
At a time, the image of the sun formed due to reflection at the air-water interface, is found to be highly polarised. If the refractive index of water is $\mu =\dfrac{4}{3}$, then the angle of the sun above the horizon is?
$\text{A}\text{. }{{37}^{\circ }}$
$\text{B}\text{. 5}{{3}^{\circ }}$
$\text{C}\text{. }{{30}^{\circ }}$
$\text{D}\text{. 6}{{\text{0}}^{\circ }}$
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: For the reflected light to be highly polarised, the angle between the refracted ray and the reflected ray must be ${{90}^{\circ }}$. Draw a ray diagram and then find the angle of incidence with Snell's law. Subtract this angle from 90 to find the angle that the sunlight makes with the horizon.
Formula used:
${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:
When sunlight falls on an interface of two mediums, it is partially reflected and partially refracted.
The reflected light is highly polarised when the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray is ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
Let the angle of incidence of the light at the interface be $i$.
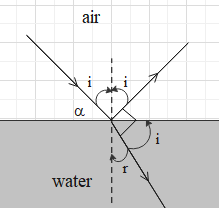
From the figure, we get that the angle of refraction is r = $(90-i)$.
From Snell’s law we get that ${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$ …. (i),
where ${{\mu }_{i}}$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the light is incident, ${{\mu }_{r}}$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the light is refracted.
In this case, ${{\mu }_{i}}$= 1, ${{\mu }_{r}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
Substitute the values of ${{\mu }_{i}}$, ${{\mu }_{r}}$ and r in equation (i).
$\Rightarrow 1(\sin i)=\dfrac{4}{3}\sin (90-i)$.
$\Rightarrow \sin i=\dfrac{4}{3}\cos i$
$\Rightarrow \tan i=\dfrac{4}{3}$
$\Rightarrow i={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{4}{3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow i\approx {{53}^{\circ }}$
From the given figure we get that the angle that the ray of sunlight makes with the horizon is ${{90}^{\circ }}-i$. Let this angle be $\alpha $.
$\Rightarrow \alpha ={{90}^{\circ }}-{{53}^{\circ }}={{37}^{\circ }}$.
This means that the angle of the sun above the horizon is ${{37}^{\circ }}$.
Note:
Note the point that when light is incident on the interface of two mediums, the light is partially reflected into the same medium and partially refracted into the other medium. This can be explained by the wave nature of light. When a wave hits another medium, some of it passes into the other medium and the remaining is reflected into the same medium.
Formula used:
${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:
When sunlight falls on an interface of two mediums, it is partially reflected and partially refracted.
The reflected light is highly polarised when the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray is ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
Let the angle of incidence of the light at the interface be $i$.

From the figure, we get that the angle of refraction is r = $(90-i)$.
From Snell’s law we get that ${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$ …. (i),
where ${{\mu }_{i}}$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the light is incident, ${{\mu }_{r}}$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the light is refracted.
In this case, ${{\mu }_{i}}$= 1, ${{\mu }_{r}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
Substitute the values of ${{\mu }_{i}}$, ${{\mu }_{r}}$ and r in equation (i).
$\Rightarrow 1(\sin i)=\dfrac{4}{3}\sin (90-i)$.
$\Rightarrow \sin i=\dfrac{4}{3}\cos i$
$\Rightarrow \tan i=\dfrac{4}{3}$
$\Rightarrow i={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{4}{3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow i\approx {{53}^{\circ }}$
From the given figure we get that the angle that the ray of sunlight makes with the horizon is ${{90}^{\circ }}-i$. Let this angle be $\alpha $.
$\Rightarrow \alpha ={{90}^{\circ }}-{{53}^{\circ }}={{37}^{\circ }}$.
This means that the angle of the sun above the horizon is ${{37}^{\circ }}$.
Note:
Note the point that when light is incident on the interface of two mediums, the light is partially reflected into the same medium and partially refracted into the other medium. This can be explained by the wave nature of light. When a wave hits another medium, some of it passes into the other medium and the remaining is reflected into the same medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




