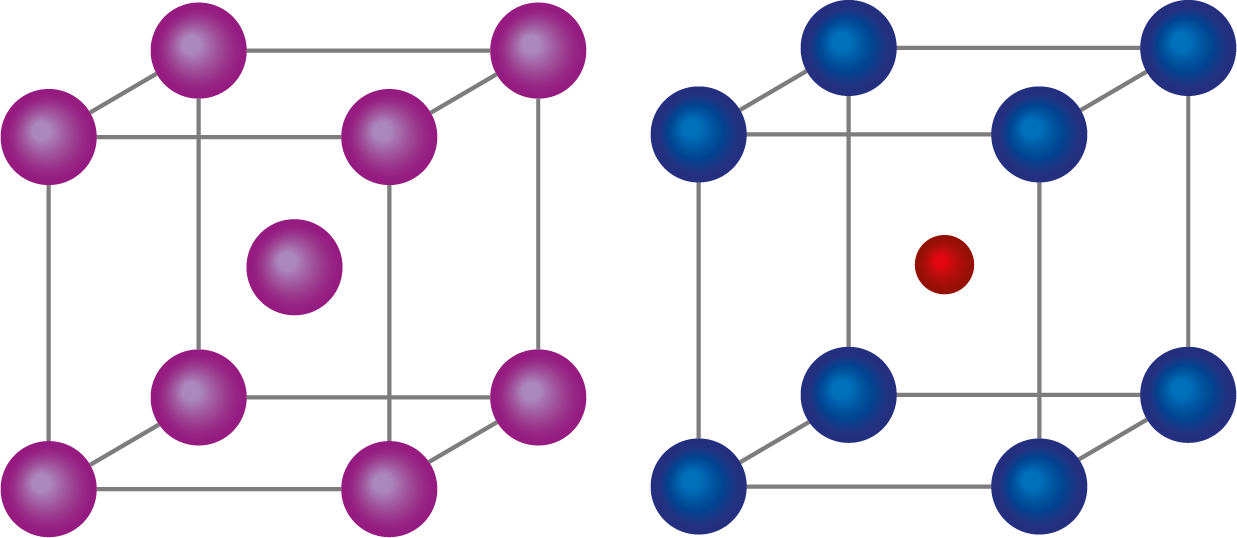
Body centred cubic lattice
Additional information
The packing efficiency of body centred cube is $68%$
The coordination no of an atom is $8$
The void present in body centred cubic lattice is distorted octahedral
When the lattice gets inflated they touch each along the diagonals of the cube, so the radius of closed packed unit cell is $4r=\sqrt{3}a$
Note:
Unit cell is defined as the smallest group of atoms that can form an entire lattice by repetition of three dimensions.
Lattice is defined as the three dimensional in which a whole crystal is built.
Density of a unit cell is defined as mass per volume of the unit cell.
Packing efficiency is defined as the fraction of crystals occupied by the atoms and it should always be less than $100%$
Formula used: $Density=\dfrac{Z\times M}{{{N}_{\circ }}\times V}$
Where, $Z$ Denotes as the no. of atom in a unit cell
$M$ denotes as the molar mass
${{N}_{A}}$ Denotes as the avogadro number
$V$ denotes as the volume of the unit cell
Complete step by step answer:
Body centred cube has eight corners which is shared by eight cells and has one lattice at its centre.
Therefore, the no of atoms in a unit cell$\left( N \right)=8\times \dfrac{1}{8}+1=2$
Here the atomic mass of sodium is $23$
Volume of the unit cell $={{a}^{3}}={{\left( 4.24\times {{10}^{-8}} \right)}^{3}}c{{m}^{3}}$
$\rho =\dfrac{z\times M}{{{N}_{A}}\times V}$
Where, $\rho $ is the density
$Z$ Is the number of atoms
${{N}_{A}}$ Denotes as the Avogadro number
$V$ denotes the volume of the unit cell
On substituting the values in the above given formula we get,
Hence, Density$=\dfrac{2\times 23}{\left( 6.023\times {{10}^{23}} \right){{\left( 4.24\times {{10}^{-8}} \right)}^{3}}}$
Density $=1.002gc{{m}^{-3}}$
Therefore, the correct option is $\left( A \right)$

Body centred cubic lattice
Additional information
The packing efficiency of body centred cube is $68%$
The coordination no of an atom is $8$
The void present in body centred cubic lattice is distorted octahedral
When the lattice gets inflated they touch each along the diagonals of the cube, so the radius of closed packed unit cell is $4r=\sqrt{3}a$
Note:
Unit cell is defined as the smallest group of atoms that can form an entire lattice by repetition of three dimensions.
Lattice is defined as the three dimensional in which a whole crystal is built.
Density of a unit cell is defined as mass per volume of the unit cell.
Packing efficiency is defined as the fraction of crystals occupied by the atoms and it should always be less than $100%$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




